Removing
1. We install the car on a viewing hole or overpass (see "Vehicle preparation for maintenance and repair").
2. Remove the engine oil pan (see "Engine oil pan - removal and installation").
3. Remove the holder with the gland from the cylinder block (see "Rear crankshaft oil seal - replacement").
4. Remove the camshaft drive cover with gasket and chain from the crankshaft sprocket (see "Timing chain - replacement").
5. We mark the relative position of the connecting rods relative to their caps and main bearing caps relative to the cylinder block.
6. socket wrench by 14 mm unscrew the two nuts securing the connecting rod cover.

7. Remove the connecting rod cover along with the insert.

8. Disconnect the rest of the connecting rods from the crankshaft and move them up.

We take out the liners from the connecting rods and their covers.
9. socket wrench by 17 mm loosen the crankshaft main bearing cap bolts.

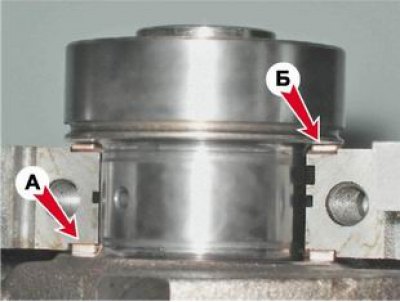
10. Having unscrewed two bolts, we remove a cover of the back radical bearing. In the grooves of the rear support of the crankshaft, two thrust half rings are installed. The front ring A is steel-aluminum, and the rear ring B is cermet. The rings can be removed by pressing on their ends with a thin screwdriver.
11. We turn off the bolts of the remaining caps of the main bearings, keeping the crankshaft from falling. We remove the covers one by one and remove the crankshaft from the crankcase. All lid inserts (except for the third), installed in the beds of main bearings, have a groove. On the caps of the main bearings, marks are made corresponding to their serial number (counting from the toe of the crankshaft), facing the left side of the cylinder block. The fifth cover has two marks spaced along the edges.

First main bearing cap mark
12. To replace, remove the crankshaft main bearing shells from the cylinder block and covers.
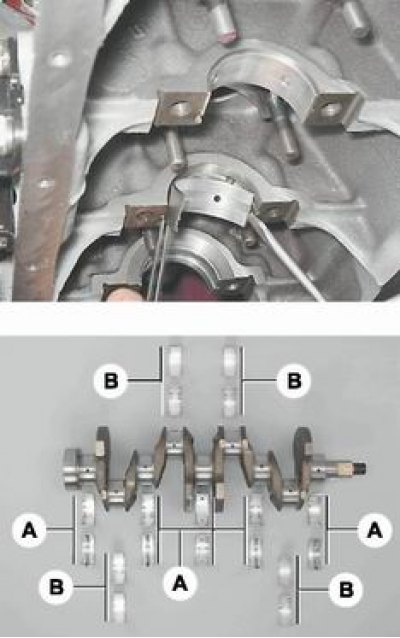
Indigenous (A) and connecting rod (B) crankshaft bearings
The note At the presence of any cracks on necks or cheeks the cranked shaft is subject to replacement.
13. We measure the diameters of the main and connecting rod journals with a micrometer and compare them with the data given in Table 8.1.27.1. If the wear or ovality is greater than 0.03 mm, then the necks must be ground in a specialized workshop where the necessary equipment is available (in the same place it is necessary to check the axial runout of the main surfaces of the crankshaft). After grinding, we re-measure the diameters of the crankshaft journals to determine the repair size of the liners.
Table 8.1.27.1. Diameters of crankshaft journals
|
Nominal |
Repair (reduced) dimensions (mm) |
|||
|
025 |
050 |
075 |
100 |
|
|
crankpins |
||||
|
47,814 |
47,564 |
47,314 |
47,064 |
46,814 |
|
47,834 |
47,584 |
47,334 |
47,084 |
46,834 |
|
Indigenous necks |
||||
|
50,775 |
50,525 |
50,275 |
50,025 |
49,775 |
|
50,795 |
50,545 |
50,295 |
50,045 |
49,795 |
Installation
1. We wash the crankshaft in kerosene and blow its internal cavities with compressed air. We install new liners of main bearings of the crankshaft of nominal or repair size. On the outer cylindrical surface of the liners, numbers are engraved indicating the repair size: 025 - the first repair, for the crankshaft journal, reduced in diameter by 0.25 mm. Accordingly, for the second, third and fourth repair sizes, there will be values: 050, 075, 100. It is easy to distinguish connecting rod bearings from main bearings. Ha upper main bearings (other than average) annular grooves are made. In addition, the middle support bushings are wider than the others. The connecting rod bearings are all the same and interchangeable, their diameter is smaller than the diameter of the main ones. To increase the contact area, there are no annular grooves on the connecting rod bearings.
2. We install in the grooves of the bed of the fifth main bearing the thrust half rings with grooves to the crankshaft. Half rings are made of normal thickness (2.310-2.360 mm) and increased (2.437-2.487 mm).
3. We check the axial clearance between the thrust half rings and the thrust surfaces of the crankshaft, which should be within 0.06-0.26 mm. If the clearance exceeds the maximum allowable (0.35 mm),
we replace the thrust half rings with new ones, increased by 0.127 mm.
4. Lubricate the connecting rod and main journals of the crankshaft with engine oil and install the shaft in the block.
5. In accordance with the marks, install the main bearing caps and tighten the bolts of their fastening to a torque of 68.4-84.3 Nm. Check the free rotation of the shaft.
6. We install connecting rods with liners and covers on the crankshaft. We tighten the fastening nuts with a torque of 43.4-53.5 N·m.
7. Install the engine oil pan (see "Engine oil pan - removal and installation").
8. We install a holder with an oil seal on the cylinder block (see "Rear crankshaft oil seal - replacement").
9. Installation of the remaining removed parts is carried out in reverse order.
10. Adjust the chain tension (see "Timing chain - replacement").
11. Adjust the tension of the alternator drive belt (see "Alternator drive belt - tension adjustment and replacement").
12. On a carburetor engine, we check and, if necessary, correct the ignition timing (see "Ignition timing - check and adjustment").
