Piston
Diameter of pistons of various classes, measured perpendicular to the axis of the pin at a distance of 55 mm from the piston crown, mm.
- class A - 81.965-81.975
- class B - 81.975-81.985
- class C - 81.985-81.995
- class D - 81.995-82.005
- class E - 82.005-82.015
In the manufacture of the mass of pistons is strictly maintained. Therefore, it is not required to select pistons by weight when assembling the engine.
On fig. 9-1 shows the markings of the pistons. Marks 2 in the form of a square or a triangle refer to repair pistons. A triangle corresponds to an increase in diameter of 0.4 mm, and a square to 0.8 mm.
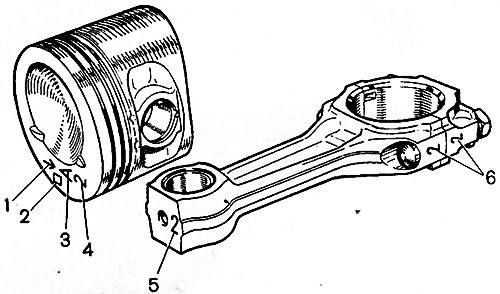
Pic. 9-1. Piston and connecting rod markings: 1 - arrow for orienting the piston in the cylinder; 2 - repair size; 3 - piston class; 4 - hole class for the piston pin; 5 - connecting rod class according to the hole for the piston pin; 6 - cylinder number
Arrow 1 on the bottom of the piston shows how to correctly orient the piston when it is installed in the cylinder. It should be directed towards the camshaft drive.
Piston pin
Piston pin - steel hollow, floating type, i.e. rotates freely in the piston bosses and the connecting rod bushing. The pin is fixed in the piston with two steel retaining rings.
Connecting rod
A steel-bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod. According to the diameter of the hole of this bushing, the connecting rods are divided into three classes through 0.004 mm (just like pistons). Class number 5 is stamped on the upper head of the connecting rod.
By the mass of the upper and lower heads, the connecting rods are divided into classes (tab. 9-1), marked with paint on the rod of the connecting rod. Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine. You can adjust the mass of connecting rods by removing metal from the bosses on the heads to the minimum sizes of 16.5 and 32.5 mm (pic. 9-2).
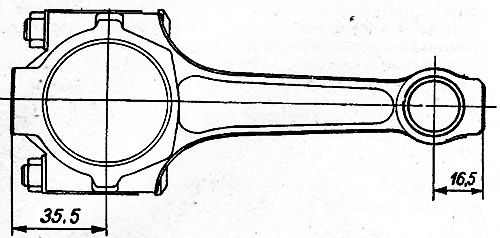
Pic. 9-2. Places where metal is allowed to be removed when adjusting the mass of the upper and lower connecting rod heads
Before assembling the connecting rod and piston group, a finger is selected to the piston and connecting rod. For new parts, the class of the pin holes in the connecting rod and piston must be identical to the class of the pin. For used parts, the selection of the pin to the piston and connecting rod is identical to that described in section II (see chapter «Pistons and connecting rods»).
Table 9-1. Connecting rod classes by weight of the upper and lower heads