Open large image in new tab »
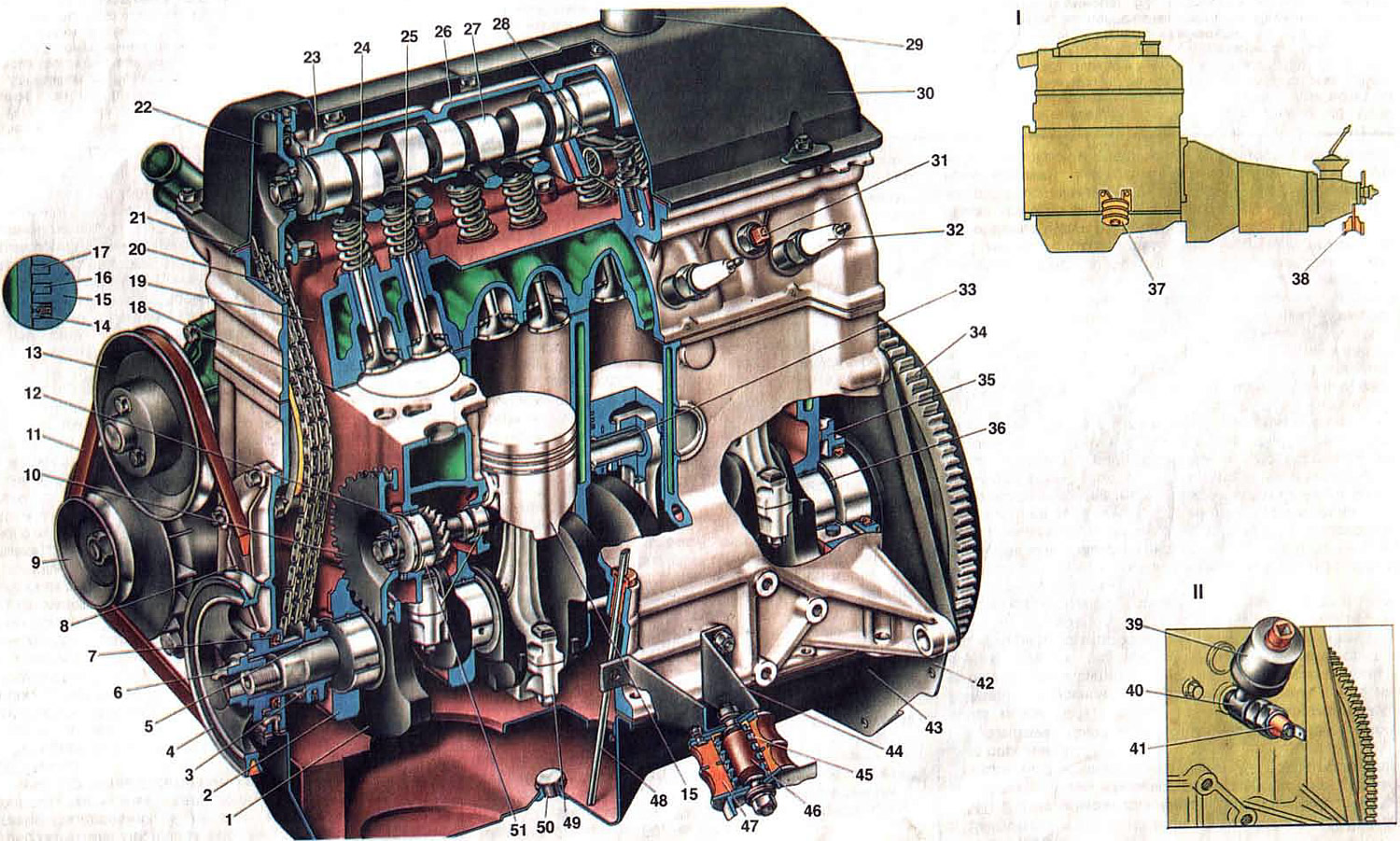
Pic. 3. Engine (lengthwise cut).
