Removing
1. We install the car on a viewing hole or overpass (see "Vehicle preparation for maintenance and repair").
2. Remove the cylinder head from the engine (see "Cylinder head gasket - replacement").
3. Remove the engine oil pan (see "Engine oil pan - removal and installation").
4. Turn off the nuts of the connecting rod caps (without removing the crankshaft) and push the piston with the connecting rod out of the cylinder block (see "Crankshaft - removal and installation").
5. We take out the steel-aluminum insert from the connecting rod cover.
The number of the cylinder in which they are installed is stamped on the connecting rod and cap.
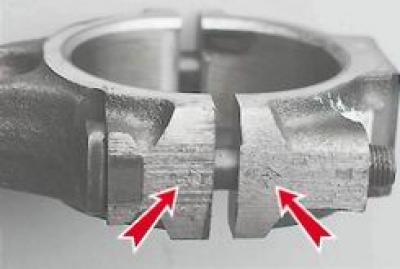
6. We install the connecting rod in a vice and remove two compression rings and one oil scraper ring with an expander from the piston.
7. Through the mandrel, we press out the finger from the connecting rod and remove the piston.

Similarly, remove the pistons of the remaining cylinders.
Before installing the piston group on the connecting rod, it is necessary to select its parts.
Selection of parts of the connecting rod and piston group
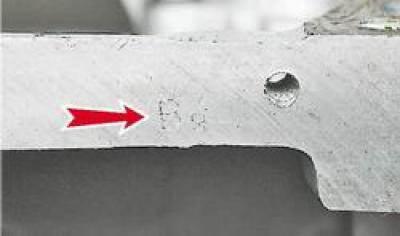
1. We select the piston to the cylinder. The estimated gap between the cylinder and the engine piston should be 0.06-0.08 mm. It is determined by measuring the cylinders and pistons and is ensured by installing pistons of the same class as the cylinders. The maximum allowable clearance is 0.15 mm. The piston diameter is measured in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 52.4 mm from the piston crown. Pistons are manufactured according to the outer diameter of five classes (A, B, C, D and E) through 0.01 mm, and according to the diameter of the hole for the piston pin - three categories through 0.004 mm. Pistons of groups A, C and E are available as spare parts. Piston class (letter) and piston pin bore category (number) stamped on the bottom of the piston.

For the correct orientation of the piston relative to the cylinder on the piston wall (next to the boss) mark completed "P", which should be directed towards the front of the cylinder block.
We measure the cylinder diameter with a caliper in four zones, both in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the engine.
In the belt zone 1, the cylinders practically do not wear out. Therefore, by the difference in measurements in the first and other belts, we judge the amount of cylinder wear.
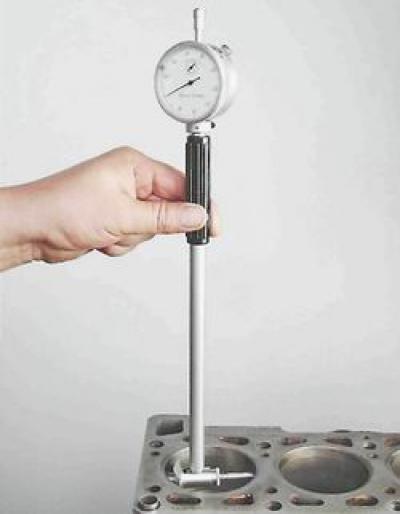

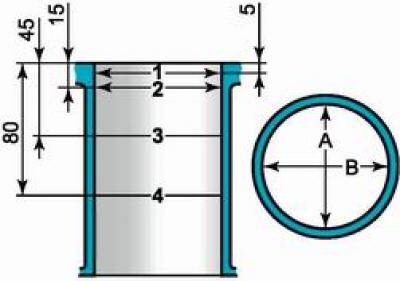
Scheme for measuring cylinder diameters: 1, 2, 3 and 4 - belt numbers; A and B - measurement directions
Cylinders are divided by diameter into five classes every 0.01 mm: A, B, C, D and E. The cylinder class is stamped on the lower plane of the block.
2. We select a finger to the piston. The pin is installed in the upper head of the connecting rod with an interference fit and rotates freely in the cylinder bosses. According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three categories through 0.004 mm. Categories are indicated by a colored mark on the end of the finger: blue - the first category, green - the second, red - the third. We check the pairing of the piston pin and piston by inserting the piston pin (lubricated with engine oil) into the holes of the piston bosses. The piston pin must be installed by simply pressing the thumb and not fall out when the finger is in a vertical position.
3. Check the gap between the grooves and piston rings. Clearances must correspond to the values given in table. 8.1.3 (see below). Increased clearance leads to rapid wear (breaking) piston grooves.

