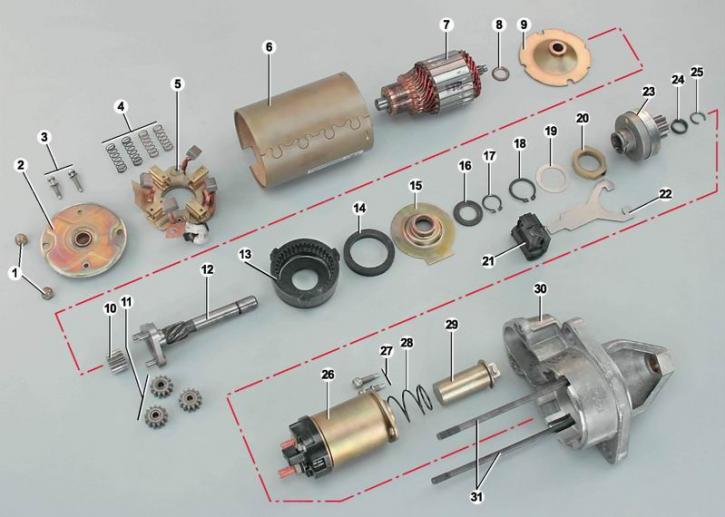
Starter details: 1 - nuts for fastening the rear cover; 2 - back cover; 3 - screws for fastening the brush assembly; 4 - brush springs; 5 - brush assembly; 6 - stator (with magnets); 7 - anchor; 8 - thrust washer; 9 - armature shaft support; 10 - the central gear of the gearbox; 11 - planetary (satellite) reducer gears; 12 - drive shaft; 13 - external gear of the gearbox with internal teeth; 14 - sealing ring; 15 - drive shaft support; 16 - thrust washer; 17 - retaining ring of the drive shaft; 18 - retaining ring of the drive lever coupling; 19 - washer; 20 - drive lever clutch; 21 - drive lever support; 22 - drive lever; 23 - drive; 24 - drive stroke limitation ring; 25 restrictor locking ring; 26 - starter traction relay; 27 - screws for fastening the traction relay; 28 - return spring; 29 - core of the traction relay; 30 - front cover; 31 - tie rods
The engine armature shaft and the drive shaft rotate in bronze-graphite bushings, which are installed in the rear and front covers of the starter, in the armature shaft support and in the drive shaft support. The armature shaft transmits rotation to the drive shaft through a planetary gearbox. The planetary gears of the reducer rotate on needle bearings.
The starter drive consists of a drive gear and an overrunning clutch. The drive can move along the helical splines of the drive shaft.
The traction relay is designed for remote switching of the high current consumed by the starter when starting the engine, as well as for the mechanical connection of the starter drive with the engine flywheel ring gear. The relay coil has two windings, retracting and holding.
When the ignition key is turned to position "starter" to the control output of the traction relay "50", and from it voltage is supplied to both windings of the relay from the battery. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the metal core of the traction relay, overcoming the force of the return spring, is drawn into the coil. At the same time, it drives the starter drive lever. The drive lever, with its horseshoe-shaped fork, extends the starter drive, introducing the drive gear into engagement with the engine flywheel ring gear. At the same time, a copper contact plate located in the plastic cover of the traction relay closes the contact bolts. Current begins to flow through the windings of the starter armature, and the armature rotates, starting the engine.
The negative terminal of the solenoid winding of the relay is connected to "weight" through the starter armature windings (see diagram). After closing the contact bolts, the current stops flowing through this winding and the core of the traction relay is held by only one winding. This allows you to reduce the heating of the relay windings and reduce power consumption at the time of starting the engine.
The overrunning roller clutch of the drive transmits rotation only in one direction - from the starter to the flywheel. After starting the engine, when the crankshaft speed increases sharply, the clutch protects the starter from destruction.
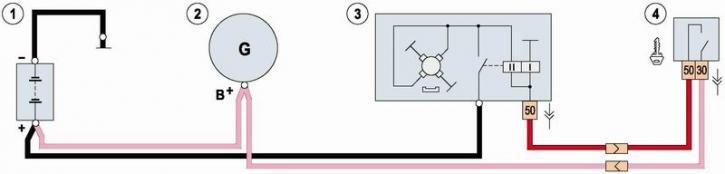
Starter Wiring Diagram: 1 - battery; 2 - generator; 3 - starter; 4 - switch (lock) ignition.
Note. On cars of recent years of production in the starter circuit (between the traction relay and the ignition switch) an additional relay is installed.
After the driver releases the ignition key, the output of the traction relay stops receiving control voltage. The electromagnetic field holding the anchor disappears. The drive lever, under the influence of a spring, moves the starter drive back and disengages the drive gear from the flywheel crown. At the same time, the power contacts open, supplying current to the starter motor windings.
Warning! The starter is the most powerful consumer of electrical energy in a car. When starting the engine, the current consumed by the starter can reach more than 400 A. Therefore, all electrical connections between the battery and the starter must be in good and reliable contact.
Advice. Do not turn on the starter for more than 15 seconds. Between attempts to start the engine, pause for 20-30 seconds. If the engine does not start after three attempts, you need to find out what is the reason (see "Diagnostics of car malfunctions and ways to eliminate them"), and remove it.
