Warning! The cylinder head is replaced with bearing housing assemblies as they are machined together.
You will need: keys «at 13», «at 17», «at 21», spark plug wrench, screwdriver, round nose pliers (tweezers), valve spring compression tool.
1. Remove the cylinder head (see «Replacing the cylinder head gasket»).

2. Turn away two nuts of fastening and remove an eye.
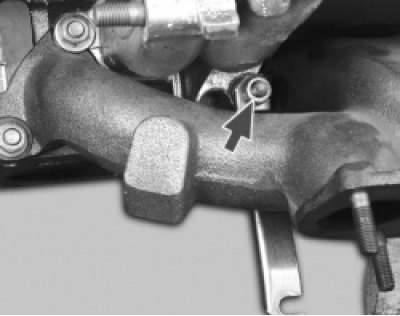
3. Turn away on one-two turns a fastening nut and remove an arm of an inlet pipe of the water pump.
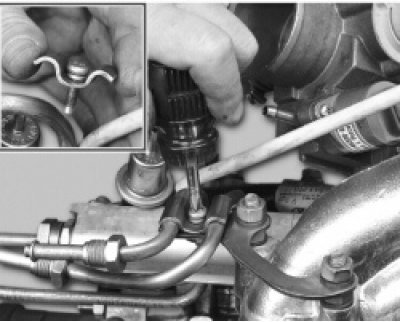
4. Turn out the screw of fastening of the holder of fuel tubes and remove the holder.
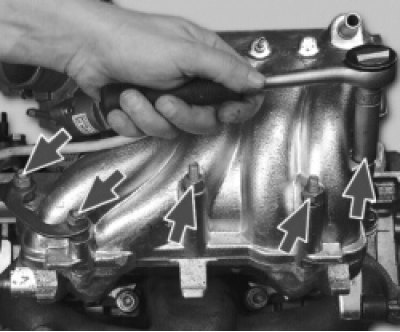
5. Turn away three nuts of fastening of a receiver and two nuts of fastening of an arm of fuel tubes.

6. Remove the fuel pipe bracket.

7. Turn away the remained two nuts of fastening of a receiver.

8. Loosen the nut securing the receiver bracket.

9. Remove the receiver.

10. Turn away three nuts of fastening of an arm of a receiver and remove an arm.
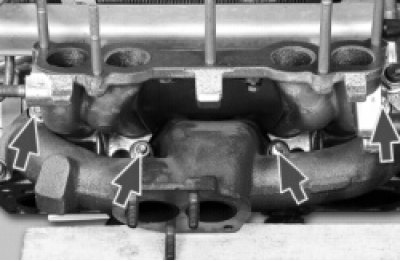
11. Turn away four nuts of fastening of an inlet pipe.

12. Remove the intake pipe.

13. Turn away two nuts of fastening of a final collector and remove a collector.

14. Carefully remove the two gaskets for the intake pipe and exhaust manifold.
Helpful advice. Even if the gaskets are not damaged and slightly compressed, it is better to replace them and not reuse them.
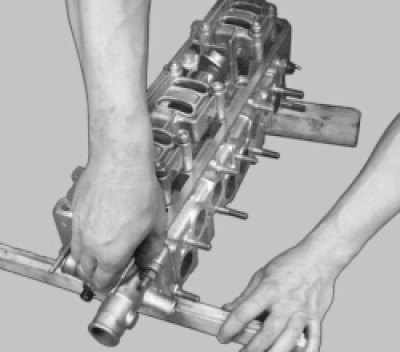
15. Establish a head of the block of cylinders by cases of bearings up, having placed under it wooden linings not to damage valves.
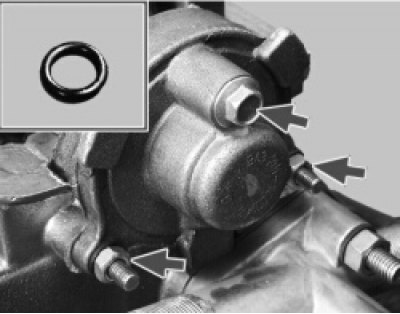
16. Turn away two nuts and a bolt of fastening of a back cover of a head of the block and remove a cover. Note that there is an o-ring under the bolt head.
17. Turn out spark plugs.
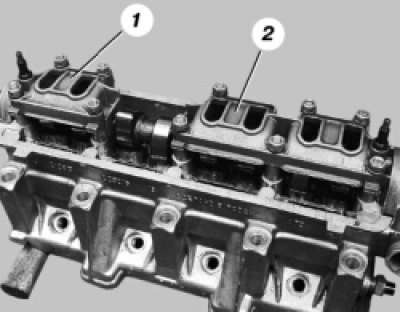
18. Turn away evenly four nuts of fastening of forward 1 and six nuts of fastening of back 2 housings of bearings of a camshaft and remove washers. Then remove both housings.

