Attention! If you have the slightest doubt about self-diagnosis, get the towline. Serious repairs will cost more than the services of a towing vehicle.

Engine knocking zones:
1. Knock main bearings - very dangerous; stop engine immediately, we go to the car service in tow. Low tone knock. It is audible in the lower part of the crankcase, noticeably increases under load and with an increase in speed. Often its appearance is accompanied by a drop in oil pressure (low oil pressure light stays on).
2. Knocking rod bearings - very dangerous; stop engine immediately, we go to the car service in tow. The sound is rhythmic, ringing, metallic, medium tone. Significantly increases with increasing load and completely disappears when the spark plug is turned off.
3. Knock of piston pins - dangerous; without loading the engine, we go to the car service on our own. Rhythmic, high tone with a sharp metallic tint, audible in all engine operating modes and intensifies with increasing engine load. Completely disappears when the spark plug is turned off.
4. Knock of worn pistons and cylinders - is not dangerous; avoiding heavy load on the engine, we go to the car service on our own. A sound reminiscent of the clatter of pottery. It is especially well heard on a cold engine, as it warms up it decreases or disappears.
5. Detonation knocks - dangerous, but, as a rule, are eliminated by installing a later ignition. Avoiding heavy load on the engine, we go to the car service on our own. Voiced metallic knocks that occur, as a rule, during acceleration of the car. The reason is incorrect ignition setting, the use of low-octane fuel, engine overload when overdrive is engaged too early, significant carbon formation in the combustion chambers. Necessary go to car service to adjust the ignition and apply a special fuel additive to remove carbon deposits on the valves and in the combustion chambers.
6. Valve knock - not dangerous, we go to the car service on our own. A metallic thump against the background of a general muffled noise. It is well audible at low and medium speeds of the crankshaft from the side of the cylinder head above the valve locations. Valve clatter is often confused with tappet clatter (the latter is very high-pitched and variable in volume, practically unavoidable).
Knocks in the suspension and transmission
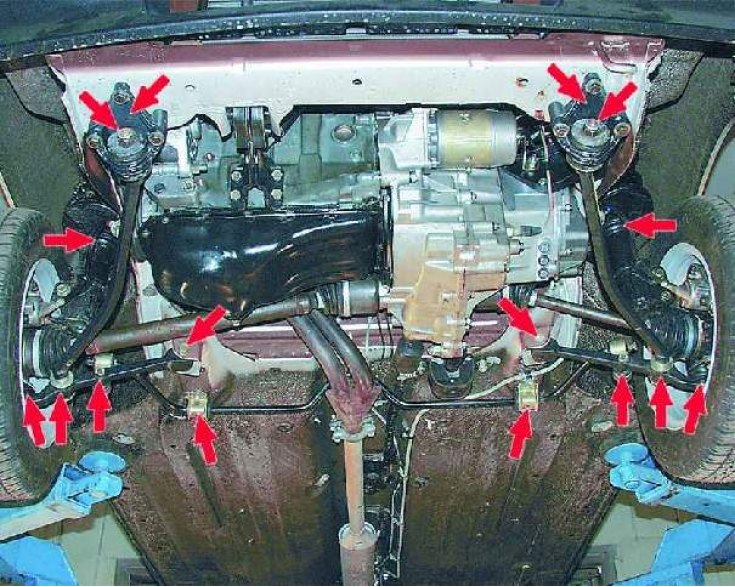

Warning! Malfunctions in the suspension and steering of the car can lead to a serious accident!
If extraneous knocks appear in the suspension of a moving car, it is necessary to immediately establish their source, regardless of whether it is a constant knock or appears only when driving through bumps.
Check suspension condition it is better to put the car on a flyover, a viewing ditch or a lift, and if this is not possible, you can do this work on a free flat area, albeit with less convenience. In any case, you will need an assistant.

1. Start by carefully checking the condition of the suspension parts. Pay attention to the condition of the rubber protective covers of the ball bearings of the front suspension. Ruptures of the covers and the presence of cracks on them are unacceptable, since in this case moisture and dirt enter the hinge, which lead to premature wear of the hinge. Be sure to replace damaged parts.

