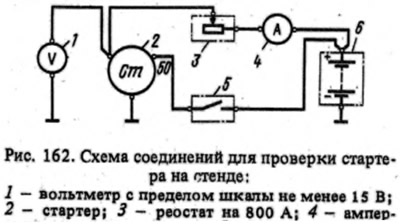
Health check
Closing the switch 5, when the voltage is (no text) starter motors with different braking conditions. For example, with braking torques; 0.2–0.24; 0.55-0.66; 0.9-1.08 and 1.15-1.25 kgf·m. The duration4 of each starter activation should be no more than 5 s, and the intervals between starts should be at least 5 s.
If the starter does not rotate the ring gear of the stand or its operation is accompanied by abnormal noise, then the starter is disassembled and its parts are checked.
Full brake test
The ring gear of the stand is braked, the starter is turned on and the current strength, voltage and braking torque are measured, which should be no more than 500 A, no more than 6.5 V and no less than 1.4 kgf·m, respectively. The duration of the starter activation should be no more than 5 s.
If the braking torque is lower and the current strength is higher than the specified values, then the interturn short circuit in the stator and armature windings or the short circuit of the windings to ground may be the reason for this. When the braking torque and current consumption are below the above values, the cause may be oxidation and contamination of the collector, severe wear of the brushes or a decrease in the elasticity of their springs, hanging in the brush holders, loosening of the stator winding leads, oxidation or burning of the contact bolts of the traction relay.
When the gear is fully braked, the starter armature should not rotate. If this happens, the freewheel is defective. To troubleshoot, disassemble the starter and replace damaged parts.
Idling test
The ring gear of the stand is disengaged from the starter gear. The starter is turned on and the consumed current and armature speed are measured, which should be no more than 35 A, respectively (60 A for starter 35.3708) and 5000+500-800 rpm at a voltage at the starter terminals of 11.5-12 V.
If the current strength and rotational speed of the armature shaft differ from the indicated values, then the reasons may be the same as in the previous test.
Checking the traction relay
Installed between restrictive ring 1 (see fig. 161) and gear spacer 12.8 mm thick and include a relay. For a single-winding relay, the strength of the consumed current is checked, which should be no more than 23 A. For a two-winding relay, the relay turn-on voltage is checked, which should be no more than 9 V at ambient temperature (20±5) °C.
Checking mechanical data
Check the pressure of the springs on the brushes with a dynamometer, which for new brushes should be (1±0,1) kgf. If the brushes are worn out to a height of 12 mm, then they are replaced after grinding them to the collector.
The axial play of the armature shaft should be 0.07-0.70 mm. If it is not in this limit, then disassemble the starter and select the thickness and number of shims 20 (see fig. 163).
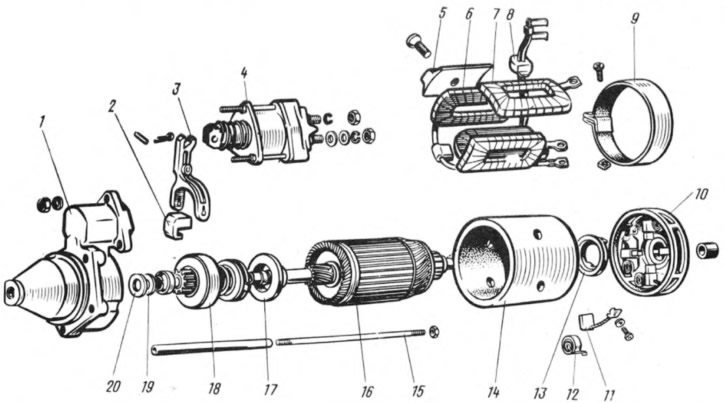
Pic. 163. Starter details:
1 - starter cover on the drive side; 2 - rubber plug; 3 - drive lever; 4 - traction relay; 5 - stator pole; 6 - series stator winding; 7 - shunt winding of the stator; 8 - rubber plug; 9 - protective tape; 10 - cover from the side of the collector; 11 - brush; 12 - brush spring; 13 - brake disc cover; 14 - body; 15 tie rod; 16 - anchor; 17 - gear stroke limiter; 18 - overrunning clutch with drive gear; 19 - thrust washer; 20 - adjusting washer.
The starter drive must move freely, without noticeable jamming, along the splined shaft and return from its working position to its original position under the action of the relay armature return spring. When turning the drive gear in the direction of rotation of the armature, the latter should not rotate. The gear must rotate relative to the armature shaft under the action of a moment of no more than 2.8 kgf cm.
