The rear axle in the VAZ-2121 car is leading. He (pic. 33) made in the form of a solid beam 7 with a developed central part of the annular shape. The bridge beam is welded from two stamped steel halves. On the one hand, a cover 12 is welded to the middle part of the bridge beam, and on the other, a crankcase 16 is bolted. Flanges 4 are welded to both ends of the beam. Support cups 6 rear suspension springs and brackets 8 and 26 for fastening parts of the suspension are also welded to the rear axle beam.
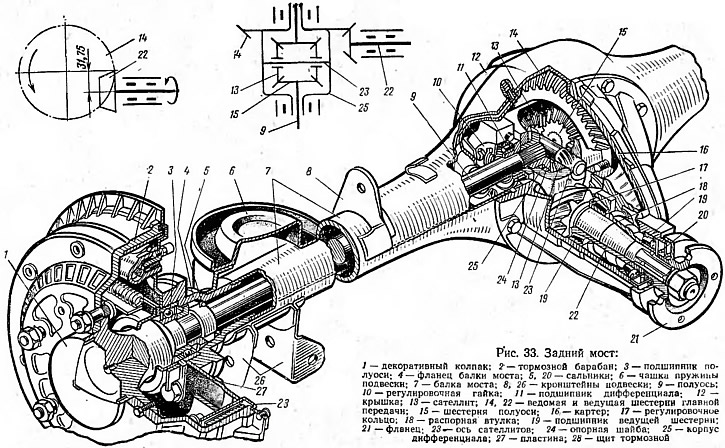
Pic. 33. Rear axle:
1 - decorative cap; 2 - brake drum: 3 - half shaft bearing; 4 - bridge beam flange; 5, 20 - glands; 6 - suspension spring cup; 7 - bridge beam; 8, 26 - suspension brackets; 9 - axle shaft; 10 - adjusting nut; 11 - differential bearing; 12 - cover; 13 - satellite; 14, 22 - driven and driving gears of the main gear; 15 - axle gear; 16 - crankcase; 17 - adjusting ring; 18 - spacer sleeve; 19 - drive gear bearing; 21 - flange; 23 - axis of the satellites; 24 - support washer; 25 - differential housing; 27 - plate; 28 - brake shield.
The rear axle houses the main gear, differential or axle shafts.
main gear serves to increase the torque supplied to the driving wheels of the car.
The main gear is used on the car, single, hypoid with a gear ratio of 4.3.
The main gear has one pair of bevel gears with a spiral tooth. The axes of the gears do not intersect, but cross and lie at some distance (pinion axle below axle. slave), i.e., have a hypoid displacement. The hypoid offset slightly lowers the vehicle's center of gravity and increases its stability. In addition, the hypoid final drive has increased strength and durability, as well as smooth gear engagement and quiet operation.
The axis of the drive gear 22 is shifted down by 31.75 mm relative to the axis of the driven gear 14. The drive gear 22, made together with the shaft, is installed in the crankcase 16 on two tapered roller bearings 19. Between the bearings there is a spacer sleeve 18, which ensures the correct tightening of the bearings. The driven gear 14 is bolted to the differential case 25. The correct position of the drive gear relative to the driven gear is ensured by the adjusting ring 17.
Differential designed to distribute torque between the driving wheels of the car. The differential allows the drive wheels to rotate at different speeds when the vehicle is moving around curves and on rough roads.
The car uses a cross-axle differential conical, symmetrical. It distributes torque equally between the driving wheels of the car.
The housing 25 of the differential is mounted in bearings 11. Adjustment of the tightening of the bearings, as well as the engagement of the teeth of the drive 22 and driven 14 gears of the main gear, is carried out by adjusting nuts 10. An axle 23 with two satellites 13 is fixed inside the differential housing. The satellites are in constant engagement with the gears of the axle shafts 15, which are connected to the splined ends of the axle shafts 9. All differential gears are spur gears.
The axle shafts are designed to transmit torque from the differential to the drive wheels of the vehicle.
The car uses semi-unloaded axle shafts. They transmit torque and perceive bending moments in the vertical and horizontal planes.
The axle shaft 9 is made in the form of a solid shaft. The inner end of the axle shaft has splines, and the outer end has a flange. The axle shaft is connected by its inner end to the gear 15 located in the differential case 25. The outer end of the axle shaft is installed in the bearing 3, which is located in the flange 4 of the axle beam. A brake drum 2 and a wheel with a tire are bolted to the axle shaft flange. The semi-axis is kept from displacement by a special plate 27, which fixes the bearing 3, which, together with the brake shield 28, is attached to the flange 4 of the axle beam.
