The electrical equipment of the car includes sources and consumers of electric current. A single-wire system is used to connect current sources and consumers. The second wire is the mass of the car (its metal parts), with which the negative poles of electrical appliances are connected. Electrical appliances are powered by 12 V direct current.
A simplified diagram of the general electrical circuit of the electrical system and the connection of devices without taking into account their actual location on the vehicle is shown in fig. 16.
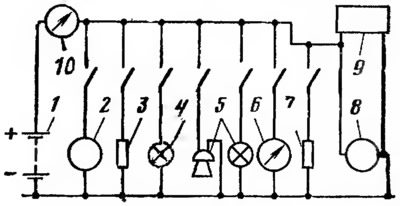
Pic. 16. Schematic diagram of electrical equipment:
1 - battery; 2 - starter; 3 - devices of the ignition system; 4 - devices of the lighting system; 5 - devices of the alarm system; 6 - control electrical appliances; 7 - additional equipment, 8 - generator; 9 - voltage regulator; 10 - ammeter.
Current sources
The sources of current in the car are the generator and the battery. A voltage regulator is connected to the current sources.
Generator converts the mechanical energy received from the engine into electrical energy. The generator supplies all consumers of electric current when the engine is running. By car «Niva» installed alternator G-221 (pic. 17). The main parts of the generator are the stator 12 with a fixed winding, in which an alternating current is induced, and the rotor 11, which creates a moving magnetic field. The generator rotor is mounted in two ball bearings. It is driven through the alternator pulley by a V-belt from the engine crankshaft.
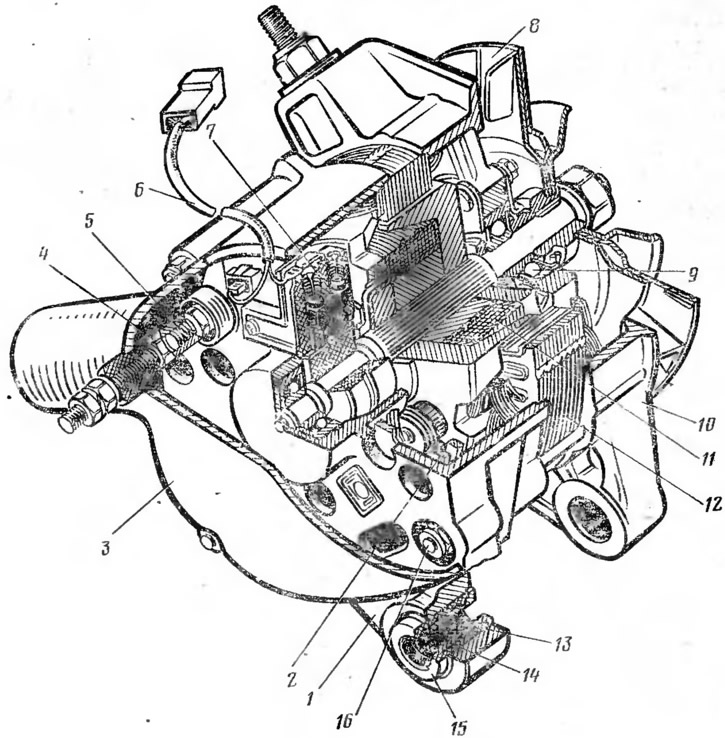
Pic. 17. Generator G-221:
1 - back cover: 2 - rectifier unit; 3 - protective cover; 4 - contact bolt extension; 5 - contact bolt; 6 - wires; 7 - brush holder with brushes; 8 - a pulley with a fan; 9 - ball bearing; 10 - front cover; 11 - rotor; 12 - stator; 13 - buffer sleeve; 14 - bushing; 15 - clamping sleeve; 16 - coupling bolt.
The generator has a rectifier unit 2, which converts alternating current into direct current. The generator is cooled by the generator pulley fan.
Accumulator battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The battery supplies the consumers of electric current when the engine is not running. A 6ST-55P battery is installed on the car. Lead-acid battery, starter, voltage 12 V, capacity 55 Ah.