19. If the key in the groove of the camshaft is loose, remove it so as not to lose it.
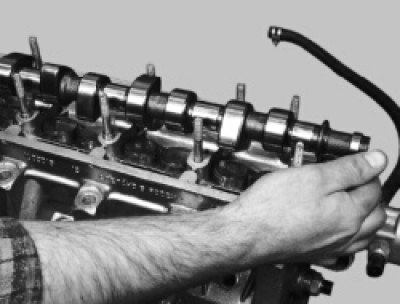
20. Remove the camshaft from the block head.

21. Remove the oil seal from the camshaft.

22. Take out pushers of valves together with adjusting washers.
Warning! Having taken out the next pusher, mark it and the adjusting washer with a serial number in order to install them in their places during assembly. Unless necessary, do not remove the adjusting washers from the pushers, so as not to confuse them.
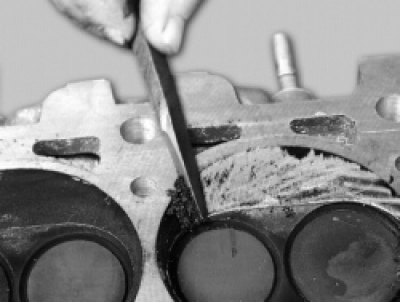
23. Clean the combustion chambers from carbon deposits. Examine the block head. If it has cracks or traces of burnout in the combustion chambers, replace the head. Remove burrs and nicks on the plane of the block head.
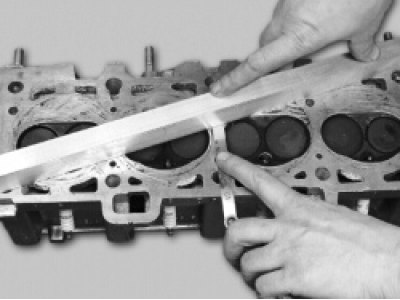
24. Check up flatness of the surface adjoining to the block of cylinders. To do this, place the ruler with an edge on the surface of the head, first in the middle along, and then along the diagonals and with a feeler gauge, measure the gap between the plane of the head and the ruler. Replace the head if the gap exceeds 0.1mm.
25. To check the tightness of the block head, unscrew the two fastening nuts, remove the outlet pipe of the cooling system.
26. Plug the hole in the head of the block under the exhaust pipe. This can be done, for example, by installing a blank gasket made of thick cardboard under the branch pipe and tightening the nuts for its fastening.
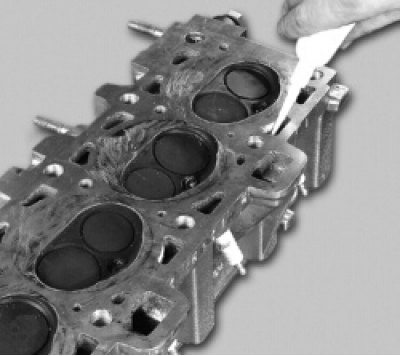
27. Pour kerosene into the channels of the water jacket. If the level of kerosene goes down, then there are cracks in the head and it must be replaced. After checking, do not forget to remove the cardboard gasket.
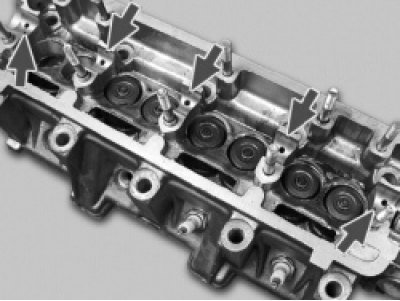
28. Check up a condition of basic surfaces under necks of a shaft on a head of the block and cases of bearings. If at least one of them has signs of wear, scuffing or deep scratches, replace the head and bearing housings.

