Open large image in new tab »
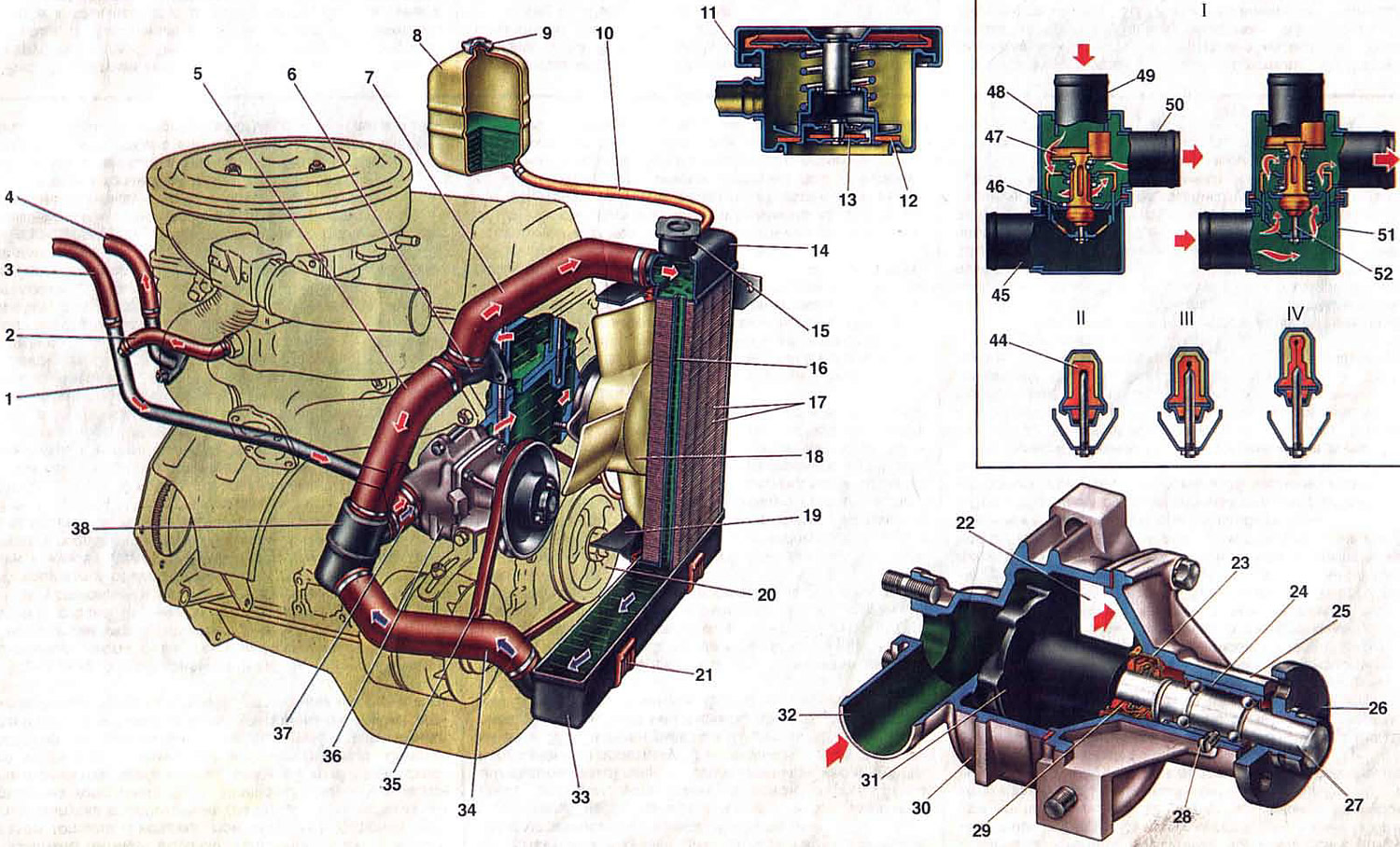
Pic. 6. Engine cooling system.
