Open large image in new tab »
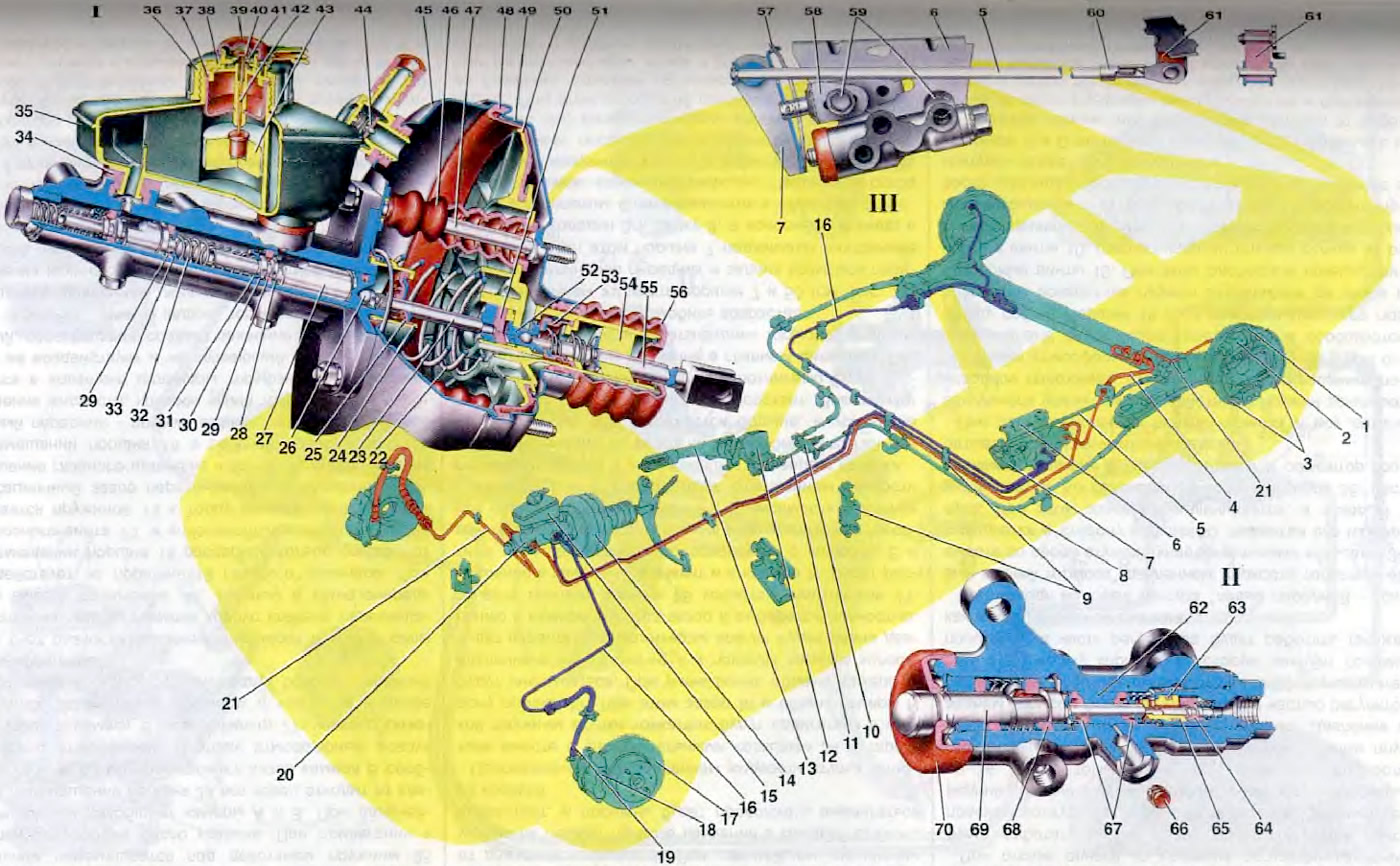
Pic. 28. Brake drive: 1. Rear wheel brake shield; 2. Rear brake wheel cylinder; 3. Rear brake pads; 4. Rear brake hose; 5. Elastic lever drive pressure regulator; 6. Bracket for fastening the pressure regulator; 7. Lever drive pressure regulator; 8. Rear parking brake cable assembly; 9. Bracket for fastening pipelines; 10. Rope equalizer; 11. Parking brake link; 12. Bracket for parking brake lever; 13. Parking brake lever; 14. Vacuum amplifier; 15. Reservoir of the master cylinder; 16. Loop piping "left front - right rear brakes"; 17. Front wheel brake disc; 18. Caliper assembly with wheel cylinder and guide pads; 19. Front brake hose; 20. The main cylinder of the hydraulic drive of the brakes; 21. Loop piping "right front - left rear brakes"; 22. Diaphragm return spring; 23. Stock; 24. Amplifier body cup; 25. Stem seal; 26. Adjusting bolt; 27. Circuit drive piston "left front - right rear brakes"; 28. Spacer ring; 29. High pressure sealing ring; 30. O-ring retainer spring; 31. Spring plate; 32. Piston return spring; 33. Support washer; 34. Connecting sleeve; 35. The body of the reservoir of the main cylinder; 36. Tank cover; 37. Reflector; 38. Sensor body; 39. Protective cap. 40. Moving contact; 41. Fixed contact; 42. Pusher; 43. Float; 44 Vacuum valve; 45. Amplifier case; 46. Sealing cover; 47. Hairpin; 48. Diaphragm; 49. Amplifier housing cover; 50. Valve body; 51. Buffer rod; 52. Piston; 53. Valve; 54. Air filter; 55. Pusher; 56. Protective cover of the valve body; 57. Lever spring; 58. Bracket for pressure regulator drive lever; 59. Pressure regulator mounting bolts; 60. Bracket earrings; 61. Earring; 62. Pusher bushing; 63. Valve seat O-ring; 64. Pressure regulator valve; 65. Valve seat; 66 Plug; 67. O-ring pusher; 68. Piston head seal; 69. Pressure regulator piston; 70. Protective cap; I. Master cylinder and vacuum booster; II. Pressure regulator; III. Scheme of the brake drive.