1. Crankshaft; 2. Cover of the first main bearing; 3. Crankshaft sprocket; 4. Crankshaft pulley; 5. Key pulley and crankshaft sprocket; 6. Ratchet; 7. Front crankshaft oil seal; 8. Timing mechanism drive cover; 9. Alternator pulley; 10. Asterisk drive oil pump, fuel pump and ignition distributor; 11. Belt drive coolant pump and generator; 12. Oil pump drive shaft, fuel pump and ignition distributor; 13. Coolant water pump pulley; 14. Oil scraper ring; 15. Piston; 16. Lower compression ring; 17. Top compression ring; 18. Cylinder block; 19. Cylinder head; 20. Timing mechanism drive chain; 21. Cylinder head cover gasket; 22. Camshaft sprocket; 23. Mounting protrusion on the camshaft bearing housing; 24. Exhaust valve. 25. Inlet valve; 26. Camshaft bearing housing; 27. Camshaft; 28. Valve drive lever; 29. Oil filler neck. 30 Cylinder head cover; 31. Coolant temperature indicator sensor; 32. Spark plug; 33. Piston pin; 34. Flywheel; 35. The holder of the rear oil seal of the crankshaft; 36. Thrust half ring of the crankshaft; 37. Front engine mount; 38. Rear engine mount; 39. Oil pressure indicator sensor; 40. Fitting; 41. Sensor control lamp oil pressure; 42. Front cover of the clutch housing; 43. Oil sump; 44. Bracket front support; 45. Front support spring; 46. Buffer pillow front support; 47. Rubber pad front support; 48. Oil level indicator; 49. Connecting rod with cover assembly; 50. Oil sump drain plug; 51. Bushings of the oil pump drive shaft, fuel pump and ignition distributor.
1. Crankshaft; 2. Cover of the first main bearing; 3. Crankshaft sprocket; 4. Crankshaft pulley; 5. Key pulley and crankshaft sprocket; 6. Ratchet; 7. Front crankshaft oil seal; 8. Timing mechanism drive cover; 9. Alternator pulley; 10. Asterisk drive oil pump, fuel pump and ignition distributor; 11. Belt drive coolant pump and generator; 12. Oil pump drive shaft, fuel pump and ignition distributor; 13. Coolant water pump pulley; 14. Oil scraper ring; 15. Piston; 16. Lower compression ring; 17. Top compression ring; 18. Cylinder block; 19. Cylinder head; 20. Timing mechanism drive chain; 21. Cylinder head cover gasket; 22. Camshaft sprocket; 23. Mounting protrusion on the camshaft bearing housing; 24. Exhaust valve. 25. Inlet valve; 26. Camshaft bearing housing; 27. Camshaft; 28. Valve drive lever; 29. Oil filler neck. 30 Cylinder head cover; 31. Coolant temperature indicator sensor; 32. Spark plug; 33. Piston pin; 34. Flywheel; 35. The holder of the rear oil seal of the crankshaft; 36. Thrust half ring of the crankshaft; 37. Front engine mount; 38. Rear engine mount; 39. Oil pressure indicator sensor; 40. Fitting; 41. Sensor control lamp oil pressure; 42. Front cover of the clutch housing; 43. Oil sump; 44. Bracket front support; 45. Front support spring; 46. Buffer pillow front support; 47. Rubber pad front support; 48. Oil level indicator; 49. Connecting rod with cover assembly; 50. Oil sump drain plug; 51. Bushings of the oil pump drive shaft, fuel pump and ignition distributor.