The battery case is made of acid-resistant plastic and is divided into six sections by partitions. Each section has a separate element, consisting of positive and negative plates, and separators (separators) between them. The elements have a voltage of 2 V and are connected in series with each other by bridges. The battery case is closed with a plastic cover common to all elements. The cover is heat-welded along the periphery to the outer walls of the housing. The connections of the cover with the partitions of the body are sealed during assembly with a sealant, which eliminates the overflow of electrolyte from one section to another. For each section in the cover there is a threaded hole with a plug for filling and monitoring the electrolyte level. The plugs are provided with holes for connecting the internal cavity of the battery with the atmosphere.
The battery has two terminals; positive and negative.
Voltage regulator maintains a constant voltage generated by the generator at a variable speed of the engine crankshaft. The car uses a voltage regulator RR-380. This is a two-stage electromagnetic vibration type regulator.
When the generator voltage rises to 13-14 V, additional resistance is included in the excitation winding circuit. This is the first stage of generator voltage regulation. When the voltage rises above 14 V, the excitation winding of the generator closes to ground. This is the second stage of voltage regulation. As a result, the generator voltage is regulated within the specified limits.
Current consumers
Current consumers on the car are the starter, the ignition system, the lighting system (outdoor and indoor), alarm system (sound and light), control electrical appliances and additional equipment.
The starter motor rotates the crankshaft at the required frequency to start the engine.
Starter ST-221 is installed on the car (pic. 18). The starter is a four-pole, four-brush mixed-excitation DC motor with electromagnetic engagement of the drive gear and remote control.
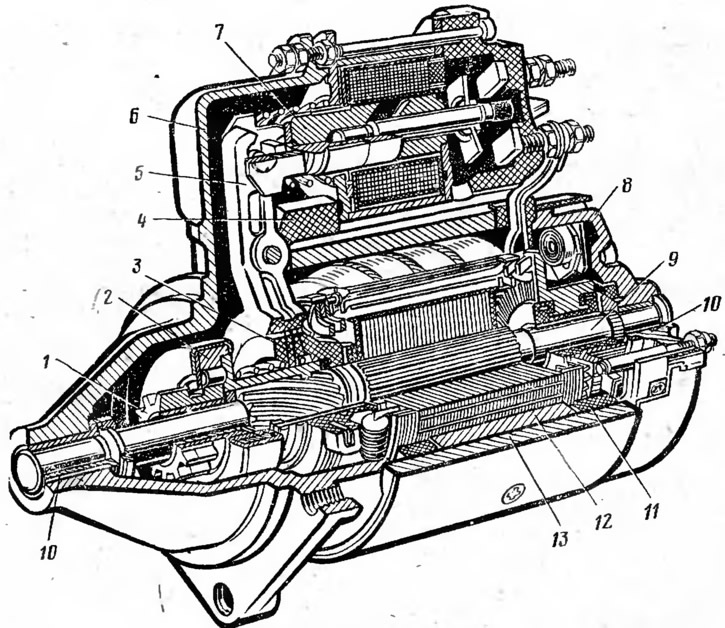
Pic. 18. ST-221 starter:
1— drive gear; 2 - freewheel; 3 - driving ring; 4 - rubber plug; 5 - drive lever; 6 - front cover; 7 - traction relay; c - back cover; 9 - anchor; 10 - bushing; 11 - winding a hundred mountains; 12 - stator pole; 13 - body.
In the case 13 of the starter there are four poles 12. Two of them are with excitation windings connected in series with the armature winding 9, and two in parallel. The starter armature shaft is installed in two bushings 10y located in covers € and 8. At the front end of the armature shaft, a starter drive is installed, consisting of a freewheel roller clutch 2 and drive gear 1, which can move along the splines of the shaft. The freewheel clutch transfers rotation from the starter armature shaft to the flywheel when the engine is started and prevents the transfer of rotation from the flywheel to the starter armature after the engine is started. A traction relay 7 is installed on the front cover 6 of the starter. When the engine is started, the relay ensures that gear 1 of the drive is engaged with the flywheel crown and the electrical circuit of the starter windings is connected to the battery. On the rear cover 8 of the starter, brush holders with four brushes are fixed, which are pressed against the armature collector by springs.
