Technical specifications
The steering mechanism is a worm gear with a globoid worm on ball bearings and a double-ridged roller on needle bearings. Gear ratio 16.4.
Steering gear - symmetrical with three transverse rods (one middle and two extreme), bipod, pendulum arm and levers on the steering knuckles of the wheels. Extreme transverse rods are symmetrical and independent for each wheel.
The maximum effort on the steering wheel when turning in place on a smooth plate is 25 kgf.
Steering wheel free play no more than 5° (18-20 mm on the rim).
Steering - safety, with anti-theft device.
Open large image in new tab »
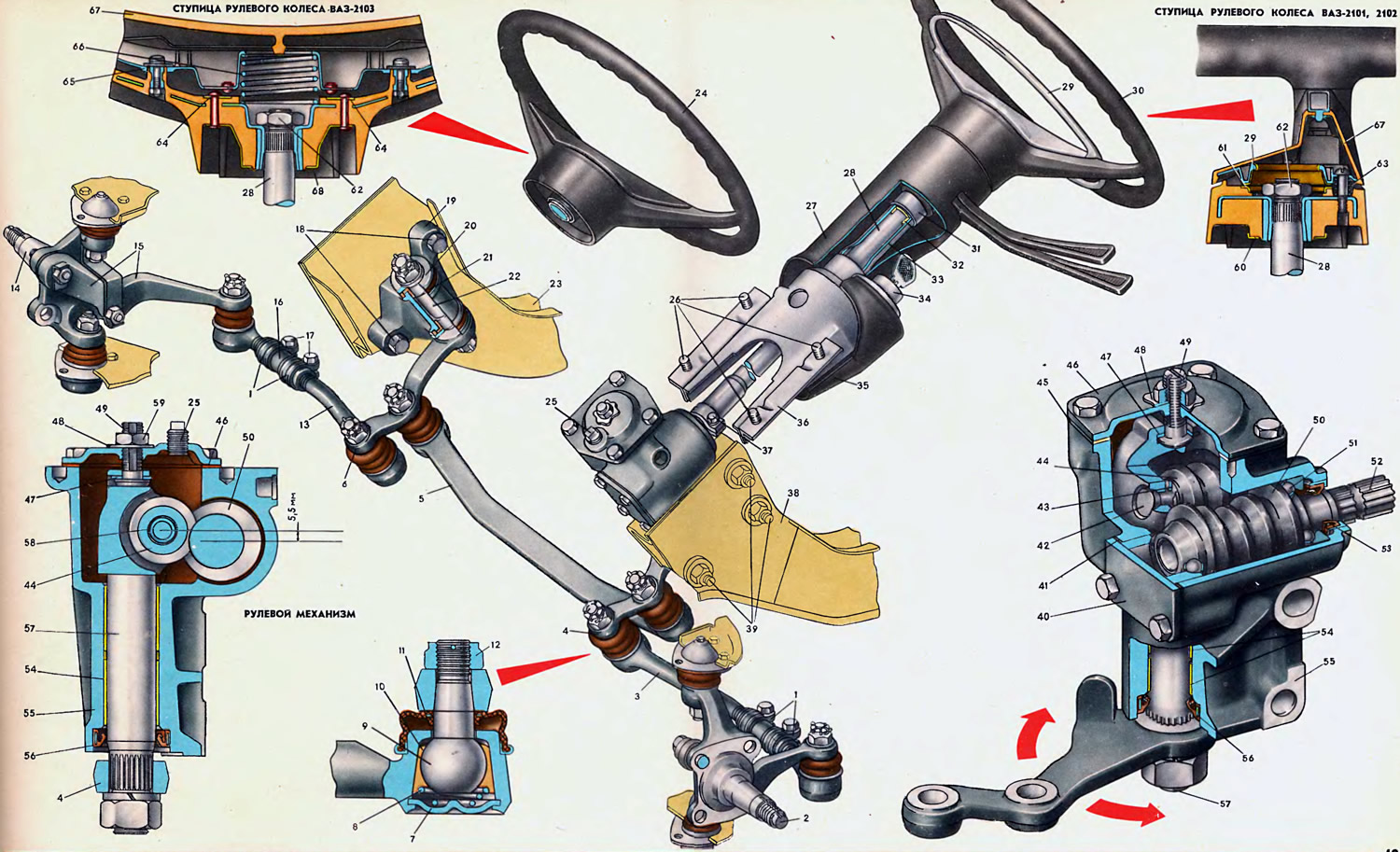
1. Clamp. 2. Left knuckle. 3. Extreme left thrust. 4. Bipod. 5. Medium thrust. 6. Pendulum lever. 7. Thrust washer of the tip. 8. Conical spring. 9. Ball joint pin. 10. Insert. 11. Protective cover. 12. Pin nut. 13. Extreme right thrust. 14. Right knuckle. 15. Swivel arm. 16. Adjusting clutch. 17. Coupling bolt. 18. Bracket mounting bolt. 19. Bracket. 20. Axle washer. 21. Sealing sleeve. 22. The axis of the pendulum lever. 23. Right front spar. 24. Steering wheel VAZ-2103. 25. Cork. 26. Bracket mounting bolts. 27. Upper shaft cover. 28. Steering shaft. 29. Switch ring. 30. Steering wheel. 31. Switch for direction indicators and headlights. 32. Bushing of the upper shaft support. 33. Pipe of the upper shaft support. 34. Ignition switch. 35. Lower shaft cover. 36. Shaft mounting bracket. 37. Tie bolt of the tip. 38. Left front spar. 39. Steering gear mounting bolt. 40. Bottom case cover. 41. Shims. 42. Roller axle. 43. Roller thrust washer. 44. Double ridge roller. 45. Sealing gasket. 46. Top case cover. 47. Adjusting screw washer. 48. Lock washer. 49. Adjusting screw. 50. Steering gear worm. 51. Ball bearing. 52. Worm roller. 53. Self-clamping gland. 54. Bipod shaft bushing. 55. Steering gear housing. 56. Self-clamping gland. 57. Bipod shaft assembly. 58. Distance ring. 59. Locknut. 60. Lower contact ring. 61. Top slip ring. 62. Nut. 63. Switch spring. 64. Upper contact plate. 65. Horn switch. 66. Switch spring. 67. Decorative covers. 68. Lower contact ring.
The steering mechanism includes the following main components: steering wheel, steering shaft and worm gear.
The steering wheel is made of plastic reinforced with a steel frame.
Contact rings 61 and 60 of the horn switch are riveted to the steering wheel hub of the VAZ-2101 and 2102 on both sides.
Instead of the upper ring 61, two contact plates 64 are riveted to the hub of the steering wheel VAZ-2103. The upper contact ring 61 and the contact plates 64 are closed to ground by the ring 29 of the horn switch (VAZ-2101 and 2102), compressed by three springs 63, or a switch 65 of a sound signal (VAZ-2103) with one central spring 66. Decorative plastic covers 67 are installed on the switch ring and the sound signal switch.
The steering wheel hub is mounted on the steering shaft with a splined hole with a double cavity located in the plane of the wheel hub.
