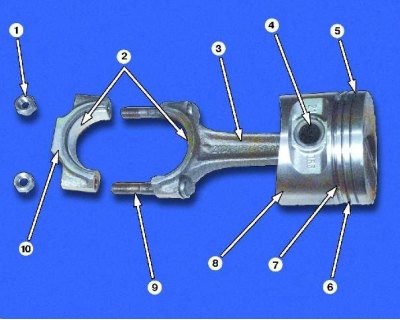
Piston with connecting rod: 1 - connecting rod bolt nut; 2 - connecting rod bearings; 3 - connecting rod; 4 - piston pin; 5 - groove of the upper compression ring; 6 - groove of the lower compression ring; 7 - oil scraper ring groove; 8 - piston; 9 - connecting rod bolt; 10 - connecting rod cover
For the convenience of selecting pistons by cylinders, cylinders and pistons are divided into five size groups depending on the diameter: A, B, C, D, E.
As spare parts, pistons are supplied in nominal size of three classes: A, C, E and two oversizes. The first repair size is increased by 0.4 mm, the second - by 0.8 mm.
By weight, the pistons are divided into three groups: normal, increased by 5 g and reduced by 5 g. Pistons of the same group must be installed on the engine.
For oversized pistons, oversized rings of 0.4 mm and 0.8 mm are available as spare parts. On the rings of the first repair size, a number is engraved "40", and the second "80".
Nominal sizes of cylinders and pistons
| Size group | Engine model VAZ-2108 | Engine model VAZ-21083 | ||
Cylinder diameter, mm | Piston diameter, mm | Cylinder diameter, mm | Piston diameter, mm | |
A | 76,00-76,01 | 75,965-75,975 | 82,00-82,01 | 81,965-81,975 |
B | 76,01-76,02 | 75,975-75,985 | 82,01-82,02 | 81,975-81,985 |
C | 76,02-76,03 | 75,985-75,995 | 82,02-82,03 | 81,985-81,995 |
D | 76,03-76,04 | 75,995-76,005 | 82,03-82,04 | 81,995-82,005 |
E | 76,04-76,05 | 76,005-76,015 | 82,04-82,05 | 82,005-82,015 |
To match pistons to cylinders, calculate the gap between them. The clearance is defined as the difference between the measured piston and cylinder diameters. The nominal gap is 0.025-0.045 mm, the maximum allowable gap is 0.15 mm. If the gap does not exceed 0.15 mm, pistons from subsequent classes can be selected so that the gap is as close to the nominal as possible. If the clearance exceeds 0.15 mm, bore the cylinders to the next oversize and install pistons of the correct oversize.

1. We recommend removing the piston rings with a special puller. If not, carefully spread the ring lock and remove the ring from the piston. Remove the remaining rings in the same way.

2. Using a special mandrel, press the pin out of the connecting rod.

3. Examine the pistons. If they have scuff marks, traces of burnout, deep scratches, replace the pistons.

4. To determine the clearance, measure the diameter of the cylinder (see subsection 11.8.) and the piston diameter, which is measured with a micrometer in a plane perpendicular to the axis of the piston pin, at a distance of 51.5 mm from the piston crown.

5. Measure the gap between the rings and grooves on the piston with a feeler gauge in several places around the perimeter. If the gap exceeds the maximum allowable (see note 1), replace pistons with rings.

6. Insert the piston ring into a special mandrel and measure the clearance in the lock. Instead of a mandrel, you can insert the ring into the cylinder and advance it with the piston so that the ring stands without distortion. If the gap exceeds the limit, replace the ring (see note 2). If the gap is less than 0.25 mm, carefully file the ends of the ring with a needle file.
Note 1
Gap between rings and piston grooves, mm | |
Nominal: | |
top compression ring | 0,04-0,075 |
lower compression ring | 0,03-0,065 |
oil scraper ring | 0,02-0,055 |
Maximum allowable clearance for all rings | 0,15. |
Note 2
| Clearance in piston ring locks, mm: | |
Nominal | 0,25-0,45 |
Maximum allowable | 1,0 |
Piston pins are divided by diameter into three classes (1st, 2nd, 3rd) through 0.004 mm. The class of the finger is marked on its end face with paint.
Piston pin and piston classes
| Class | Finger diameter, mm | Piston hole diameter, mm | Marking | |
finger | piston | |||
1 | 21,970-21,974 | 21,982-21,986 | Blue | 1 |
2 | 21,974-21,978 | 21,986-21,990 | Green | 2 |
3 | 21,978-21,982 | 21,990-21,994 | Red | 3 |

