The main dimensions for checking the attachment points of the units
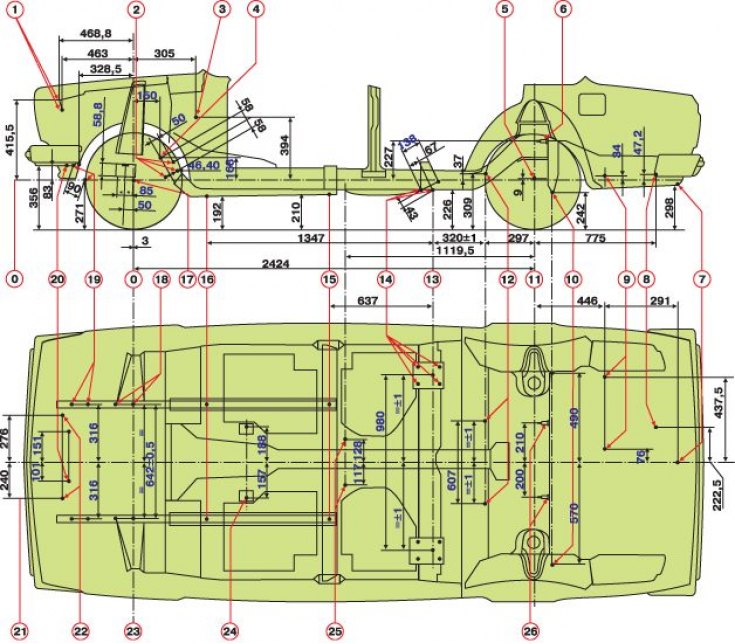
0 - baseline; 1 – the top fastening of a radiator; 2 - fastening of the crankcase of the steering mechanism and pendulum lever; 3 - the axis of the brake and clutch pedals; 4 – the center of the steering mechanism; 5 - the center of the wheel; 6 – fastening of shock-absorbers of a back suspension bracket; 7 - the center of the rear technological hole of the central amplifier of the trunk floor; 8 – back fastening of the muffler of release of gases; 9 - front mounting muffler; 10 - fastening of the transverse rod of the rear suspension; 11 – an axis of back wheels; 12 - axes of bolts for fastening the upper longitudinal rods of the rear suspension; 13 – axes of bolts for fastening the lower longitudinal rods to the body brackets; 14 - fastening brackets of the lower longitudinal rods; 15 - the center of the rear technological hole of the front spar; 16 - the center of the technological hole of the front spar; 17 - the center of the wheel; 18 - attachment points of the front suspension cross member; 19 – fastening of the anti-roll bar; 20 - lower radiator mount; 21 – an axis of the car; 22 - upper radiator mount; 23 - the axis of the front wheels; 24 – fastening of a back suspension bracket of the engine; 25 - fastening of the cardan shaft support; 26 - mounting shock absorbers rear suspension
Body floor checkpoints
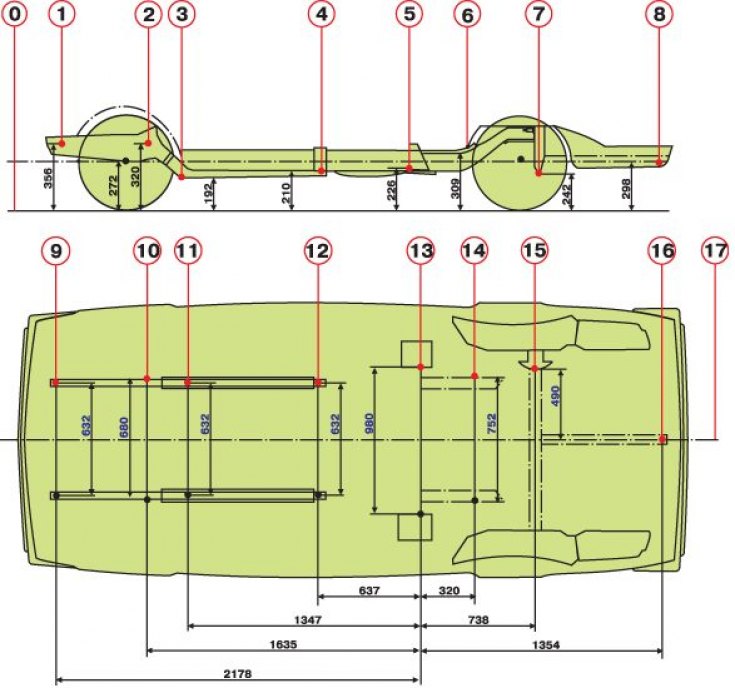
0 – reference line; 1 - intersection of the axes of the front bolts of the anti-roll bar with the surfaces of the side members; 2 - the center of the axes of the lower bolts for fastening the crankcase of the steering mechanism and the pendulum arm bracket; 3 - intersection of the centers of the front technological holes of the front floor with the surfaces of the spars; 4 - intersection of the rear technological holes of the spars of the front floor with the surfaces of the spars; 5 - the center of the axes of the bolts of the lower longitudinal rods; 6 - the center of the axes of fastening of the upper longitudinal rods; 7 - intersection of the axis of the bolt of the transverse rod with the body bracket; 8 - intersection of the center of the rear technological hole of the central amplifier of the rear floor with the surface of the amplifier; 9 - the center of the axes of the front bolts of the anti-roll bar; 10 - intersection of the centers of the axes of the lower bolts for fastening the crankcase of the steering mechanism and the bracket of the pendulum lever with the surfaces of the mudguards of the spars; 11 - centers of the front technological holes of the side members of the front floor; 12 - centers of the rear technological holes of the spars of the front floor; 13 - intersection of the axes of the bolts of the lower longitudinal rods with the outer surfaces of the body brackets; 14 - intersection of the axes of the bolts of the upper longitudinal rods with the outer surfaces of the middle spars; 15 - intersection of the axis of the bolt of the transverse rod with the body bracket; 16 - the center of the rear technological hole of the central amplifier of the rear floor; 17 - the longitudinal axis of the car
