The switch is checked using an oscilloscope and a square-wave generator according to the circuit shown in fig. 141,a, with a supply voltage of 12 V. It is desirable to use a two-channel oscilloscope. One channel is used to monitor the pulses of the generator, and the second for the pulses of the commutator.
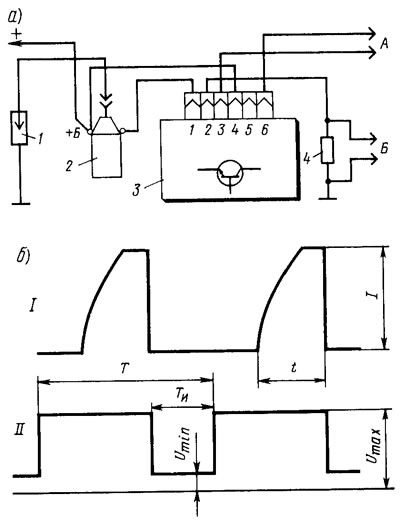
Pic. 141. Scheme for checking the switch (A) and the shape of the pulses on the oscilloscope screen (b): 1 - arrester; 2 - ignition coil; 3 - switch; 4 resistor 0.01±1% Ohm, not less than 20 W, A - to the generator of rectangular pulses; B - to the oscilloscope; t - current accumulation time; l - the maximum value of the current strength; I - commutator impulses; II - generator pulses
When assembling the circuit to test the switch, make sure that the low voltage wires are not in the same bundle with the high voltage wires. In addition, it is not allowed to disconnect the plug connector from the switch when the ignition is on (when power supply is on), since in this case voltage up to 400 V may occur on individual elements of the switch circuit and the switch will be damaged.
On terminals «3» and «6» The switch receives rectangular pulses with a frequency of 3.33 to 233 Hz from the generator, simulating sensor pulses. Pulse duty cycle, i.e. the ratio of the period to the pulse duration Y/GAnd=3. Maximum voltage Umax=10 V, and the minimum Umin≤0.4V (pic. 141.6). The output impedance of the generator should be 100-500 ohms.
For a serviceable switch, the shape of the current pulses should correspond to the oscillogram I. The current value l should be 8-9 A, and the time t of its accumulation should not exceed 8.5 ms at a frequency of 33.3 Hz and not less than 4 ms at a pulse frequency of 150 Hz.
If the shape of the commutator pulses is distorted, then there may be interruptions in sparking or it may occur with a delay. In this case, the engine will overheat and not develop rated power.