The piston is mounted on the connecting rod so that the arrow on the piston head is directed in the opposite direction from the part number cast on the connecting rod. If there is an oil outlet hole on the bottom end of the connecting rod, the arrow on the piston must point towards that hole.
7. Check the fit of the piston pin in the piston. To do this, lubricate the piston pin with engine oil and insert it into the piston. The finger must enter the piston without being pressed by the thumb.
8. Turn the piston upside down so that the pin is upright without dropping out of the piston under its own weight. If the pin falls out of the piston, take the next grade pin. If the third class pin falls out of the piston, replace the piston and pin.

9. Inspect the connecting rod bearings. If they have cracks, scuffs, chipping, replace the liners.

10. Inspect the connecting rods with caps. Replace bent connecting rods.
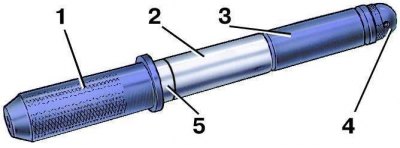
11. Put the piston pin 2 on the shaft 1 of the piston pin installer with the distance ring 5 put on it. Then put on the guide sleeve 3 and fix it with the screw 4 without tightening the screw. Distance ring dimensions: outer diameter 22 mm, inner diameter 15 mm, thickness 4 mm.

12. Heat the connecting rod head to 240°C in an oven for 15 minutes. Clamp the connecting rod in a vice, install the piston on it (see note), so that the pin holes line up, and insert the pin tool all the way into the piston and connecting rod holes. To properly install the pin, the piston must be pressed with the boss against the upper head of the connecting rod in the direction of pressing.

13. After the connecting rod has cooled, lubricate the piston pin through the hole in the piston bosses.
The connecting rods are processed together with the covers, so they cannot be dismantled.

If new parts are installed during the assembly of the connecting rod and piston group, match the pistons to the cylinders by class, group and weight. Piston pins and pistons also need to be selected by class.
Note. The assembly of the piston with the connecting rod must be done as quickly as possible, since the connecting rod cools quickly. After the connecting rod has cooled, it will not be possible to change the position of the pin.
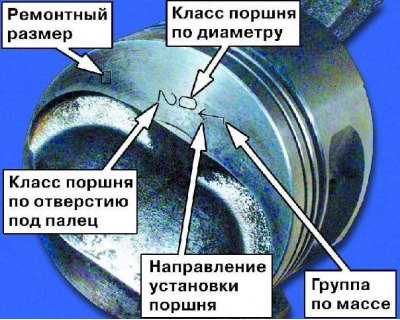
Repair size designation:
- 1st repair - triangle,
- 2nd repair - square.
Weight group designation:
- normal - "G",
- increased by 5 grams - "+",
- reduced by 5 grams - "-".
14. Lubricate the piston rings and grooves on the piston with engine oil. Put on the piston rings with a puller or by hand, orienting them accordingly. Check the ease of movement of the rings in the grooves.

15. If the ring is inscribed "Top", "Top" or "VAZ", install the ring with the inscription facing upwards towards the piston crown.

16. There is a groove on the lower compression ring. The ring must be installed with the groove down. Before installing the oil scraper ring, turn the spring expander so that its lock is on the opposite side from the ring lock.
17. Turn the piston rings so that their locks are at an angle of 120°to each other.

18. Insert the bushing into the bottom end of the connecting rod, making sure that the locking lug on the bushing fits into the groove of the connecting rod head.

19. Insert the liner into the connecting rod cap so that the locking tab on the liner fits into the groove of the connecting rod cap.