When the starter is running, current flows through its windings. A strong excitation magnetic field is created around the poles. This field interacts with the magnetic field of the armature winding and causes the armature to rotate, which is transmitted through the starter drive to the flywheel.
Ignition system serves to ignite the working mixture in the cylinders in accordance with the order and mode of operation of the engine.
The ignition system includes: an ignition coil, an ignition distributor including a low voltage current breaker and a high voltage current distributor, spark plugs and an ignition switch.
Schematic diagram of the ignition system of a car engine «Niva» VAZ-2121 is shown in fig. 19.
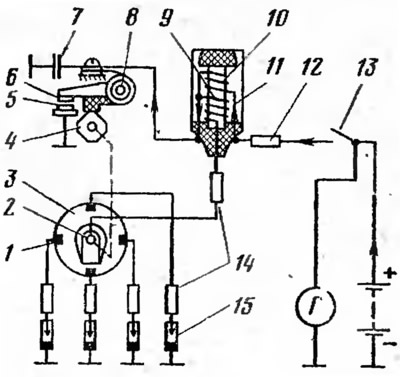
Pic. 19. Schematic diagram of the ignition system:
1 - contact; 2 - rotor; 3 - high voltage current distributor; 4 - cam; 5 - fixed contact; 6 - moving contact; 7 - capacitor; 8 - low voltage current interrupter;, 9 - secondary winding; 10 - primary winding; 11 - ignition coil; 12 - additional resistance; 13 - ignition switch; 14 - suppressive resistance; 15 - spark plug.
The ignition system diagram includes: two electrical circuits - a low voltage circuit (primary) and high voltage circuit (secondary). The primary circuit includes: ignition switch 13, additional resistance 12, primary winding 10 of the ignition coil, breaker 8 of the low voltage circuit: voltage and capacitor 7 The secondary circuit includes: secondary winding 9 of the ignition coil, high voltage current distributor 3 and spark plugs 15.
With the ignition switch on and terminals 5 and 6 of the low voltage breaker closed, the low voltage circuit carries current from the battery or alternator. Passing through the primary winding of the ignition coil, the current creates a strong magnetic field. When opening the contacts of the breaker 8 (cam 4 runs with a ledge on the lever with contact 6) the current in the low voltage circuit is interrupted and the generated magnetic field disappears. In this case, the magnetic field crosses the secondary winding of the ignition coil and induces a high voltage current in it. The high voltage current is supplied to the rotor 2 of the ignition distributor, which rotates together with the cam 4. At the moment the contacts of the breaker open, the high voltage current flows to one of the contacts 1 of the ignition distributor, which are connected to the spark plugs 15. The spark discharge between the electrodes of the spark plug occurs in that engine cylinder, in which the compression of the working mixture ends at this time, i.e. in the sequence corresponding to the order of engine operation (1-3-4-2).
Ignition coil converts low voltage current (12 V) into a high voltage current, which can reach 16-20 kV.
The ignition coil B-117A is used on the car. On the core of the ignition coil, consisting of thin sheets of electrical steel, a secondary winding is wound, which has a large number of turns (~21000) copper insulated wire with a diameter of ~ 0.07 mm. The primary winding has ~308 turns of insulated copper wire with a diameter of ~0.57 mm. The internal cavity of the case is filled with transformer oil, which improves the cooling and insulation of the windings! ignition coils. In the cover of the coil there are terminals of the primary and secondary windings. Outside the coil body there is an additional resistance connected in series with the primary winding and automatically adjusting the current in the winding depending on the engine crankshaft speed.
Distributor performs closing and opening of low voltage current and distribution of high voltage current to engine cylinders.
The car uses an ignition distributor R125-B (pic. 20). The ignition distributor consists of a breaker and a distributor installed in one common housing. In the housing 3 of the distributor, the shaft 1 of the breaker cam drive, the distributor rotor 14 and the centrifugal regulator are also installed, which automatically changes the ignition timing depending on the engine crankshaft speed. When the shaft 1 rotates, the cam 8 opens the contacts 7 of the breaker. Together with the shaft, the rotor 14 and the centrifugal regulator 20 rotate, the weights of which, overcoming the force of the springs 21, diverge under the action of centrifugal forces. The weights of the centrifugal regulator are connected to the chopper cam and, as the shaft speed increases, they rotate the cam relative to the shaft, changing the ignition timing. Depending on the octane number of the fuel used, the ignition timing is changed manually using an eccentric 9 octane corrector connected through a rod with a movable plate 24, on which contacts 7 of the interrupter are installed.