1. Pipe for draining fluid from the heater radiator to the coolant pump: 2. Hose for draining coolant from the intake pipe; 3. Hose for draining coolant from the heater radiator; 4. Hose for supplying liquid to the heater radiator; 5. Thermostat bypass hose; 6. Outlet pipe of the cooling jacket; 7. Radiator inlet hose; 8. Expansion tank; 9. Tank stopper; 10. Hose from the radiator to the expansion tank; 11. Radiator plug; 12. Graduation (steam) stopper valve; 13. Inlet valve; 14. Upper radiator tank; 15. Radiator filler neck; 16. Radiator tube; 17. Radiator cooling plates; 18. Fan cover; 19. Electric fan; 20. Coolant pump drive pulley; 21. Rubber support; 22. Window on the side of the cylinder block for supplying coolant; 23. Gland clip; 24. Coolant pump roller bearing; 25. Pump cover; 26. Pump drive pulley hub; 27. Pump roller; 28. Locking screw; 29. Gland seal; 30. Pump housing; 31. Pump impeller; 32. Inlet pipe of the pump; 33. Lower radiator tank; 34. Outlet radiator hose; 35. Coolant pump drive belt; 36. Coolant pump; 37. Hose for supplying coolant to the pump; 38. Thermostat; 39. Rubber insert; 40. Inlet pipe (from the radiator); 41. Main valve; 42. Bypass valve; 43. Thermostat housing; 44. Branch pipe of the bypass hose; 45. Hose connection for supplying coolant to the pump; 46. Thermostat cover; 47. Piston of the working element; I. Scheme of thermostat operation; II. Liquid temperature less than 80°C; III. Liquid temperature 80 - 94°C; IV. Fluid temperature over 94°C.
1. Pipe for draining fluid from the heater radiator to the coolant pump: 2. Hose for draining coolant from the intake pipe; 3. Hose for draining coolant from the heater radiator; 4. Hose for supplying liquid to the heater radiator; 5. Thermostat bypass hose; 6. Outlet pipe of the cooling jacket; 7. Radiator inlet hose; 8. Expansion tank; 9. Tank stopper; 10. Hose from the radiator to the expansion tank; 11. Radiator plug; 12. Graduation (steam) stopper valve; 13. Inlet valve; 14. Upper radiator tank; 15. Radiator filler neck; 16. Radiator tube; 17. Radiator cooling plates; 18. Fan cover; 19. Electric fan; 20. Coolant pump drive pulley; 21. Rubber support; 22. Window on the side of the cylinder block for supplying coolant; 23. Gland clip; 24. Coolant pump roller bearing; 25. Pump cover; 26. Pump drive pulley hub; 27. Pump roller; 28. Locking screw; 29. Gland seal; 30. Pump housing; 31. Pump impeller; 32. Inlet pipe of the pump; 33. Lower radiator tank; 34. Outlet radiator hose; 35. Coolant pump drive belt; 36. Coolant pump; 37. Hose for supplying coolant to the pump; 38. Thermostat; 39. Rubber insert; 40. Inlet pipe (from the radiator); 41. Main valve; 42. Bypass valve; 43. Thermostat housing; 44. Branch pipe of the bypass hose; 45. Hose connection for supplying coolant to the pump; 46. Thermostat cover; 47. Piston of the working element; I. Scheme of thermostat operation; II. Liquid temperature less than 80°C; III. Liquid temperature 80 - 94°C; IV. Fluid temperature over 94°C.
Engine cooling system - liquid, closed type, with forced circulation of liquid. The system capacity is 9.85 liters, including the body interior heating system. The cooling system consists of the following elements: coolant pump 36, radiator, expansion tank 8, pipelines and hoses, electric fan 19, cooling jackets for the block and cylinder head.
When the engine is running, the liquid heated in the cooling jackets enters through the outlet pipe 6 through hoses 5 and 7 into the radiator or thermostat, depending on the position of the thermostat valves. Next, the coolant is sucked in by pump 36 and fed back into the cooling jackets.
The engine cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation of liquid. The system capacity is 9.85 liters, including the body interior heating system. The cooling system consists of the following elements: coolant pump 36, radiator, expansion tank 8, pipelines and hoses, fan 19, cooling jackets for the block and cylinder head.
When the engine is running, the liquid heated in the cooling jackets enters through the outlet pipe 6 through hoses 5 and 7 into the radiator or thermostat, depending on the position of the thermostat valves. Next, the coolant is sucked in by pump 36 and fed back into the cooling jackets.
Checking the coolant level is carried out on a cold engine (at a temperature of plus 15-20°C) according to the liquid level in the expansion tank 8, which should be 3-4 mm above the mark "MIN".
