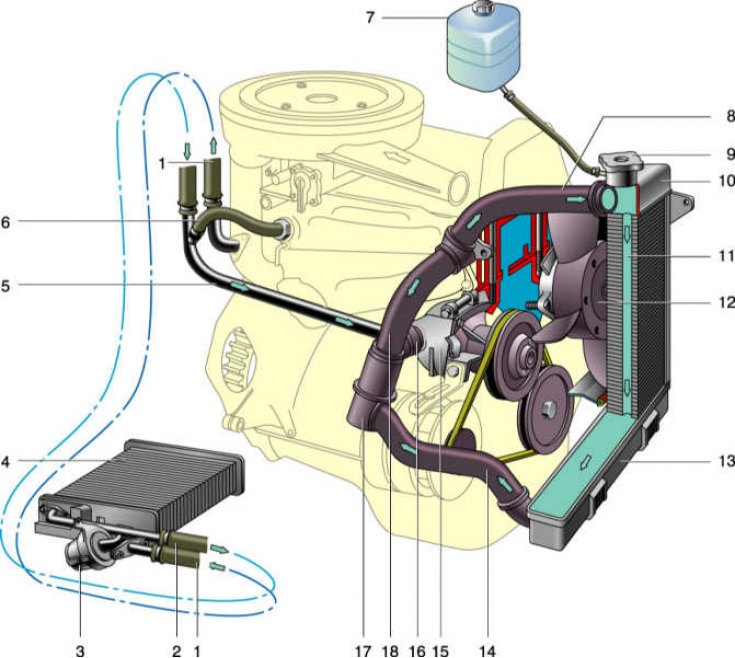
1 - hose for supplying coolant to the heater radiator; 2 – a hose of removal of a cooling liquid from a heater radiator; 3 - heater valve; 4 - heater radiator; 5 – liquid outlet tube; 6 – a hose of removal of a cooling liquid from an inlet pipe; 7 - expansion tank; 8 - inlet hose of the radiator; 9 - radiator cap; 10 - the upper tank of the radiator; 11 - radiator tube; 12 - electric fan; 13 - the lower tank of the radiator; 14 - outlet hose of the radiator; 15 - coolant pump; 16 - hose for supplying coolant to the pump; 17 - thermostat; 18 - thermostat bypass hose.
The position of the thermostat valves at different coolant temperatures
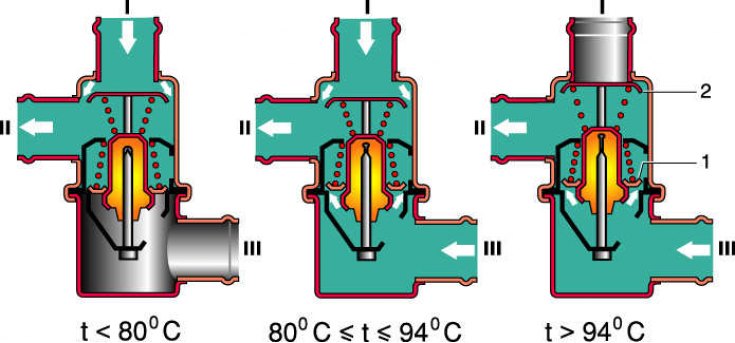
I - from the cylinder head; II - to the coolant pump; III - from the lower radiator pipe; 1 - main valve, 2 - bypass valve.
Engine cooling system - liquid, closed type with forced circulation. On a cold engine, fluid circulates through «small circle». It includes the cooling jackets of the block and cylinder heads of the engine, the coolant pump, the thermostat, and the heater radiator when its valve is open. When the liquid temperature reaches 80–85°, two thermostat valves come into action, blocking the small circle and opening the way for the liquid through the engine radiator, which is intensively blown by the oncoming air flow during movement, as well as with the help of an electric fan.
The radiator consists of two horizontal tanks connected by tubes. Plates are pressed onto them for better heat dissipation. The liquid is supplied to the radiator through the upper pipe, and is discharged through the lower one.
Passing through the radiator, the liquid is cooled, after which it enters the engine again. The change in the volume of the coolant when it is heated or cooled is compensated by the expansion tank. For visual control of the coolant level, the tank is made of translucent polyethylene.
The tightness of the system is ensured by the inlet and outlet valves of the radiator filler cap. On a hot engine, the exhaust valve maintains increased pressure in the system. This raises the boiling point of the liquid. When it cools, the inlet valve opens, passing part of the liquid from the expansion tank into the radiator and thereby compensating for the decrease in the volume of liquid.
There is a hole in the plug of the expansion tank, so the pressure in its internal cavity is always atmospheric.
The coolant pump is centrifugal type. The pump housing is made of aluminium, dismountable, and consists of two parts. The pump shaft rotates in a double-row sealed type bearing that does not require maintenance. A flange of the pump drive pulley is pressed onto the front end of the shaft - with a V-belt from the engine crankshaft pulley.
Recently, cars are equipped with radiators with plastic tanks and an aluminum core.
It is not recommended to pour water into the engine cooling system. This leads to the formation of scale on the walls of the system, corrosion of parts, deterioration of heat transfer and a reduction in the life of the pump seal.
