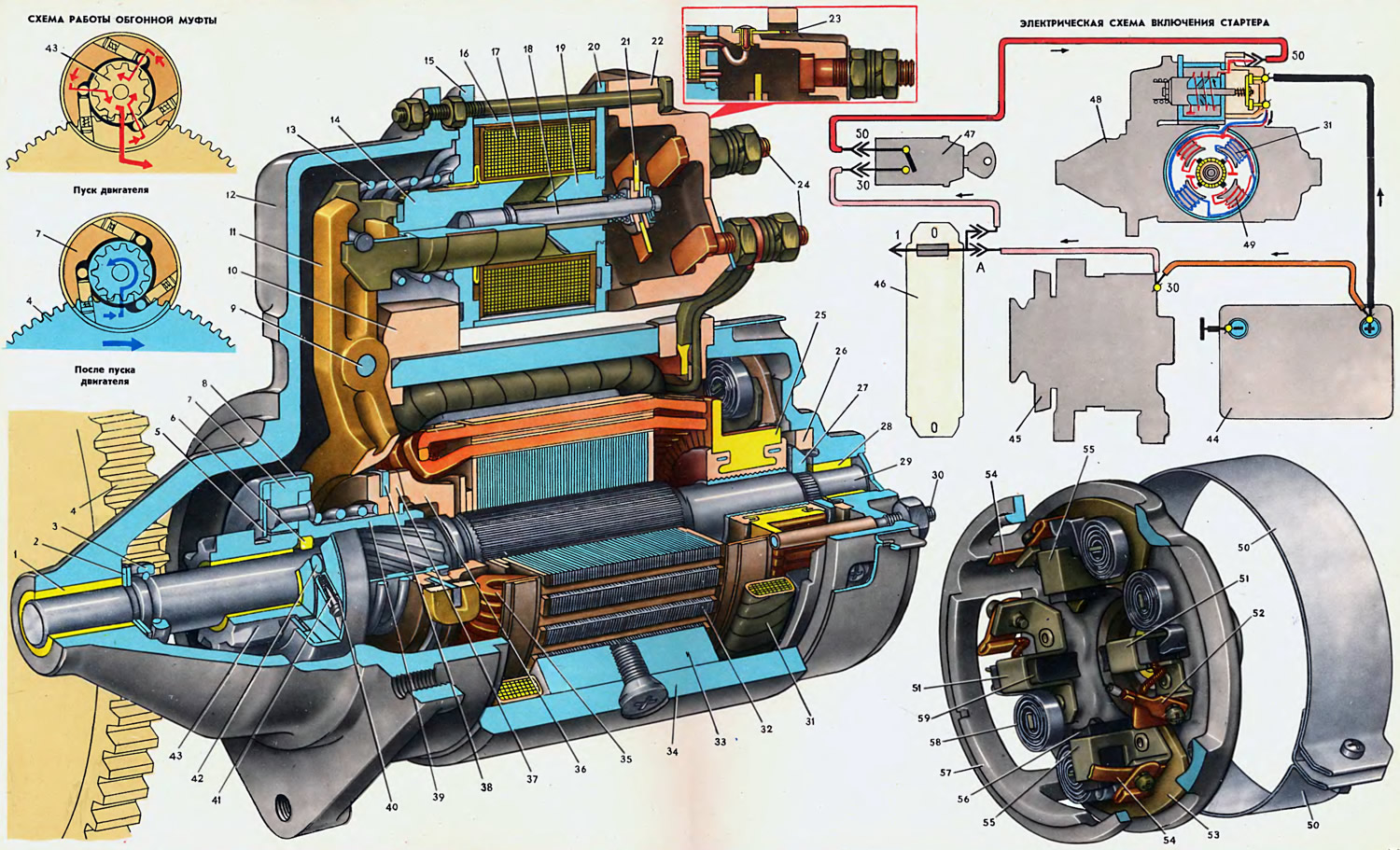
Open large image in new tab »
1. Cover bearing bush. 2. Adjusting washer for axial play. 3. Restrictive ring of a course of a gear wheel. 4. Flywheel ring. 5. Thrust half ring freewheel. 6. Freewheel hub bushing. 7. Free wheel outer ring. 8. Overrunning clutch cover. 9. The axis of the starter drive lever. 10. Starter cover sealing plug. 11. Starter drive lever. 12. Starter cover on the drive side. 13. Starter relay armature return spring. 14. Anchor relay. 15. Relay front flange. 16. Relay yoke. 17. Relay winding. 18. Anchor rod. 19. Relay core. 20. Relay core flange. 21. Contact plate. 22. Relay cover. 23. Relay winding output plug (plug «50»). 24. Contact bolts. 25. Collector. 26. Brake disc cover. 27. Brake disc armature shaft. 28. Bearing sleeve. 29. Anchor shaft. 30. Coupling pin. 31. Shunt coil of the stator winding. 32. Anchor core. 33- Stator pole. 34. Starter housing. 35. Anchor marking. 36. Drive gear stroke limiter. 37. Restrictive disk. 38. Driving ring. 39. Overrunning clutch hub. 40. Plunger 41. Guide rod. 42. Overrunning clutch roller. 43. Drive gear. 44. Battery. 45. Generator. 46. Safety block. 47. Ignition switch 48. Starter. 49. Serial stator winding coil. 50. Protective tape. 51. Brush holders for negative brushes. 52. Output of the shunt coil of the stator winding. 53. Internal insulating plate. 54. Conclusions of serial coils of the stator winding. 55. Brush holders for positive brushes. 56. Positive brush. 57. Starter cover on the manifold side. 58. Brush holder spring. 59. Negative brush.