Open large image in new tab »
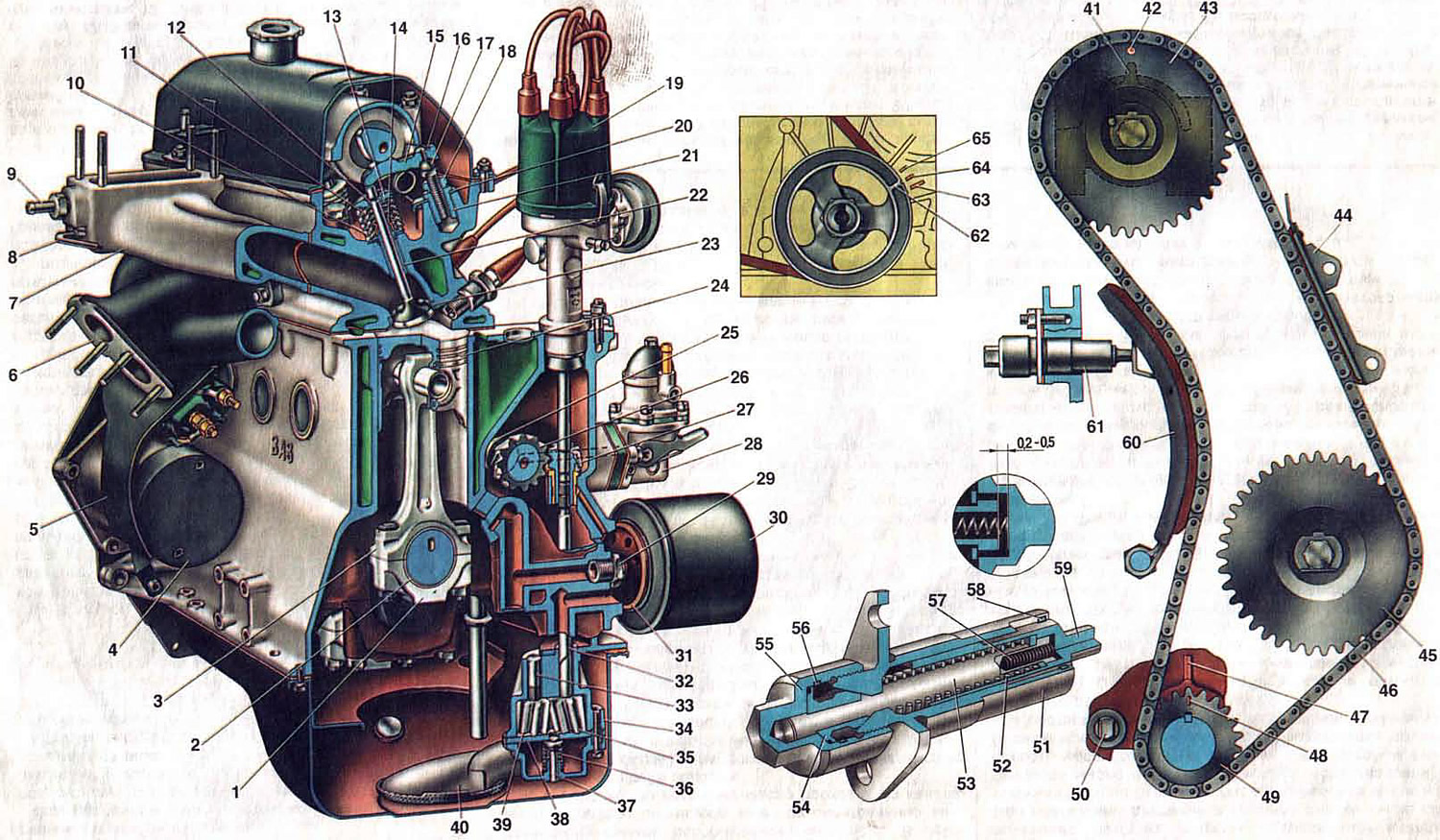
Pic. 4. Engine (cross section).
1. Connecting rod cap; 2. Connecting rod contributions; 3. Connecting rod; 4. Starter; 5. Heat shield starter; 6. Exhaust manifold; 7. Inlet pipe; 8- Drain tube inlet pipe; 9. Pipe fitting for draining coolant; 10. Outer valve spring; 11. Internal valve spring; 12. Valve cracker; 13. Spring plate; 14. Oil cap; 15. Valve drive lever; 16. Valve lever spring; 17. Valve adjusting bolt; 18. Locknut adjusting bolt; 19. Ignition distributor; 20. Valve lever spring retainer plate; 21. Bushing adjusting bolt; 22. Valve guide; 23. Valve seat; 24. Piston; 25. Eccentric for driving the fuel pump; 26. Auxiliary drive roller; 27. Gear drive oil pump and ignition distributor; 28. Fuel pump; 29. Oil filter mounting fitting; 30. Oil filter: 31. Gasket; 32. Oil pump roller; 33. The axis of the driven gear of the oil pump; 34. Oil pump housing; 35. Oil pump drive gear; 36. Pressure reducing valve spring; 37. Oil pump pressure reducing valve; 38. Oil pump cover; 39. Oil pump driven gear; 40. Oil pump inlet pipe; 41. Mounting protrusion on the camshaft bearing housing; 42. Mounting mark on the camshaft sprocket; 43. Camshaft sprocket; 44. Chain guide; 45. Asterisk drive auxiliary units; 46. Camshaft drive chain; 47. Installation mark on the cylinder block; 48. Mounting mark on the crankshaft sprocket; 49. Crankshaft sprocket; 50. Restrictive finger; 51. Chain tensioner housing; 52. Chain tensioner spring; 53. Tensioner rod; 54. Clamping cracker of the rod; 55. Cap nut; 56. Snap ring; 57. Plunger spring; 58. Plunger retaining ring; 59. Plunger tensioner; 60. Tensioner shoe; 61. Tensioner; 62. TDC mark on the crankshaft pulley; 63. Ignition advance mark by 0°; 64. Ignition advance mark by 5°; 65. 10°spark advance mark.
