The engine cooling system uses special liquids based on a mixture of water and ethylene glycol. They have a low freezing point and a high boiling point. In addition, thanks to the complex of added additives, the coolant prevents corrosion of the channel walls, does not foam, and prolongs the life of the coolant pump seal. The volume of coolant in the engine cooling system is 7.8 liters.
The circulation of the coolant in the system is provided by a centrifugal pump installed in the engine block. The water pump is driven by a toothed timing belt.
The coolant in the cooling system, depending on the temperature of the engine, can circulate both in a small and in a large circle.
The thermostat controls the direction of coolant flow in the engine cooling system.
It has two valves - the main and additional (bypass). The main valve controls the circulation of the coolant in a large circle, and the bypass valve in a small one. The valves are interconnected - when one opens, the second closes and vice versa.
On a cold engine, the thermostat bypass valve is open and coolant circulates in a small circle through the cylinder block, cylinder head, bypass valve and water pump, as well as the throttle assembly and heater core. The heater radiator is built into the engine cooling system and is designed to heat the passenger compartment by circulating hot coolant through it.
At a temperature of 85±2°C, the main thermostat valve begins to open, and the bypass valve closes and the coolant circulates for some time
small and large circles at the same time. At a temperature of 102°C, the main thermostat valve is fully open, and the bypass valve is closed and the main coolant flow passes through the engine radiator, where it is cooled by the oncoming air flow. In this case, the coolant continues to circulate through the throttle assembly and the heater core. When the air flow is not enough to cool the radiator, the electric fan turns on. It is installed behind the engine radiator and turns on automatically at the signal of the ECU (electronic control unit) engine.
To compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant, an expansion tank is installed in the cooling system. In the plug of the expansion tank there are inlet and outlet valves, which allows you to maintain optimal pressure in the system when the coolant is heated, and also compensate for the vacuum when it cools.
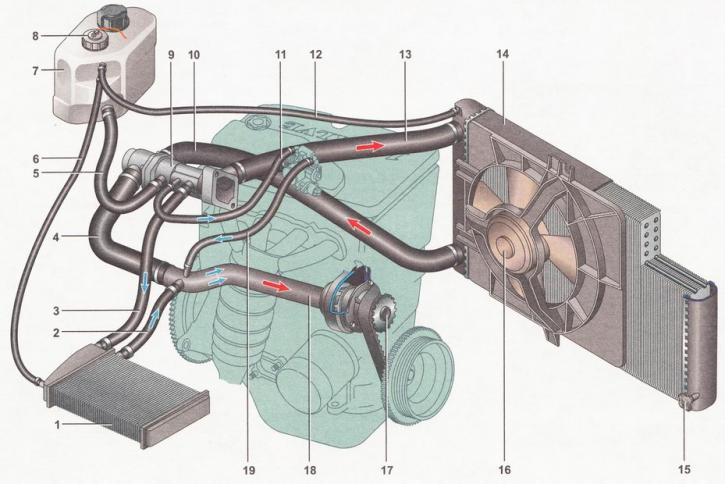
Engine cooling system: 1 - heater radiator; 2 - hose for draining coolant from the heater radiator; 3 - hose for supplying coolant to the heater radiator; 4 - coolant pump hose; 5 - expansion tank hose; 6 - steam outlet hose of the heater radiator; 7 - expansion tank; 8 - liquid level sensor in the expansion tank *; 9 - thermostat; 10 - hose for draining coolant from the engine radiator; 11— fluid supply hose to the throttle assembly; 12 - steam outlet hose of the engine radiator; 13 - hose for supplying fluid to the engine radiator; 14 - engine radiator; 15 - radiator drain plug; 16 - electric fan of the engine radiator; 17 - coolant pump; 18 - supply pipe to the coolant pump; 19 - coolant outlet hose from the throttle assembly
* Installed on car parts.