Installation for the repair and control of bodies with a device for straightening
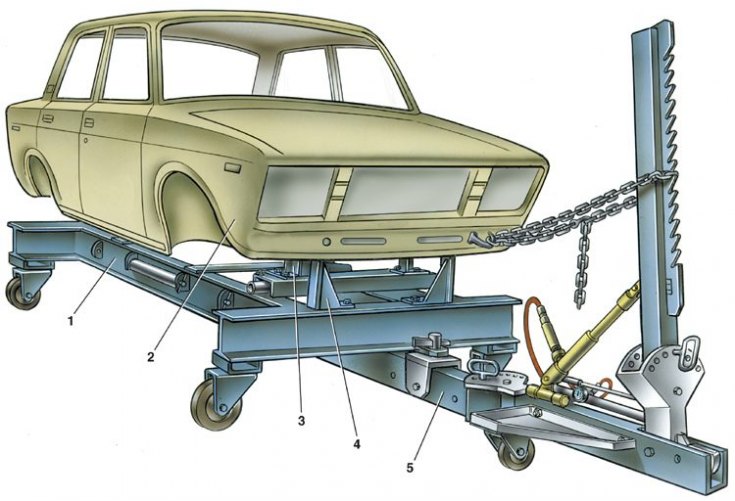
1 - installation frame: 2 - car body; 3 – an arm of fastening of a crossbar of a forward suspension bracket; 4 – an arm of fastening of the stabilizer of cross-section stability; 5 - dressing device with boom and hydraulic device
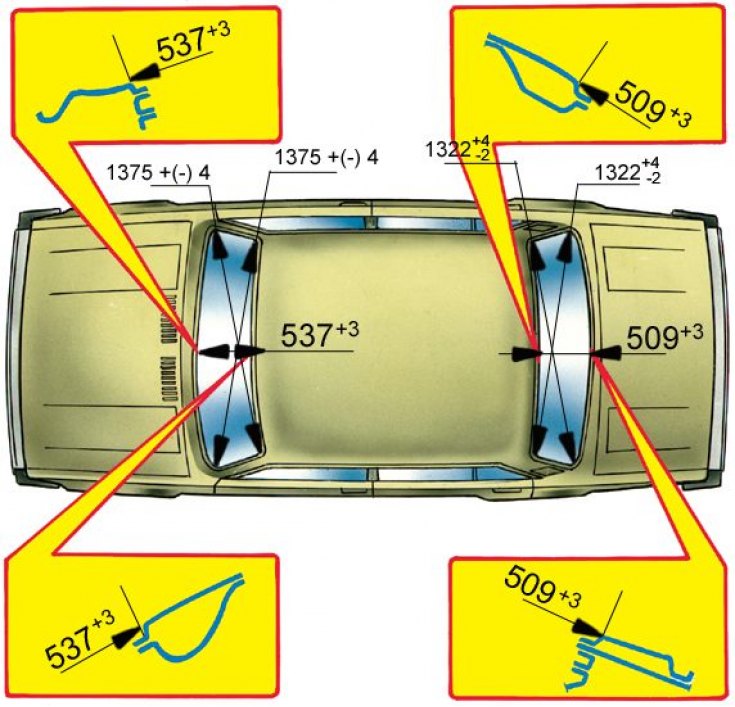
Reference linear dimensions of the openings of the wind and rear windows
A significant part of the body repair work falls on emergency vehicles, which in most cases require checking the geometry of the attachment points of the vehicle chassis units and assemblies.
To control the geometry of the attachment points of the chassis nodes shown in fig. The main dimensions for checking the attachment points of the units and fig. Control points for checking the floor of the body, as well as for complex repairs with simultaneous control, a body repair and control unit is used in combination with dressing devices (see fig. Installation for the repair and control of bodies with a device for straightening).
The dressing device is fixed on the frame from the side of the deformed part of the body.
Body damage can be very different. Therefore, the repair rules in each individual case should be their own, the most suitable for these damages.
In almost all cases of damage, it is necessary to remove some parts in order to locate the damage, straighten and align the frame. In cases of serious damage, remove all easily removable inner upholstery parts to facilitate measurement, control and installation of hydraulic or screw jacks to eliminate distortions and deflections.
Editing is necessary to restore the original linear dimensions of the body frame.
The diagonal dimensions of the window openings should be for the wind window (see fig. Reference linear dimensions of the openings of the wind and rear windows) 1375±4 mm, for the rear - 1322+4 (1322–2) mm. The distances between the flanges of the window openings along the axis of the vehicle must be equal, respectively, for the wind window 537 mm3, for the rear - 509 mm3.
The difference in the diagonal dimensions of the opening of the wind window, as well as the openings of the rear window, hood, trunk lid of the same body must not exceed 2 mm.
Most often, the repair of the skeleton requires the replacement of wings, roof panels, front and rear. Methods for replacing and repairing these parts can be taken as a basis for repairing other parts of the frame. You also need to know the location of the welds.