The hydraulic drive of the working brake system consists of a pedal, a vacuum booster 14. a master cylinder 20 with a reservoir 15, a pressure regulator, wheel cylinders 2 and 18, brake mechanisms and pipelines of diagonal circuits.
The vacuum booster reduces the force on the brake pedal Between the body 45 and the cover 49, the diaphragm 48 is clamped, which, together with the valve body 50, divides the cavity of the vacuum booster into two chambers; vacuum A and atmospheric B (see fig. 27). Chamber A is connected to the engine intake pipe through a nozzle and a hose and is isolated from chamber B. Housing 50 (see fig. 26) valve under the action of spring 22, together with the diaphragm, is pressed towards the amplifier cover. The shank of the body at the exit from the cover is sealed and at the same time protected by a cover 56. The valve body contains the rod 23 of the main cylinder drive with a support sleeve, a piston 52, a valve body sleeve, a buffer 51, a valve 53, two springs, an air filter 54 and a pusher 55. Support the sleeve is pressed onto the stem 23. It abuts through the rubber buffer 51 and the plastic sleeve into the valve body. An adjusting bolt 26 is screwed into the end hole of the rod. To seal the gap between the flange of the main cylinder and the vacuum booster housing, a rubber ring is installed in the housing socket.
Piston 52 is rigidly connected to the valve body by rolling the disk at the end of the valve. The ball head of the pusher is crimped into the piston seat. Thus, the piston, valve body and tappet form a single non-separable unit. A rubber valve 53 is pressed against the end of the piston by a spring. A support sleeve is pressed against the rear end of the valve by another spring. The other end of the spring rests against the air filter support washer 54.