Table 8.1.2. Dimensions of the main mating engine parts
|
Mating Parts |
Dimensions of parts, mm |
Permissible |
||
|
Shaft |
Hole |
|||
|
Piston - cylinder (for VAZ-2103 engine) |
Class A |
75,94-75,95 |
76,00-76,01 |
0,15 |
|
Class B |
75,95-75,96 |
76,01-76,02 |
||
|
Class C |
75,96-75,97 |
76,02-76,03 |
||
|
Class D |
75,97-75,98 |
76,03-76,04 |
||
|
Class E |
75,98-75,99 |
76,04-76,05 |
||
|
Piston - cylinder (for engines VAZ-2106, VAZ-21011) |
Class A |
78,94-78,95 |
79,00-79,01 |
0,15 |
|
Class B |
78,95-78,96 |
79,01-79,02 |
||
|
Class C |
78,96-78,97 |
79,02-79,03 |
||
|
Class D |
78,97-78,98 |
79,03-79,04 |
||
|
Class E |
78,98-78,99 |
79,04-79,05 |
||
|
Piston pin - piston |
1st category (blue label) |
21,970-21,974 |
21,982-21,986 |
- |
|
2nd category (green label) |
21,974-21,978 |
21,986-21,990 |
||
|
3rd category (red label) |
21,978-21,982 |
21,990-21,994 |
||
|
Piston pin - connecting rod head |
21,970-21,982 |
21,940-21,960 |
- |
|
Table 8.1.3. Clearances in mating grooves and piston rings
|
Mating Parts |
Dimensions of parts, mm |
Permissible |
|
|
ring height |
Groove width |
||
|
Upper compression ring - piston groove |
1,478-1,490 |
1,535-1,555 |
0,15 |
|
Lower compression ring - piston groove |
1,978-1,990 |
2,015-2,035 |
0,15 |
|
Oil scraper ring - piston groove |
3,925-3,937 |
3,957-3,977 |
0,15 |
Table 8.1.4. Piston ring gaps
|
Name of the ring |
Gap size, mm |
|
Top compression ring |
0,30-0,45 |
|
Lower compression ring |
0,25-0,40 |
|
Oil scraper ring |
0,25-0,40 |
Assembling the connecting rod and piston group
1. We put the finger 4 on the mandrel 2, without tightening the stop 3 too much.
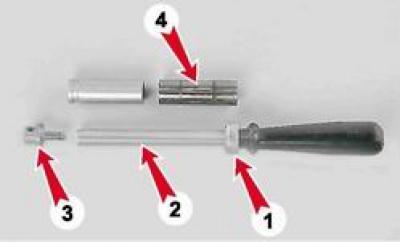
2. Cool the connecting rod finger in the freezer. We heat the upper head of the connecting rod to 240°C with a blowtorch or an industrial hair dryer, clamp the connecting rod in a vice and put a piston on it (label "P" on the piston must be on the side of the oil outlet hole on the bottom head of the connecting rod).

3. We push the finger mounted on the mandrel into the holes of the piston bosses and the upper head of the connecting rod until the annular belt 1 stops on the handle into the piston.

4. After cooling the connecting rod, lubricate the finger with engine oil through three holes in each piston boss and through the gap between the boss and the connecting rod.
5. Lubricate the piston rings and grooves with engine oil. We install rings on the piston and orient the locks of the rings. The lock of the upper compression ring should be located at an angle of 30-45°to the axis of the piston pin, the lock of the lower compression ring should be directed in the opposite direction, and the lock of the oil scraper ring - at an angle of 30-45°to the axis of the piston pin between the locks of the compression rings. Install the lower compression ring with the groove down. If the ring is marked "TOP" or "TOR", it should be directed towards the bottom of the piston. The joint of the spring expander of the oil scraper ring must be located on the side opposite to the ring lock.
6. After installing the rings, install the crankshaft according to the mark (pistons of the 1st and 4th cylinders must be in BMT) and alternately introduce pistons with rings and connecting rods into the 2nd and 3rd cylinders. At the same time, the labels "P" on the pistons must point towards the front of the cylinder block. To crimp the rings, it is recommended to use the mandrel shown in the photo.

After that, we install the connecting rod bearings in place, having previously lubricated them and the crankshaft journals with engine oil, and connect the connecting rods to the crankshaft journals. We install the covers according to the marks and tighten them with nuts to a torque of 43.4-53.5 Nm. Turning the crankshaft 180°, we connect the connecting rods of the 1st and 4th cylinders to the crankshaft. Check the ease of rotation of the crankshaft.
7. Installation of the remaining removed parts is carried out in reverse order.
8. Fill the engine with engine oil (see "Engine oil - level check and change").
10. Adjust the chain tension (see "Timing chain - replacement").
11. Adjust the gap between the levers and camshaft cams (see "Clearance between valve levers and camshaft lobes - adjustment"). We check the free rotation of the crank mechanism.
12. Adjust the tension of the generator drive belt (see "Alternator drive belt - tension adjustment and replacement").
13. On a carburetor engine, we check and, if necessary, adjust the ignition timing (see "Ignition timing - check and adjustment").
14. Fill the system with coolant (see "Coolant - level check and replacement").
15. We start the engine and run it in idle for 20-30 minutes, gradually increasing the crankshaft speed to 2000 rpm. During engine operation, we control the tightness of engine systems, oil pressure, coolant temperature. If extraneous noises are detected during engine operation, we stop the engine to eliminate the causes of their appearance.
