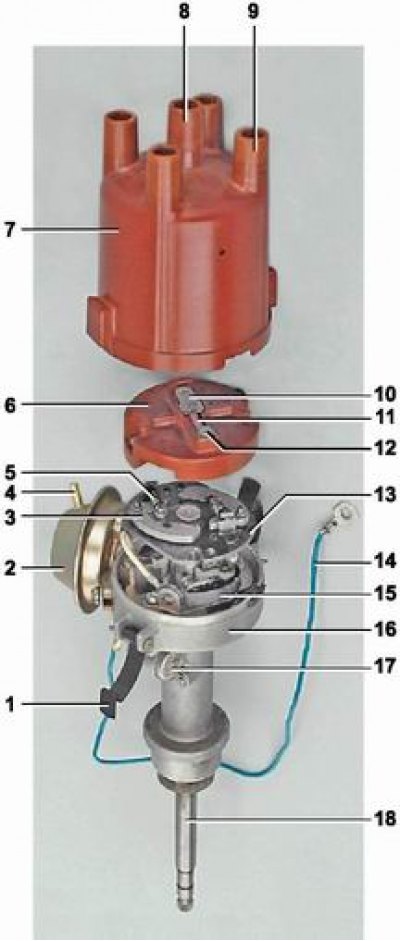
Distributor details: 1 - spring cover holder; 2 - vacuum ignition timing regulator; 3 - weight; 4 - vacuum supply fitting; 5 - spring; 6 - rotor (slider); 7 - cover of the ignition distributor; 8 - central electrode with a terminal for the wire from the ignition coil; 9 - side electrode with a terminal for a wire to a spark plug; 10 - central contact of the rotor (runner); 11 - resistor; 12 - outer contact of the rotor; 13 - base plate of the ignition timing regulator; 14 - wire connecting the distributor with the output of the primary winding of the ignition coil; 15 - contact group of the breaker; 16 - distributor housing; 17 - capacitor; 18 - distributor roller
On cars with a contact ignition system, a distributor model 30.3706 is installed.
The distributor consists of an aluminum housing, a roller, a contact breaker, centrifugal and vacuum ignition timing regulators, a rotor (runner) and fixed on top of the body with two spring holders of a plastic cover.
The ignition distributor is installed in the bore of the cylinder block on the left front of the engine. The distributor roller is driven by the accessory drive gear, into the slotted hole of which the roller shank is inserted. The roller rotates in a porous ceramic-metal sleeve pressed into the upper part of the distributor housing. Grease is supplied to the bushing from a grease fitting on the side of the housing.
A plastic rotor is fixed on the top of the roller (slider) distributor. The slider has a central and outer contacts connected through a resistor designed to suppress radio interference. The slider is fixed in a certain position with two screws on the base plate of the centrifugal ignition timing controller.
A spring-loaded carbon electrode of the distributor cap rests against the central contact of the slider, the output of which is connected to the high-voltage output of the coil. When the runner rotates, high voltage impulses are transmitted from the outer contact of the runner to the side electrodes of the ignition distributor cover and further along the high-voltage wires to the candles.
The breaker consists of a contact group and a cam with four lugs. The contact group is fixed with two screws on the movable plate. To adjust the position of the contact group on the plate, one of the mounting holes of the group is made oblong. The plate rotates on a ball bearing mounted in the distributor housing. The interrupter cam is made as part of the roller. The surface of the cam is lubricated with a special wick - a felt mounted on a movable plate. One contact of the contact group is located on a movable spring-loaded lever, the other contact of the group is fixed. When the roller rotates, the cam, pressing the protrusion on the plastic block of the moving contact lever, opens the circuit that supplies voltage to the primary winding of the ignition coil.
In order to avoid sparks on the open contacts of the breaker, caused by a change in the magnetic flux in the primary winding of the coil, a capacitor is connected in parallel to the breaker circuit, fixed with a screw on the distributor housing.
The initial setting of the ignition timing is set at idle speed of the engine and is manually adjusted by turning the distributor housing (see "Ignition timing - check and adjustment"). Turning the housing clockwise decreases the lead, while turning it counterclockwise increases it.
In other engine operating modes, the lead is automatically adjusted - by centrifugal and vacuum regulators.
The centrifugal regulator changes the ignition timing depending on the engine speed. The regulator consists of a base plate and a drive plate. The base plate is soldered to the bushing mounted on the distributor shaft with the possibility of rotation by 15°relative to the shaft. Above (on base plate) two weights are installed on the riveted axles. The drive plate is pressed onto the upper end of the distributor shaft. The plates are interconnected by two springs of different stiffness. The springs, turning the base plate counterclockwise, press the weights against the drive plate and prevent the weights from dispersing under the action of centrifugal forces at low engine speeds. When the engine speed reaches 1000 rpm, the centrifugal force acting on the weights first overcomes the resistance of one spring, and with an increase in speed - the other. The weights, turning on the axes and resting their cam surface against the drive plate, turn the base plate together with the slider clockwise (in the direction of roller rotation), by increasing the ignition timing.
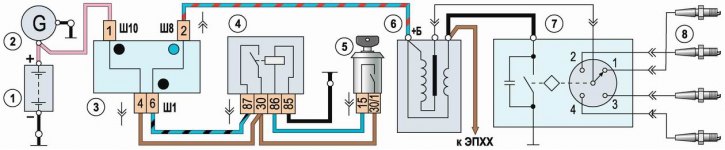
Scheme of the contact ignition system: 1 - battery; 2 - generator; 3 - block of relays and fuses; 4 - ignition relay; 5 - switch (lock) ignition; 6 - ignition coil; 7 - ignition distributor; 8 - spark plugs
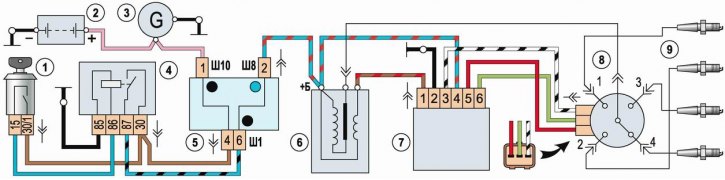
Scheme of a contactless ignition system: 1 - switch (lock) ignition; 2 - battery; 3 - generator; 4 - ignition relay; 5 - block of relays and fuses; 6 - ignition coil; 7 - switch; 8 - ignition distributor; 9 - spark plugs
The vacuum regulator is fixed with two screws on the distributor housing and changes the ignition timing depending on the engine load. The regulator diaphragm rod is connected by a rod to the movable breaker plate. The cavity behind the diaphragm of the vacuum regulator is connected by a hose to the cavity above the throttle valve of the primary chamber of the carburetor. When a vacuum is created in the regulator cavity, the diaphragm depresses the return spring and, by means of a rod, turns the movable breaker plate counterclockwise (against the direction of the roller), by increasing the ignition timing.
Distributor 3810.3706 is installed on cars with a contactless ignition system. Structurally, it is made similar to the distributor 30.3706, but instead of the contact group and the cam, it has a sensor and a screen with four cutouts, rigidly connected to the roller. The operation of the sensor is based on the principle of induction. As the roller rotates, the notches and protrusions of the screen pass through the groove in the sensor, causing a change in the magnetic field. The control pulses from the sensor are sent to the switch, which converts them into current pulses in the primary winding of the ignition coil.