2. Check the condition of the rubber-metal hinges and rubber bushings of the lower arms, stabilizer and extensions.
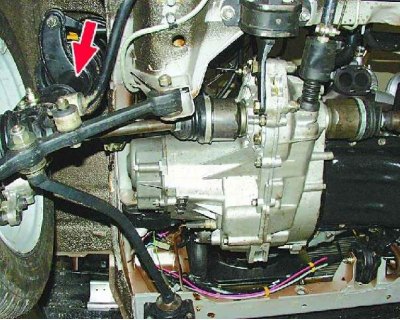
The photo shows the right side of the car. On the left side, check the same places by analogy.

3. Open the hood, remove the plastic protective caps from the top supports of the telescopic struts and check the condition of the top support. There should be no cracks, tears, swelling, etc. on the rubber part of the support. After a preliminary inspection, you can proceed to a more detailed check.

4. Ask an assistant to take hold of the top of the front wheel of a car standing on the road with both hands and shake it sharply in the transverse direction. In this case, you should observe the presence of gaps in the hinges of the front suspension. Pay special attention to the ball joint.
Tip: Having a gap (backlash) in a ball joint, it is easier to determine if, when swinging the wheel, touch the ball joint with your hand.
Are there gaps in the suspension joints?
No: see point 6.
5. Worn hinges require replacement.

6. Check the tightness of the nut securing the shock absorber rod to the upper strut support.

7. Jack up the vehicle on the side to be checked until the wheel is off the road. Place a sturdy stand under the threshold of the body (tripod) and lower the vehicle slightly to load the stand. Rock the wheel in a vertical plane, holding the top with one hand and the bottom of the wheel with the other.
Increased knocking from the side of the central part of the wheel indicates a large gap in the hub bearing. It is better to entrust the replacement of a worn bearing to specialists who have the necessary tools.
Warning! Don't be persuaded "craftsmen", recommending to tighten the hub nut with a force that is higher than recommended by the manufacturer to eliminate the gaps. This can lead to destruction of the bearing.
8. Inspect the telescopic suspension strut. Oil leaks indicate a malfunction of the shock absorber. In this case, the shock absorber requires repair or replacement. Check the integrity of the spring and compression buffer.

9. Check the brackets for attaching the stretch marks to the car body. The brackets must be securely bolted to the body and not damaged.

10. When checking the rear suspension, pay attention to the condition of the hub bearings, shock absorbers, springs, bumpers and the fastening of the shock absorber rods to the body.
11. You can tighten the shock absorber rod nuts from the luggage compartment by removing the seat belt reels and trim.
Tip: After replacing individual suspension parts, be sure to check and adjust the alignment of the front wheels. This operation must be carried out on a special stand in a car service, since improper wheel alignment leads to accelerated tire wear, increased fuel consumption and deterioration in vehicle stability and controllability.
Adviсe
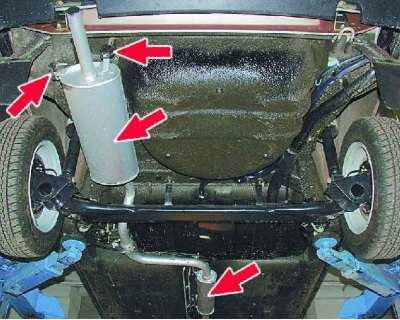
Pay attention to the exhaust system. Very often, due to the use of non-standard elements or the breakage of the silencer suspension elements, it can be a source of strong knocking, especially during regassing. To check, stop the engine, carefully inspect the exhaust system, check the reliability of mounting and muffler suspension. Grasping the end of the exhaust pipe, shake the muffler up and down and from side to side - there should be no knocking.

Knocks in the suspension are often confused with the knocks of constant velocity joints (SHRUS) semi-axes of drive wheels. The sound is a sonorous metallic clicking, which is especially evident when the accelerator pedal is pressed sharply with the front wheels turned at a large angle. As the CV joints wear out, the duration of the click increases. The only radical way to deal with the knock of CV joints is to replace them.