1. Connecting rod cap; 2. Connecting rod contributions; 3. Connecting rod; 4. Starter; 5. Heat shield starter; 6. Exhaust manifold; 7. Inlet pipe; 8- Drain tube inlet pipe; 9. Pipe fitting for draining coolant; 10. Outer valve spring; 11. Internal valve spring; 12. Valve cracker; 13. Spring plate; 14. Oil cap; 15. Valve drive lever; 16. Valve lever spring; 17. Valve adjusting bolt; 18. Locknut adjusting bolt; 19. Ignition distributor; 20. Valve lever spring retainer plate; 21. Bushing adjusting bolt; 22. Valve guide; 23. Valve seat; 24. Piston; 25. Eccentric for driving the fuel pump; 26. Auxiliary drive roller; 27. Gear drive oil pump and ignition distributor; 28. Fuel pump; 29. Oil filter mounting fitting; 30. Oil filter: 31. Gasket; 32. Oil pump roller; 33. The axis of the driven gear of the oil pump; 34. Oil pump housing; 35. Oil pump drive gear; 36. Pressure reducing valve spring; 37. Oil pump pressure reducing valve; 38. Oil pump cover; 39. Oil pump driven gear; 40. Oil pump inlet pipe; 41. Mounting protrusion on the camshaft bearing housing; 42. Mounting mark on the camshaft sprocket; 43. Camshaft sprocket; 44. Chain guide; 45. Asterisk drive auxiliary units; 46. Camshaft drive chain; 47. Installation mark on the cylinder block; 48. Mounting mark on the crankshaft sprocket; 49. Crankshaft sprocket; 50. Restrictive finger; 51. Chain tensioner housing; 52. Chain tensioner spring; 53. Tensioner rod; 54. Clamping cracker of the rod; 55. Cap nut; 56. Snap ring; 57. Plunger spring; 58. Plunger retaining ring; 59. Plunger tensioner; 60. Tensioner shoe; 61. Tensioner; 62. TDC mark on the crankshaft pulley; 63. Ignition advance mark by 0°; 64. Ignition advance mark by 5°; 65. 10°spark advance mark.
The cars are equipped with engines of the same design, but with different cylinder sizes. They differ mainly in the size of the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft and chain drive parts.
Cylinder block
Cylinder block 18 is cast from special cast iron. The cylinders of the block are subdivided by diameter through 0.01 mm into five classes, denoted by the letters A, B, C, D, E. The cylinder class is indicated on the lower plane of the block opposite each cylinder. The cylinder and the piston mating with it must be of the same class to ensure a gap between the piston and the cylinder of 0.05-0.07 mm. The cylinder diameters of each class are as follows, mm:
| Class | Bore of engines 2101, 2103 | Engine cylinder diameter 21011, 2106 |
| A | 76,000-76,010 | 79,000-79010 |
| IN | 76,010-76,020 | 79,010-79,020 |
| WITH | 76,020-76,030 | 79,020-79,030 |
| D | 76,030-76,040 | 79,030-79,040 |
| E | 76,040-76,050 | 79,040-79,050 |
In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five crankshaft main bearing supports with thin-walled steel-aluminum liners. The holes for the crankshaft bearings in the cylinder block are machined complete with covers 2. Therefore, the bearing covers are not interchangeable, and risks are made on their outer surface to distinguish them.
In the rear support there are sockets for installing thrust half rings 36 that hold the crankshaft from axial movement. A steel-aluminum semi-ring is installed in front, and a metal-ceramic one in the back (yellow color), oil soaked. The value of the axial clearance of the crankshaft when assembling the engine is provided in the range of 0.06-0.26 mm. If the clearance in operation exceeds the maximum allowable (0.35 mm), it is necessary to replace the thrust half rings with new or repair ones, increased by 0.127 mm. The grooves located on one side of the half rings must face the thrust surfaces of the crankshaft.