Technical specifications:
- Rated voltage, V - 12
- Rated power, h.p. - 1.77
- Direction of rotation (gear side) - Right
- Starter weight, kg - 8.5
To start the engine, a ST-221 starter with an electromagnetic traction relay is used. It is mounted on the right side of the engine and is flanged to the clutch housing with three bolts.
The ST-221 starter is a four-brush, four-pole DC motor with mixed excitation and consists of a housing 34 with excitation windings, a powered armature, two covers 12 and 57 and a traction relay.
The housing is made of coiled and welded steel strip and has four 33 steel poles fixed with screws. Winding coils are put on the poles. The housing together with the poles and winding forms the starter stator. Two stator winding coils are serial and two are shunt. Therefore, the excitation of the starter is called mixed. It provides relatively low idle armature speeds (without load), and this reduces wear on the bearing bushes and prevents armature runaway.
Two serial coils are connected to each other in parallel, and with the armature winding - in series. Since the main current passes through them, consumed by the starter and depending on the braking torque on the armature shaft (the greater the torque, the greater the current), then the coil winding consists of a copper tape.
Shunt coils are connected to each other in series, and with the armature winding - in parallel. A relatively small current flows through them, depending mainly on the voltage of the battery. All stator coils are wrapped with cotton tape and impregnated with varnish.
The starter armature consists of a shaft 29, a core 32 with a winding 35 and a collector 25. The armature shaft rotates in two porous ceramic-metal bushings 1 and 28. Pressed into the starter covers and impregnated with oil. The axial play of the armature shaft is regulated by the selection of washers 2 and should be in the range of 0.07-0.7 mm. The armature core is made of electrical steel plates 1 mm thick, pressed onto the middle part of the shaft, which has a longitudinal knurling. The core has semi-closed grooves, in which the wave winding of the armature from a copper tape is laid. In each groove there are two winding conductors, isolated from the core and between themselves by electrical insulating cardboard. The edges of the winding coming out of the grooves of the core are tightened with bandages that protect the winding conductors from bending by centrifugal force at high armature speeds. Bandages are made of copper wire wound on a cardboard lining. Some starters have a bandage only on the drive side and are made of nylon fiber. The ends of the winding are soldered to the collector plates 25 pressed onto the shaft.
The collector consists of a plastic base reinforced with two steel rings, on which copper plates isolated from each other - collector lamellas are installed. For some starters, the plastic base of the collector can be with a steel hub-sleeve.
In the cover 57, cast from an aluminum alloy, four steel brush holders with copper-graphite brushes are riveted. Two brush holders 55 are isolated from the cover by plastic plates - inner 53 and outer. These are brush holders for positive brushes. They are joined by the conclusions of 54 serial coils. The other two brush holders 51 are riveted directly to the cover 57 and are therefore grounded. These are negative brush holders. One of these brush holders is connected to the output of 52 shunt coils. The brushes are pressed against the collector by spiral springs 58.
At the front end of the armature shaft, a starter drive is installed, consisting of a roller overrunning clutch and gear 43. The purpose of the overrunning clutch is to transmit torque from the starter armature shaft to the flywheel crown when the engine is started, and after starting, to disconnect the armature shaft and the drive gear, since after Starting the engine starts to rotate the armature shaft at high speed and can damage it.