The main hydraulic brake cylinder assembly with reservoir 15 is mounted on the studs of the vacuum booster. Two pistons are located in series in the cavity of the main cylinder, each of which controls its own circuit. The piston 27 is sealed in the cylinder with two rubber rings. The high-pressure sealing ring 29 is pressed by the spring 30 to the end of the spacer ring 28. The other end of the spring rests against the plate 31. On the other hand, the return spring 32 rests against the plate. The stroke of the piston in the cylinder is limited by a locking screw screwed in from below into the cylinder body. The end of the screw enters the piston groove. A low pressure O-ring is installed in the back groove of the piston. Piston 27 pressurizes the circuit "left front - right rear brakes".
The front floating piston has a similar design, front end seal and stroke limitation. Only the rear part is also sealed with a high-pressure ring 29, which is pressed against the end of the piston by a spring 32 through a washer 33. A tank 15 is attached to the main cylinder using two connecting sleeves 34, on the neck of which a cover 36 is screwed, fastening the emergency liquid level sensor. Two fixed contacts 41 with terminals are riveted in the sensor housing, on which the wire ends are put on. Pusher 42 passes through the hole in the base of the tank, at the upper end of which contact 40 is rigidly attached. At the lower end of the pusher, a polypropylene float 43 is attached through a plastic connecting sleeve. From above, the sensor contacts are closed with a plastic cap 39.
The pressure regulator is attached with two bolts 59 to the bracket shelf, which, in turn, is attached to the body floor bracket. In this case, the front, longer bolt 59 simultaneously fastens the fork bracket 58 of the lever 7 of the pressure regulator drive. To prevent the bracket 58 from turning relative to the bolt 59, its protrusion enters the groove of the regulator bracket. Thanks to this groove and oval holes in the bracket 58 for the fastening bolt 59, the bracket 58, together with the lever 7 of the regulator drive, can be moved relative to the pressure regulator. This regulates the drive of the pressure regulator.
A finger is welded to the fork bracket 58, which is a stop for the lever 7. A pin is pressed into the hole of the stop, relative to which the two-arm lever 7 rotates, in the upper hole of which there is an axis, through the hole of which the end of the elastic lever 5 of the regulator drive passes. The axis of the lever and the elastic lever are locked by a single lock. The other end of the elastic arm 5 is pivotally connected to the earring 61, which swings on the pin of the suspension arm bracket.
A plug is screwed into the regulator body on one side, and a sleeve is installed on the other side, which is fixed in the body with a retaining ring. Piston 69 is installed in the sleeve. At the cylinder outlet, it is sealed with a protective cover 70. The piston head with a gap enters the sleeve of the regulator body. The spring presses the sealing rings 67 and 68 through the washers to the ends of the bushings. A rubber-metal valve is installed in the regulator plug, which is pressed against the seat 65 by a spring. The tightness of the seat in the plug is ensured by the sealing ring 63. The valve seat is rolled in the regulator plug. The protruding part of the valve 64 abuts against the pusher. It is installed in the sleeve 62 and is sealed with it with two rubber rings 67. The spring through the plate presses the pusher sleeve with sealing rings to the washer, which is held on the pusher by a retaining ring.
The pressure regulator has four chambers, two of which are connected to the master brake cylinder, and the other two to the wheel cylinders of the rear wheel brakes.
The mechanical drive of the hand brake consists of a lever 13 with a bracket 12, an adjusting rod 11, a cable equalizer 10, two rear cables 8 and levers 38 (see fig. 25) manual drive pads.
Lever 13 (see fig. 26) mounted on the bracket 12 together with the toothed sector. This unit is not separable, it is attached to the floor of the body. In engagement with the gear sector there is a latch, which is controlled through the rod by the lever button. All these parts are assembled in the cavity of the lever 13. The lever 13 of the parking brake is pivotally connected with a finger to the rod 11. At the other end of the rod, an equalizer 10 of the cables is attached with an adjusting nut with a thrust washer. The position of the nut on the rod is fixed with a lock nut. Both ends of the equalizer are put on the front tips of the rear cables. The rear tips of the cables are connected to the levers of the manual drive of the brake pads of the rear wheel (see fig. 25).