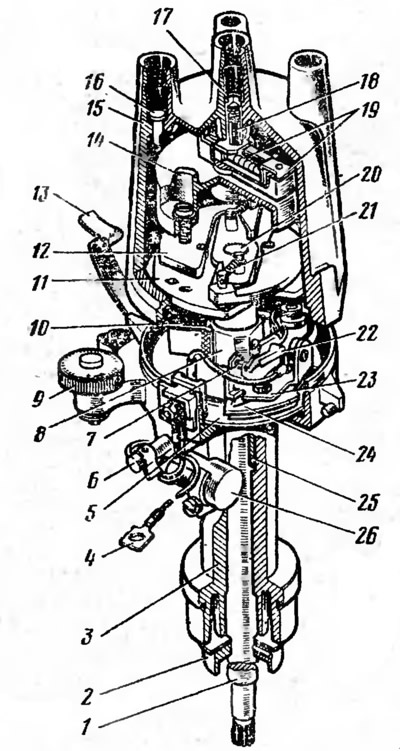
Pic. 20 Ignition distributor R-125B:
1 - shaft; 2 - oil slinger: 3 - body; 4 - low voltage wire; 5 - fixed breaker plate; 6 - oiler; 7 - breaker contacts; 8 - cam; 9 - eccentric octane corrector; 10 - cam filter; 11 - cam drive plate; 12 - centrifugal regulator weight; 13 - latch; 14 - rotor; 15 - cover; 16 - cover electrode; 17 - central electrode; 18 - carbon contact; 19 - rotor electrode; 20 - centrifugal regulator; 21 - weight spring; 22 - breaker lever; 23 - fixed contact holder; 24 - movable breaker plate; 25 - shaft sleeve; 26 - capacitor.
The cover 15 of the ignition distributor has four side electrodes 16 and a central electrode 17. The side electrodes are connected with spark plugs by high-voltage wires, and the central electrode is connected to the ignition coil. The high voltage current through the central electrode is supplied to the current-distributing plate of the rotating rotor 14 and through it to the side electrodes in accordance with the order of operation of the engine.
Spark plug provides an electric spark in the engine cylinder. A17DV spark plugs are used in the ignition system of a car engine. Spark plug (pic. 21) non-separable. In a metal case 4, a core is rolled, which is a ceramic insulator 2, inside which a contact rod 1 and a central electrode 6 are placed. The candle body has an external thread 5, with which the candle is attached to the cylinder head. A side electrode 7 is attached to the body. The tip connecting the spark plug to the high-voltage wire has suppressive resistance, which reduces radio interference created by the ignition system.
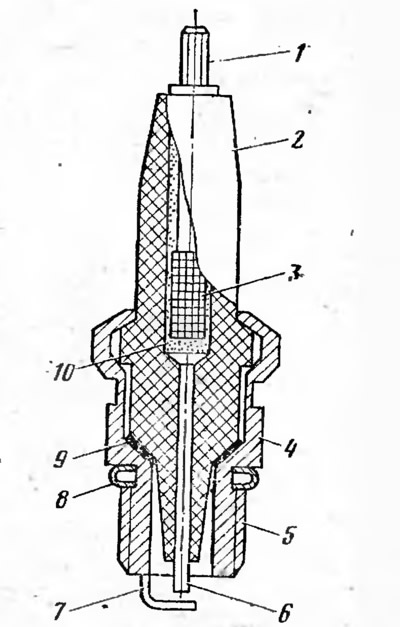
Pic. 21. Spark plug A17DV:
1 - contact rod; 2 - insulator; 3 - knurling; 4 - body; 5 - thread; 6 - central electrode; 7 - side electrode; 8 - gasket; 9 - washer; 10 - sealant.
