Attention. If the vehicle is equipped with a non-contact high energy transistor ignition system, do not disconnect the high voltage wires and check the ignition circuits for a spark while the engine is running, as this can lead to injury, as well as burnout of high voltage insulation and failure of the ignition system.
For the same reason, it is not allowed to start the engine using a spark gap between the high voltage wire and the central terminal of the ignition distributor. In addition, it is strictly forbidden to carry out preventive work with the distribution sensor with the ignition on.
When servicing the car, check the reliability of the connections of the high voltage wires with the ignition distributor, coil and spark plugs.
It is not allowed to disconnect the wires from the battery terminals while the engine is running, as this may damage the switch.
Proximity sensor
Check the performance of the contactless sensor located in the ignition distributor sensor with an indicator assembled according to the diagram shown in fig. 240. The indicator uses resistors of the MLT type, 1 W; capacitors C1 type KLS1 and C2 type K53-14. As an indicator lamp HL1, a car lamp A12, 3 W was taken. Instead of a KT816B transistor, you can use a KT814B type transistor. The indicator wires are soldered in a three-terminal block Ш1 of the same type that is connected to the ignition distribution sensor on the car.
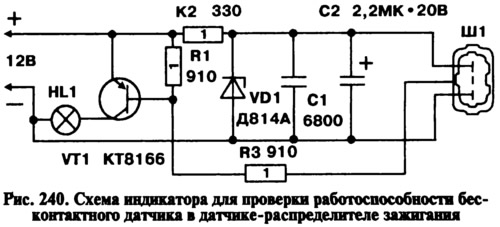
To check the non-contact sensor, connect the indicator to the ignition distributor sensor instead of the ignition system wiring harness and turn the engine crankshaft with a starter or a special key for the bolt on the crankshaft. If the HL1 lamp flashes during rotation of the crankshaft, then the proximity sensor is working.
The serviceability of the proximity sensor can also be checked at the stand. The procedure for this check is described in the instructions for the stand. This method is more accurate, as it allows you to check the magnitude of the voltage pulses generated by the sensor using a voltmeter.
Switch
The functionality of the switch can also be checked with a 3W A12 lamp. To check, disconnect the brown wire with red stripes from the ignition coil coming from the terminal «I» switch, and connect the tip of the wire to the test lamp. Connect the other output of the lamp to the terminal «+B» ignition coils and turn the engine over with the starter. If the lamp flashes during rotation of the engine crankshaft, then the switch outputs current pulses to the ignition coil.
The described method allows only a rough estimate of the operability of the switch - whether it produces current pulses or not. Pulse parameters (size and duration, shape) cannot be verified by this method. And they can seriously affect the operation of the engine, especially at high engine speeds. 'Therefore, the following test of the switch on the bench using an oscilloscope and a square-wave generator is more accurate.
Ignition coil and high voltage wires
Check the performance of these elements using a high-voltage arrester. The simplest spark gap consists of two pointed metal rods, the gap between which can be adjusted. Fix the rods on a plate of insulating material (plastic or ceramic).
To check the ignition coil, disconnect the central high voltage wire from the ignition distributor and connect it to the arrester electrode. The second output of the arrester is connected to the car body and the air gap between the electrodes of the arrester is set to 7-10 mm. If, when the engine is rotated by the starter, uninterrupted sparking is observed between the electrodes of the arrester, then the ignition coil and the central high voltage wire are in good order.
Having connected the central wire to the ignition distributor and connecting the wires leading to the spark plugs to the arrester in turn, similarly check the operability of these wires. Possible causes of interruptions in sparking may be cracks or burnouts in the cover or rotor of the ignition distributor or their surfaces are contaminated. You can verify the presence of this defect by replacing the ignition distribution sensor with a known good one.
Ignition switch
The operation of the anti-theft device is checked and the correct closure of the contacts at various key positions (tab. 13). The table shows the contact closure for the circuit breaker with the contact part used before 1986. Since 1986, the contact part is installed, which instead of contacts 15/1 and 15/2 has one common contact 15, which closes with contact 30/1, and there is no contact P. The voltage from the battery and the generator is supplied to contacts 30 and 30/1. The free INT plug is for connecting a radio receiver.
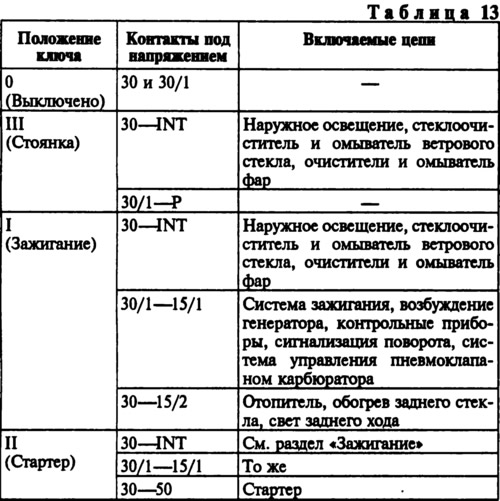
The locking rod of the anti-theft device extends after turning the key from the position «Parking» into position «Turned off». When installing the contact part in the circuit breaker body, position it so that the plugs 15 and 30 are on the side of the locking rod, while the wide protrusion of the contact part will fit into the wide groove of the circuit breaker body.
Checking elements for suppression of radio interference
These elements include high-voltage wires with a resistance of 2000±200 Ohm / m distributed along the length and an interference suppression resistor in the rotor of the ignition distributor with a resistance of 5000-6000 Ohms. Check the serviceability of these elements with an ohmmeter. In addition, an interference suppression capacitor is installed on the generator, the verification of which is described in section «Generator». In the contactless ignition system, high voltage wires of the PVPPV-40 type can be installed (of blue color) with distributed resistance (2550±270) Ohm/m or wires PVVP-8 (Red) with resistance (2000±200) Ohm / m, as well as spark plugs FE65PR or FE65CPR with a noise suppression resistor of 4-10 kOhm.