29. Flush the oil passages. To do this, plug the vertical oil passage on the side of the combustion chamber (the channel is located between the 3rd and 4th cylinders) …

30.... fill gasoline into the oil channels in all camshaft bearings and hold for 15-20 minutes. Pour out gasoline, remove the plug and finally flush the channels with gasoline using a blower.

31. To check the tightness of the valves, pour kerosene into the combustion chambers. If within 3 min. kerosene will not seep out of the combustion chambers, the valves are tight. Otherwise, rub (see «Lapping of valves») or replace valves.
Note. The valve actuator consists of the following parts:
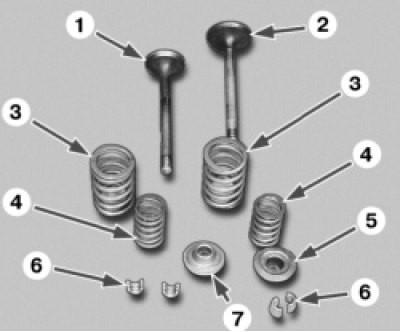
1, 2 - valves; 3 - outer spring; 4 - internal spring; 5 - top plate; 6 - cracker; 7 - bottom plate. To replace or grind the valves, all parts must be removed from the cylinder head.
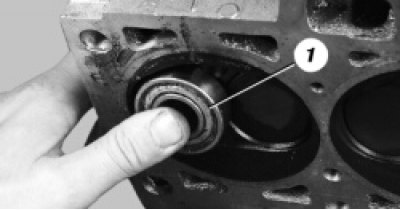
32. Install a suitable stop under the valve to be removed, for example bearing 1.
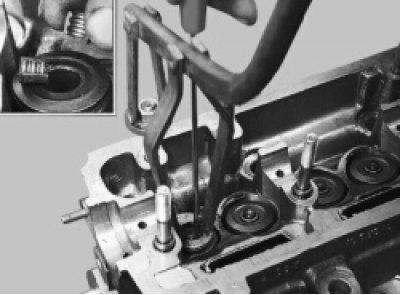
33. Install the valve spring compressor and compress the valve springs. Remove two crackers with a screwdriver or tweezers.

34. Remove the upper spring plate, outer and inner valve springs. Similarly, remove crackers, plates and springs of the remaining valves.

35. Mark the valves with cylinder numbers, for example, mark them.
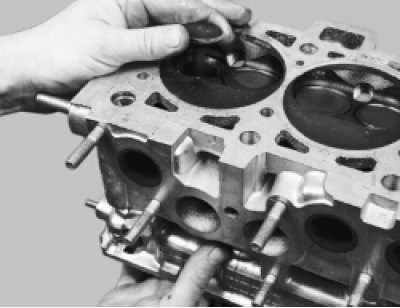
36. Pushing the valves from below, remove them from the block head.