Ignition switch. switches the ignition system, starter, instrumentation and other devices on and off.
The ignition switch VK-347 is installed on the car (pic. 22). The switch has an anti-theft device. In the body 1, with the help of a retaining ring 12, the switch mechanism is fastened, which consists of a panel 11 with plug-in clamps 13 and contacts 10, a cam 9 and a rotor 7 with contact plates 8. The cam and the rotor of the switch are turned by the key of the locking device 3. The locking rod 6 is actuated spring 2 enters the groove of the steering shaft, and locks the shaft when the key is set to the position «parking», is removed from the locking device of the switch. Lug 5 is used for the correct installation of the ignition switch in the steering column.
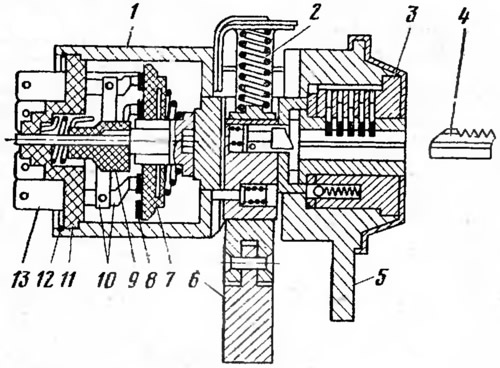
Pic. 22. Ignition switch VK-347:
1 - body; 2 - spring; 3 - locking device; 4 - key; 5 - mounting ledge; 6 - locking rod; 7 - rotor; 8 - contact plates; 9 - cam; 10 - contacts; 11 - panel; 12 - retaining ring; 13 - clamps.
Lighting system ensures the operation of the car in conditions of poor visibility (at night, in fog, etc.). The system includes outdoor and indoor lighting. The lighting system includes: headlights, front and rear lights, license plate lights, body interior lights, instrument panel and engine compartment lights, fuses and switches.
headlights illuminate the road in front of the car in conditions of poor visibility (at night, in fog, etc.). The car has a two-headlight lighting system with round headlights of the FG-140 type. There are 5 headlights in the body (pic. 23) a holder 6 of the optical element 1 is installed. The optical element of the headlight, consisting of a reflector 7, a diffuser 2 and a lamp 9, is attached to the holder with a rim 3 using screws 10. The headlight lamp is a double-filament power of 45 W for high beam and 40 W for low beam. Screws 4 and 11 allow you to change the position of the holder 6, and with it the optical element in the vertical and horizontal planes when adjusting the headlights.
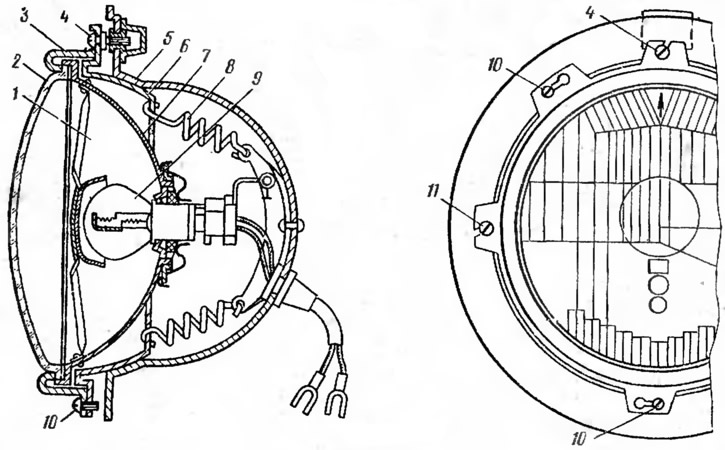
Pic. 23. Headlight FG 140:
1 - optical element: 2 - diffuser; 3 - bezel; 4, 11 - adjusting screws; 5 - body; 6 - optical element holder; 7 - reflector; 8 - spring; 9 - lamp; 10 - screw.
Front lights are used to indicate the dimensions of the car, parking lighting and light signaling when maneuvering.