The upper landing end of the steering shaft 28 is splined with one double spline for connecting the steering wheel to the shaft in a certain position. The steering wheel is attached to the shaft with a nut 62, which, after tightening with a torque of 5 kgf·m, is locked by punching at one point.
The shaft 28 is mounted coaxially on the shaft 52 of the worm with the lower splined tip and fixed with a coupling bolt 37. The installation of the shaft 28 relative to the shaft of the worm is strictly defined due to the double spline of the shaft and the double cavity in the tip.
Approximately one third of the length from the upper end, a ring is fitted and welded onto the steering shaft (not shown in the picture) with a groove for entering the locking pawl of the anti-theft device. Below the ring, a flat radius neck is machined on the shaft. The neck is necessary as a safety element, i.e. when a car collides with an obstacle, a bend (or break) of the steering shaft from a possible impact of the driver on the steering wheel passes along this neck, extinguishing the impact energy.
The upper end of the shaft 28 rotates in a bearing, which is a polyamide sleeve 32 pressed into the tube 33 of the upper support. A switch 31 for direction indicators and headlights is installed on the upper end of the pipe. The lower end of the pipe 33 of the upper support is clamped in the right seat of the bracket 36 with a coupling bolt.
An ignition switch 34 with an anti-theft device is installed in the left socket of the bracket 36 and secured with two screws. Bracket 36 is screwed to the panel bracket with four bolts 26, and the heads of the bolts break off during the final tightening. The upper end of the shaft 28 and the bracket 36 are protected by the upper 27 and lower 35 plastic casings.
The worm gear of the steering mechanism is enclosed in an aluminum housing 55, which is attached to the front left side member 38 of the body with three bolts 39 with self-locking nuts. For the correct (coaxial) installation of the body 55, two holes for the bolts are made oval, and shims are installed between the mating plane of the body 55 and the side member. The final tightening torque of the nuts is 4 kgf·m.
The worm 50 rotates in two angular contact bearings 51. The role of the inner races of the bearings is performed by the treadmills of the balls at the ends of the worm. The radial and axial clearances in the bearings are regulated by the selection of gaskets 41 with a thickness of 0.1 to 0.5 mm, which are installed between the housing 55 and the lower clamping cover 40.
The worm is pressed with a force of more than 800 kgf onto the roller 52 in a certain position, due to the key protrusion in the worm hole and the keyway of the roller. The exit of the roller from the housing is sealed with a self-clamping stuffing box 53, pressed into the bore of the housing.