37. Remove valve stem seals with tool or pliers (see «Replacement of valve stem seals»).

38. Remove the lower plates of the valve springs.
39. Clean valve deposits with a suitable tool (e.g. with a metal brush). Then carefully inspect the valves.
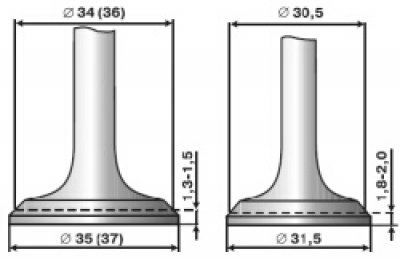
4.8. Valve seat dimensions
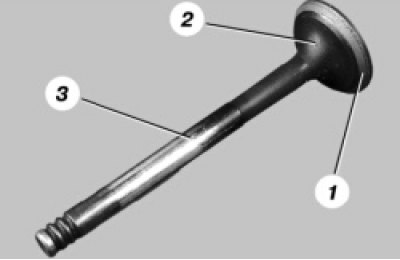
40. Replace the valves with the following defects: deep scratches and scratches on the working chamfer 1, cracks, deformation of the valve stem 3, warping of the plate 2 valves, traces of burnout. Shallow risks and scratches on the working chamfer can be removed by lapping the valves (see «Lapping of valves»).
41. In a specialized workshop, the working chamfer of valves with damage that cannot be removed by grinding can be ground on a special machine. When grinding, it is necessary to maintain the dimensions indicated in Fig. 4.8.
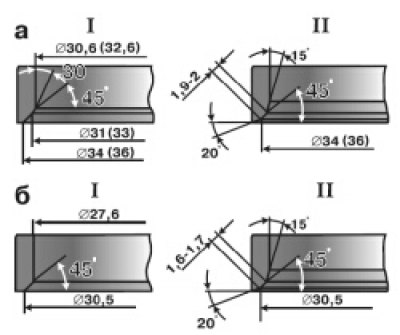
4.9. Dimensions of valve seats: a - inlet valve seat; b - exhaust valve seat; I - new village; II - seat after repair
42. Check the condition of the valve seats. Seat faces must be free of wear, pitting, corrosion, etc. The valve seats can be replaced by a specialist workshop.
Minor damage (minor scratches, scratches) can be removed by lapping valves (see «Lapping of valves»).
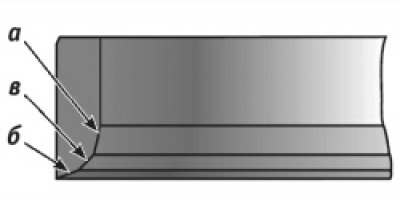
4.10. Valve seat bevelling points
43. More significant defects in valve seats are eliminated by grinding. When grinding, maintain the dimensions indicated in fig. 4.9. Saddles are recommended to be ground in a specialized workshop.
44. Having a locksmith skill, you can do it manually using a set of special cutters.
Chamfer a is processed first (pic. 4.10) at an angle of 15°, then chamfer b at an angle of 20°and chamfer c at an angle of 45°. After grinding, it is necessary to grind the valves (see «Lapping of valves»).
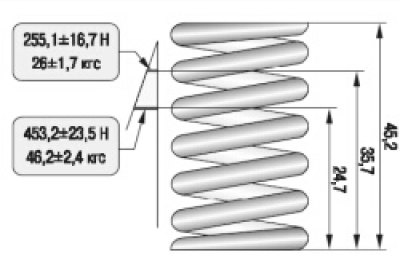
4.11. External spring test parameters