The coupling consists of a hub 39, an outer ring 7 with rollers 42, plungers 40, rods 41, springs and an inner ring combined with a drive gear 43. On the hub 39 of the coupling there is a plastic centering disk with a driving steel ring 38 and a plastic limiting disk 37, pressed by a spring against the retaining ring on the hub. The hub 39 has internal screw splines on one side and can, by turning, move along the screw splines of the armature shaft. On the other hand, an oil-impregnated ceramic-metal insert 6 is pressed into the hub, sliding along the smooth part of the armature shaft. The outer ring 7 of the overrunning clutch is attached to the hub with three rivets, in which three rollers 42 with plungers 40, springs and guide rods 41 are placed. These parts are kept from falling out by a steel casing 8. The grooves in which the rollers are located have a variable width. The rollers are pressed by springs into the narrow part of the groove.
The casing 8 also fastens two thrust half rings 5, which are included in the annular groove of the gear 43. The gear has a brass bushing with graphite inclusions and can move along the smooth end of the armature shaft and rotate on it.
The cover 12 of the starter on the drive side is cast iron, since the starter is attached to the clutch housing with the flange of the cover and it experiences the greatest loads. A starter traction relay is attached to cover 12, which turns on the starter and engages gear 43 in engagement with the flywheel crown. Winding 17 is wound in ten layers on a frame made of a brass tube and two cardboard cheeks. One end of the winding is led to plug 23, which has the designation «50», and the other end is welded to flange 20, i.e. connected to ground.
Steel flanges 15 and 20, together with the yoke 16, form the magnetic system of the relay. A core 19 is welded to the flange 20. On the armature 14 of the relay, a rod is riveted on one side for coupling with the lever 11, and on the other side, a rod 18 is rolled, passing through a hole in the core and having a spring-loaded copper contact plate 21 at the end. In order to improve sliding anchors and to eliminate jamming on the anchor 14 and the rod 18 are put on bushings made of polyamide plastic. When the relay is turned on, the contact plate 21 closes two fixed contacts made in the form of copper: bolts 24, fixed with nuts on the plastic cover 22. The stator winding leads are connected to the lower contact bolt, and the wire from the battery is connected to the upper one.
The traction force from the relay is transmitted to the starter drive through the plastic lever 11, fixed on the axle 9 in the cover 12. The lugs of the driving ring 38 enter the holes of the lever fork.
The starter works as follows. After turning the key to the STARTER position, the contacts close «30» and «50» ignition switch and current begins to flow through the winding of the traction relay. Under the action of this current, a magnetic force is generated (about 10-12 kgf), retracting the armature 14 of the relay until it comes into contact with the core 19. In this case, the contact plate 21 closes the contacts 24. The dimensions of the armature rod 18 are selected so that the contacts close even before the armature touches the core, and with the further course of the armature, the spring of the contact plate is compressed, pressing it harder to fixed contacts.
Moving, the relay armature through the lever 11 moves the overrunning clutch with the gear. Overrunning clutch hub, turning on the screw splines of the shaft. 29 of the starter anchor, also turns gear 43, which facilitates its engagement with the flywheel crown. In addition, the chamfers on the lateral edges of the gear teeth and the flywheel ring, as well as the buffer spring that transmits the force from the lever 11 to the clutch hub 39, facilitate the engagement of the gear and soften the impact of the gear on the flywheel ring. The dimensions of the parts of the relay and the drive are selected so that the closure of the relay contacts occurs when the gear 43 is only partially engaged with the flywheel crown.
After the relay contacts are closed, current begins to flow through the stator and armature windings. As a result of the interaction of the magnetic fields created by this current, the starter armature begins to rotate. The rotation of the armature through the screw splines is transmitted to the hub 39 and the outer ring 7 of the freewheel starter. Since the rollers 42 of the clutch are shifted by springs into the narrow part of the groove of the outer ring, and the gear is braked by the flywheel ring, the rollers are wedged between the outer and inner rings of the overrunning clutch and the torque from the armature shaft is transmitted through the clutch and gear to the flywheel ring. At the same time, as a result of gear braking and armature rotation, the clutch hub 39 is screwed off the splines of the armature shaft and the gear is driven all the way into ring 3, fully engaging with the flywheel.
After starting the engine, the speed of the gear begins to exceed the speed of the starter armature. Sprag Inner Ring (combined with gear) drags the rollers into the wide part of the groove of the outer ring 7, compressing the springs of the plungers. In this part of the groove, the rollers rotate freely without jamming, and the torque from the engine flywheel is not transmitted to the starter armature shaft.
When the key is returned to the IGNITION position, the power supply circuit of the traction relay winding opens, the relay armature returns to its original position under the action of spring 13, opening contacts 24 and returning the overrunning clutch with the gear to its original position. Under the action of the spring 13 through the lever 11, the disk 37 and the limiter 36, the armature is displaced towards the cover 57, resting against the plastic brake disk 26 of the cover with the steel brake disk 27, and quickly stops rotation.