A two-ridged roller 44 is engaged with the worm. The engagement is made with a shift of the axes of the roller and the worm by 5.5 mm (for the possibility of adjusting backlash-free gearing); roller axle offset angle — 7° (to improve the contact of the roller with the helical surface of the worm). The roller is mounted on an axle 42 and rotates in a double row needle full complement bearing with a spacer ring 58 between the rows of needles. The axis 42 of the roller is installed in the ears of the shaft 57; its ends after assembly are riveted with the help of electric heating. The necessary fit of the roller relative to the shaft lugs is provided by the selection of thrust washers 43 mounted on the axle from the ends of the roller.
Shaft 57 with a polished neck is installed in the body bore 55 in two bronze bushings 54. The position of the shaft is fixed by an adjusting screw 49, the head of which with a special washer 47, selected in thickness to ensure a certain fit, is inserted into the T-shaped groove of the shaft head. The adjusting screw 49 is screwed into the cover 46, locked from turning by a figured washer 48 and tightened with a lock nut 59. With an increase in the free play of the steering wheel, the gap in the engagement of the worm-roller pair is selected by screwing in the adjusting screw 49.
On the conical splines of the lower end of the shaft 57 on a tight fit bipod 4 is installed in a strictly defined position due to the double spline on the shaft and the double cavity in the bipod hole. The lower end of the shaft 57 is sealed with a self-clamping stuffing box 56 pressed into the body bore 55.
The steering mechanism is lubricated with transmission oil TAd-17i, which is poured into the housing through a hole in the cover, closed with a stopper 25; filling capacity 0.215 l or 0.195 kg.
The upper support of the steering shaft does not require lubrication during operation.
Steering gear (steering trapezoid) has a bipod 4, a middle link 5 and an extreme left link 3 pivotally connected to it, a pendulum lever 6 and an extreme right link 13 pivotally connected to it, as well as swivel levers 15. From the inside of the right front spar 23 to two bolts 18 with self-locking nuts the bracket 19 of the pendulum lever is screwed on.
The body of the bracket 19 is cast from aluminium. Two polyurethane bushings 21 are inserted into the through bore of the body, in which the axis of the pendulum lever rotates. The ends of the bore of the housing are closed with washers 20, of which the upper one is tightly fitted on the flats of the axle and is tightened with a castle nut with a tightening torque that ensures the rotation of the lever with a force of 500-1300 gf. The lower washer is pressed with a self-locking nut with a tightening torque of 10 kgf·m. The friction surfaces of the washers with the ends of the bushings 21 are protected by sealing rubber rings. When assembling, bushings 21 are lubricated, and the cavity of the bore of the bracket is filled with LITOL-24 grease, the amount of which is sufficient for lubrication for a long time.
The bipod 4 is connected to the pendulum arm 6 by an average thrust 5 using ball joints. In the steering drive for fastening the rods to the levers, six ball joints of the same type are used. The design of the hinge is quite simple, reliable and practically does not require maintenance during operation. Oval holes in the tips of the extreme (right and left) rods allow the hinge pin to deviate in the longitudinal direction by 22, and in the transverse direction by 11. The holes of the tips of the medium thrust are round.
The pin 9 together with the insert 10 is inserted into the conical bore of the thrust tip and is pressed by a spiral conical spring 8. The constantly preloaded insert having a longitudinal section automatically eliminates the gap that occurs as the friction surfaces wear out. The lower end of the spring 8 abuts against the support washer 7, rolled into the bore of the tip. From above, the connection of the finger with the insert is protected from dirt and moisture by a rubber cover 11, the lower reinforced end of which is pressed onto the bore of the tip, and the upper end compresses the cylindrical neck of the finger. When assembling, SHRB-4 grease is put into the internal free cavity of the tip bore. The same lubricant is placed at 50-70% of the volume under a protective rubber cover. This amount of grease, if the protective boot is in good condition, is sufficient for the entire service life of the ball joint.
The ball pin with a conical surface is installed in the hole of the lever (bipod, pendulum, swing arms) and tightened with nut 12 to a torque of 5.5 kgf·m. The position of the nut is fixed with a cotter pin.
Extreme thrust 3 steering trapezoid - composite of two tips. The shanks of both tips have right and left threads and are interconnected by split adjusting sleeves 16 with right and left threads. Thus, by rotating the adjusting sleeve 16, it is possible to lengthen or shorten the outer tie rod. This is necessary when adjusting the wheel alignment. After adjusting the couplings at the ends, they are pulled together by clamps 1 using bolts 17 with nuts. Before tightening the nuts, the bolts must be positioned behind the rods as shown on the sheet.
The turning forces from the extreme rods are perceived by the rotary levers 15, fixed on the steering knuckles 14.