45. Check up a condition of external and internal springs of valves. Replace springs that are bent, broken, or cracked.
46. To check the elasticity of the outer spring, measure its height in a free state (pic. 4.11), and then under two different loads. If the spring does not meet the required parameters, replace it.
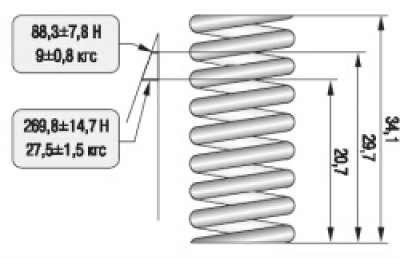
47. To check the elasticity of the internal spring, measure its height in a free state, and then under two different loads (pic. 4.12). If the spring does not meet the required parameters, replace it.
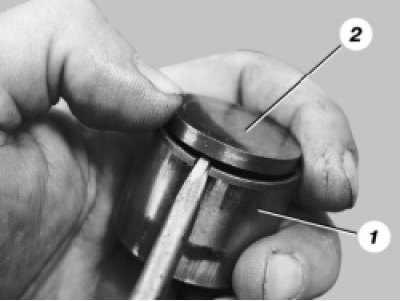
48. Inspect the valve lifters. If there are scores, scratches, etc. on the working surface of 1 pusher, replace the pushers. On the working surfaces of the adjusting washers 2 there should be no burrs, nicks, scratches, traces of stepped or uneven wear of the metahp such defects, the washers must be replaced. Concentric burn-in marks with camshaft cams are allowed on the washers.
49. Check up backlashes between directing plugs and valves.
Clearances between the valve and the guide sleeve, mm:
- nominal clearance for intake valves... 0.022-0.055
- nominal clearance for exhaust valves... 0.029-0.062
- maximum allowable clearance for intake and exhaust valves... 0.3
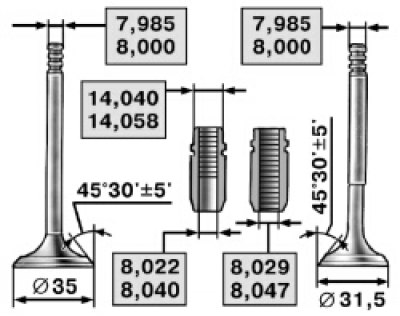
4.13. Dimensions of valves and valve guides
Clearance is calculated as the difference between the diameter of the hole in the sleeve and the diameter of the valve stem (pic. 4.13).
It is recommended to check the gap in a specialized workshop, since a special tool is needed to measure the diameter of the bushings (caliper).

50. If the gap has not reached the maximum allowable, you can try to eliminate it by replacing the valve. If this fails or the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the guide bushing. To do this, press out the defective bushing from the side of the combustion chamber with a special mandrel.

51. Spare parts are supplied bushings with retaining rings 1. The outer diameter of the bushing is increased, the diameter of the hole for the valve is reduced.

52. After lubricating the sleeve with engine oil, insert it into a special mandrel and press it from the side of the camshaft until the retaining ring stops in the head of the block. Ream the hole in the sleeve using a reamer to 8.022-8.040 mm for intake valves and to 8.029-8.047 mm for exhaust.

53. If an old valve is being installed, deburr the cracker grooves. After that, it is necessary to grind the valve to the seat [see. «Lapping of valves» in subsection «cylinder head (repair)»].

54. Install the valves in the block head in accordance with the previously made markings, after lubricating their rods with engine oil.
55. Install the lower plates of the valve springs.
56. Install valve stem seals (see «Replacement of valve stem seals»).

57. Replace the camshaft if its journals and cams show signs of wear, scoring and deep scratches. In workshops equipped with special tools and fixtures, the radial runout of the camshaft journals can be checked (it should not exceed 0.02 mm) and the gap between the holes of the supports and the camshaft journals, which should not exceed 0.2 mm (gap for new parts 0.069-0.11 mm).
58. Install the camshaft and bearing housings (see «Replacement of valve stem seals» in subsection «Replacing Engine Seal Parts»).
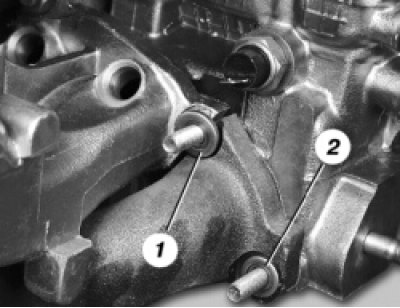
59. Install gaskets, exhaust manifold and intake pipe. Please note that under the nuts (4 things.), fastening the intake pipe and the exhaust manifold at the same time, washers 1 of a larger diameter are installed than washers 2 under the rest of the nuts..

60.... and washers are not installed under the nuts of the receiver bracket.
61. Install the head on the cylinder block (see «Replacing the cylinder head gasket» in subsection «Replacing Engine Seal Parts»), check the clearances in the valve drive and adjust if necessary (see «Valve clearance adjustment»).
