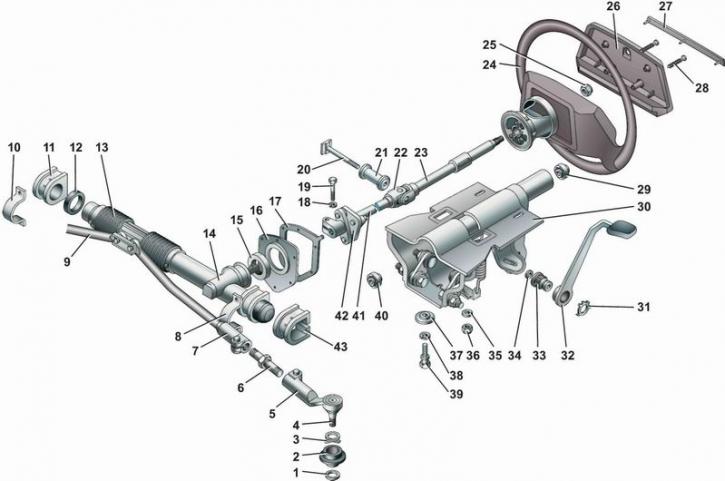
Steering Details: 1 - sealing ring; 2 - protective cover of the tie rod end; 3 - spring ring; 4 - ball pin; 5 - tie rod end; 6 - threaded insert; 7 - left steering rod; 8, 10 - brackets for fastening the steering mechanism; 9 - right steering rod; 11 - right support of the steering mechanism; 12 - spacer ring; 13 - protective cover of the steering mechanism; 14 - steering mechanism; 15 - sealant; 16 - thrust plate; 17 - gasket; 18 - spring washer; 19 - bolt; 20 - coupling bolt; 21 - spacer sleeve; 22 - universal joint; 23 - upper steering shaft; 24 - steering wheel; 25 - steering wheel nut; 26 - steering wheel pad; 27 - decorative overlay; 28 - self-tapping screw, 29, 40 - bearings; 30 - bracket for mounting the upper steering shaft; 31 - retaining ring; 32 - lever for adjusting the position of the steering column; 33 - adjusting sleeve; 34, 35 - washers; 36 - self-locking nut; 37 - fixing plate; 38 - spring washer; 39 - a special bolt with a detachable head; 41 - intermediate steering shaft; 42 - rubber elastic coupling; 43 - left steering gear support
The steering wheel is mounted on the splines of the upper shaft of the steering column and fixed with a self-locking nut.
The steering column consists of an upper and an intermediate steering shaft connected by a cardan joint, and a bracket for their fastening. The upper steering shaft rotates in two bearings pressed into the bracket tube. An ignition lock with an anti-theft device is installed on the bracket pipe.
The pipe has the ability to move in the vertical direction relative to the bracket itself, after which it is fixed in the selected position with a coupling bolt, on which an adjusting sleeve with a lever is installed. By lowering the lever, you can change the height of the steering wheel. Raising the lever locks the wheel in the selected position. The front end of the steering column bracket is attached to the body with tear-off bolts and special fixing plates. The bolts are tightened until the heads break off. This prevents them from turning away and replacing the steering column together with the ignition switch when trying to steal a car. The safety of the steering column is provided by special fixing plates. In a frontal impact, the plates deform and no longer hold the front of the steering column bracket, allowing it to drop down. In this case, the steering column is moved to a vertical position and the steering wheel moves away from the driver.
The intermediate steering shaft is connected to the steering mechanism through a rubber flexible coupling, which allows for slight misalignment between the input shaft and the lower shaft of the steering column.
The steering gear is of rack and pinion type, it consists of a crankcase, a drive gear and a rack that are engaged. The steering mechanism is attached to the engine shield with two rubber supports, two clamps and four bolts with nuts. When the steering wheel is turned, rotation is transmitted through the upper and intermediate shafts of the steering column to the drive gear, which, turning, moves the rack.
Steering rods consist of the actual steering rods, tips and threaded inserts connecting the rods and their tips. Ball pins are installed in the rod ends.
At one end, through a rubber-metal hinge, the rods are attached to the steering rack, and with the tips, with the help of ball pins, to the swing arms of the shock absorber struts of the front suspension. When the rack is moved, the rods rotate the front suspension struts, on which the drive wheels are mounted.
The length of the rods can be adjusted by rotating the threaded inserts and thereby changing the toe of the front wheels.