The front lamp is two-section, rectangular. There are two single-filament lamps in the molded body of the lantern. A 5 W lamp is used to indicate the dimensions of the car, and a 21 W lamp is used to signal the vehicle's maneuvering. Diffuser of a forward lantern plastic monolithic, two-color. The outer part of the diffuser is orange and is intended for signaling when maneuvering, and the inner part is colorless, designed to indicate the dimensions of the car.
Rear lights are used to indicate the dimensions of the car and light signaling when turning, braking and reversing.
The rear light is rectangular. The rear light housing has four sections containing three 21W bulbs and one 5W bulb. The first three are the brake, turn signal and reversing lights, and the last is the position light. The body of the lantern is closed with a diffuser. Diffuser plastic monolithic, multi-section, three-color. The outer part of the diffuser is orange and serves as a signal when maneuvering the car. The central section is colorless and serves to signal reversing. The remaining sections of the diffuser are red and are intended for signaling when braking and indicating the dimensions of the car.
Alarm system ensures the safety of the vehicle. The system includes light and sound alarms.
To signal light includes front, rear, side direction indicators and their switch, as well as brake signals (stop signal), reversing and their switches. The front direction indicators are located in the headlights of the vehicle. Rear direction indicators, brake and reverse signals are located in the rear lights of the car. Side direction indicators are located on the front fenders of the car body.
Audible alarms include audible signals. The sound signal notifies, if necessary, pedestrians and drivers of vehicles about the presence of the car. The car is equipped with two electric vibration, hornless noise-type sound signals: one high and the other low tone. The signals are tuned into a harmonic chord and act simultaneously. Current passing through the winding 8 of the signal (pic. 24), magnetizes the core 7, which attracts the armature 10 and causes the deflection of the elastic steel membrane 1. In this case, the armature acts on the elastic plate 5 and opens the contacts 2. The current in the winding 8 is interrupted, and the core 7 is demagnetized. Membrane 1 returns to its original position and contacts 2 close. The operation of the signal is repeated with a contact vibration frequency of 200–400 Hz. Air vibrations caused by the membrane create sound, and the diffuser (resonator) 3 provides melodic sound. The appropriate tone and timbre of the sound depends on the thickness and diameter of the membrane, as well as the diameter of the resonator. In a high tone signal, the membrane is thinner than in a low tone signal.
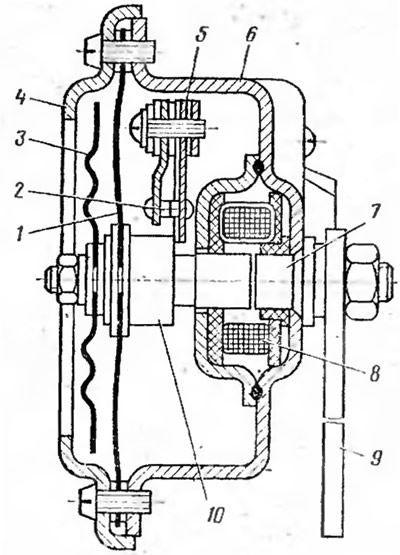
Pic. 24. Beep:
1 - membrane; 2 - contact; 3 - diffuser; 4 - ring; 5 - plate; 6 - body; 7 - core; 8 - winding; 9 - signal mounting plate; 10 - anchor.
Instrumentation designed to monitor the state and operation of individual systems and mechanisms of the car.
Control and measuring devices include: an ammeter that measures the strength of the charging and discharging currents, fuel level indicators in the tank, coolant temperature in the cooling system and oil pressure in the engine lubrication system. In addition, there are a number of indicator lamps: fuel reserve, oil pressure, battery charge, carburetor choke, outdoor lighting, direction indicators, high beam headlights, transfer case differential lock, level, brake fluid and parking brake. Instrumentation also includes a speedometer, which measures vehicle speed and distance traveled, and a tachometer, which monitors engine speed.
Additional equipment, consuming electric current, includes: windshield wipers and washers, headlight cleaners and washers, heater and cigarette lighter.
Windshield wipers and washers clean the windshield and headlights from dirt and precipitation. The heater heats the interior of the car body in cold weather, as well as blowing the inner surface of the windshield in order to protect the glass from fogging and freezing.