In front of the cylinder block there is a cavity for driving the gas distribution mechanism, closed by a cover 8. On the back side, a holder 35 of the rear oil seal is attached to the cylinder block. The cover 8 and the holder 35 are equipped with self-clamping seals. In the left part of the block, a roller 12 of the drive of auxiliary units is installed. Steel-aluminum bushings 51 are pressed into the holes for the roller bearings.
Cylinder head
Cylinder head 19 common to four cylinders, cast aluminum alloy. Cast iron seats and valve guides are pressed into the head. In the holes of the guide bushings, helical grooves are cut for lubrication. To reduce the penetration of oil into the combustion chamber through the gaps between the sleeve and the valve stem, metal-rubber oil seals are used.
The cylinder head is attached to the cylinder block with eleven bolts. Between the head and the cylinder block there is a gasket made of asbestos material on a metal frame and impregnated with graphite.
Pistons
Pistons 15 are made of aluminum alloy and coated with a layer of tin to improve run-in. The piston skirt is oval in cross section and conical in height. In addition, steel thermostatic plates are cast into the piston bosses. All this is done to compensate for uneven thermal deformation of the piston during heating. The piston bosses have holes for the passage of oil to the piston pin.
The hole for the piston pin is shifted from the axis of symmetry by 2 mm to the right side of the engine to reduce piston knock when passing through TDC. Therefore, there is a mark near the hole for the piston pin "P", which, when assembled, must face the front of the engine.
Pistons, like cylinders, are sorted according to the outer diameter into five classes through 0.01 mm, and according to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin - into three categories through 0.001 mm, denoted by the numbers 1, 2, 3. Piston class (letter) and piston pin bore category (number) stamped on the bottom of the piston. Pistons by weight in the same engine must be matched with the maximum allowable deviation (2.5 g).
Piston pins
Piston pins 14, 16 and 17 are made of cast iron. The outer surface of the upper compression ring 17 is chrome-plated to increase wear resistance and has a barrel-shaped generatrix to improve running-in. Lower compression ring 16 - scraper type (with a groove on the outer surface), phosphated.
The ring must be installed with the groove down. Oil scraper ring 14 has slots for oil removed from the cylinder and an internal coil spring (expander).
Connecting rods
Connecting rods 49 - steel, forged, with a split lower head, in which the connecting rod bearing shells are installed. The connecting rod is processed together with the cover, therefore, when assembling, the numbers on the connecting rod and the cover must be the same.
Crankshaft
Crankshaft 1 - five-bearing, cast iron. The necks of the shaft are hardened by high frequency currents to a depth of 2-3 mm. At the rear end of the crankshaft, a socket is made for the front bearing of the input shaft of the gearbox, along the outer diameter of which the flywheel 31 is centered. The flywheel is mounted on the crankshaft so that the mark (cone-shaped hole near the gear rim of the flywheel) and the axis of the connecting rod journal of the first cylinder were in the same plane and one from the axis of the crankshaft.
Inserts
Inserts of main and connecting rod bearings - thin-walled, steel-aluminum. All connecting rod bearings are identical and interchangeable. The upper shells of the 1st, 2nd, 4th and 5th main bearings are the same, with a groove on the inner surface, and the lower ones are without a groove. The 3rd main bearing shells differ from the others in their greater width and the absence of a groove on the inner surface.
Gas distribution mechanism
The gas distribution mechanism ensures that the engine cylinders are filled with a combustible mixture and exhaust gases are released in accordance with the cylinder operation order and valve timing adopted for the engine. The details of the mechanism include: camshaft, valves and guide bushings, springs with fastening parts, valve drive levers.
The camshaft that controls the opening and closing of the valves is cast iron. The rubbing surfaces of the cams are bleached. This process consists in electric arc melting of surfaces, as a result of which a layer of the so-called "white" cast iron with high hardness. The shaft rotates on five bearings in a special housing 26 (see fig. 3), and is kept from axial movements by a thrust flange placed in the groove of the front bearing journal of the shaft.
valves (inlet and outlet) located in the cylinder head obliquely in one row. The intake valve head has a larger diameter for better cylinder filling, and the exhaust valve face, which operates at high temperatures in an aggressive exhaust gas environment, has a heat-resistant alloy overlay. Springs 10 and 11 (pic. 4) press the valve to the seat and do not allow it to come off the actuator lever. The upper support plate 13 of the springs is held on the valve stem by two crackers 12, which have the shape of a truncated cone when folded.