To control the temperature of the coolant, there is a sensor installed in the cylinder head and a pointer on the instrument panel. Under normal temperature conditions of engine operation, the pointer is at the beginning of the red field of the scale within 80-100°C. The transition of the arrow into the red zone indicates an increased thermal condition of the engine, which may be caused by malfunctions in the cooling system (loose pump drive belt, insufficient coolant, malfunctioning thermostat or electric fan), and difficult road conditions.
The fluid is drained from the system through drain holes closed by plugs: one is in the left corner of the lower tank 33 of the radiator, the other is in the cylinder block on the left in the direction of the vehicle.
The car interior heater is connected to the cooling system. The heated liquid from the cylinder head enters through hose 4 through a tap into the heater radiator, and is sucked off by pump 36 through hose 3 and tube 1.
Coolant pump
The coolant pump is a centrifugal type, driven from the crankshaft pulley by the alternator drive V-belt. The pump is attached to the cylinder block on the right side through a sealing gasket.
The housing 30 and the cover 25 of the pump are cast from an aluminum alloy. In the bearing cover 24, which is locked by a screw 28, a roller 27 is installed. The bearing 24 is double-row, non-separable, without an inner race. The bearing is filled with grease during assembly and is not subsequently lubricated. The impeller 31 is pressed onto the roller 27 on one side, and the hub 26 of the pump drive pulley on the other. The end face of the impeller, in contact with the sealing ring, is hardened by high-frequency currents to a depth of 3 mm. The sealing ring is pressed against the impeller by a spring through a rubber cuff 29. The stuffing box is non-separable, it consists of an outer brass clip 23, a rubber cuff and a spring. It is pressed into the cover 25 of the pump.
The pump housing has a suction pipe 32 and a window 22 towards the cylinder block for pumping coolant. With normal tension of the pump drive belt, its deflection under a force of 10 kgf should be within 10-15 mm.
Electric fan
The fan is four-bladed, made of plastic. The fan blades have a variable installation angle along the radius and a variable pitch along the hub to reduce noise. The fan is mounted on the motor shaft and pressed with a nut. For better performance, the fan is housed in shroud 18, which is bolted to the radiator brackets. The electric motor assembly with the fan is mounted on three rubber bushings and fastened with nuts to the studs of the fan casing 18.
Switching on and off of the electric fan 19 is carried out automatically depending on the temperature of the liquid using a sensor type TM-108 installed in the lower radiator tank on the left side. The temperature of closing the sensor contacts should be within 89-95°C, and opening within 84-90°C.
In variant versions, VAZ-21061 vehicles can be equipped with mechanically driven fans from the hub of the coolant pump shaft.
Radiator
The radiator with upper and lower tanks, with two rows of brass vertical tubes and tin-plated cooling plates, is fastened with four bolts to the front end of the body and rests on rubber supports 21.
The filler neck 15 of the radiator is closed with a plug 11 and connected by a hose 10 to a translucent plastic expansion tank 8. The radiator plug has an inlet valve 13 and an outlet valve 12, through which the radiator is connected by a hose to the expansion tank. Inlet valve is not pressed against the gasket (clearance 0.5-1.1 mm) and allows the inlet and outlet of coolant into the expansion tank as the engine warms up and cools down.
Since 1988, radiators with an aluminum core and plastic tanks have been installed on cars.
Thermostat and cooling system operation
The thermostat of the cooling system accelerates the warm-up of the engine and maintains the required thermal regime of the engine. Under optimal thermal conditions, the temperature of the coolant should be 85-95°C.
Thermostat 38 consists of a body 43 and a cover 46, which are rolled together with the seat of the main valve 41. The thermostat has an inlet pipe 40 for inlet of cooled liquid from the radiator, a pipe 44 of the bypass hose 5 for bypassing liquid from the cylinder head to the thermostat and a pipe 45 for supplying coolant liquids into the pump 36.
The main valve is installed in the thermoelement cup, in which the rubber insert 39 is rolled. The rubber insert contains a polished steel piston 47, fixed on a fixed holder. A heat-sensitive solid filler is placed between the walls and the rubber insert. The main valve 41 is pressed against the seat by a spring. Two racks are fixed on the valve, on which a bypass valve 42 is installed, which is pressed by a spring.