The levers 15 transmit force from the camshaft cam to the valve. The lever rests at one end on the spherical head of the adjusting bolt 17, and at the other end on the end face of the valve. The adjusting bolt is screwed into the sleeve 21 and is locked with a lock nut 18.
Auxiliary drive
Auxiliary units of the engine and the gas distribution mechanism are driven from the crankshaft using a chain drive. It consists of a two-row bush-roller chain 46, a drive sprocket 49 on the crankshaft, a driven sprocket 43 of the camshaft, a chain guide 44 and a tensioner 61 with shoe 60. The tensioner shoe and chain guide have a steel frame with a vulcanized rubber layer.
When the fixing nut 55 is unscrewed, the chain is tensioned by shoe 60, on which springs 52 and 57 act through plunger 59. The tensioner shoe rotates around the fastening bolt. After tightening the nut 55, the rod 53 is clamped by the collets of the cracker 54, as a result of which the spring 52 of the chain tensioner is blocked. When the engine is running, only the internal spring 57 acts on the plunger 59, which, due to a gap of 0.2-0.5 mm in the tensioner mechanism, compensates for chain vibrations. The damper 44 of the chain dampens vibrations of the leading branch of the chain. When the engine is running, the chain stretches. It is considered to be operational if the tensioner provides its tension, i.e. if the chain is extended no more than 4 mm.
The shaft 26 of the oil pump drive, the ignition distributor and the fuel pump is installed along the engine and has two support journals, a helical gear and an eccentric 25, which drives the fuel pump through the pusher. Roller helical gear 26 meshes with gear 27 which drives the ignition distributor and oil pump. Gear 27 rotates in a ceramic-metal bushing pressed into the cylinder block. The gear has a slotted hole, which includes the splined ends of the rollers of the ignition distributor and the oil pump.
Engine operation
In one working cycle, four cycles occur in the engine cylinder - hot mixture intake, compression, power stroke and exhaust gases. These cycles are carried out in two revolutions of the crankshaft, i.e. each beat takes half a turn (180°) crankshaft.
The intake valve begins to open 12°before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC). This is necessary so that the valve is fully open when the piston goes down. The valve closes 40°after the piston has passed bottom dead center (NMT). Due to the inertial pressure of the jet of the combustible mixture being sucked in, it continues to flow into the cylinder when the piston has already begun to move upward, and thus a better filling of the cylinder is ensured.
The exhaust valve begins to open 42°before BDC. At this moment, the pressure in the cylinder is still quite high, and the gases begin to intensively flow out of the cylinder. The valve closes 10°after the piston has passed TDC.
There is such a moment (22°of rotation of the crankshaft about TDC), when both intake and exhaust valves are open at the same time. This position is called valve overlap. Due to the short period of time, the overlapping of the valves does not lead to the penetration of exhaust gases into the intake manifold, but, on the contrary, the inertia of the exhaust gas flow causes the combustible mixture to be sucked into the cylinder and improves its filling.
To ensure the timing of the opening and closing of the valves with the angles of rotation of the crankshaft (those. ensure the correct installation of the valve timing), on the crankshaft and camshaft sprockets there are marks 48 and 42, as well as 47 on the cylinder block and 41 (ledge) on the camshaft bearing housing. If the valve timing is set correctly, then with the position of the piston of the fourth cylinder at TDC at the end of the compression stroke, mark 41 should coincide with mark 42, and mark 48 with mark 47. When the camshaft drive cavity is closed with a cover, the position of the crankshaft can be determined from the marks on the crankshaft pulley and the camshaft drive cover.
To ensure the correct operation of the valve timing mechanism during thermal expansion of parts on a running engine, the gaps between the cams and valve actuation levers are set to 0.15 mm on a cold engine. If the gaps are larger, then the valves will open with a delay and close ahead. If there is no gap, then the valves on the running engine will remain slightly ajar. As a result, the durability of valves and seats will be sharply reduced, and engine power will drop.
