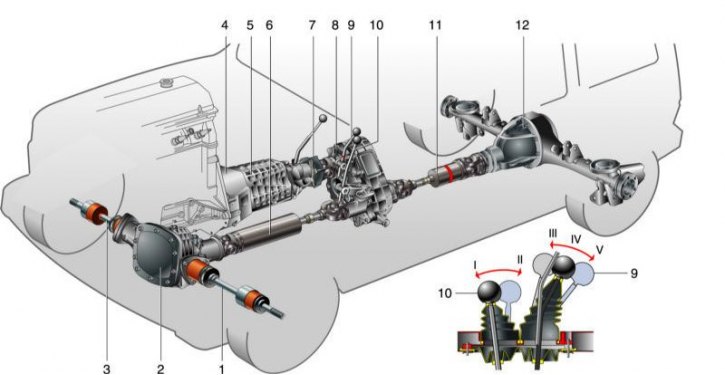
Transmission units: 1, 3 - front wheel drives; 2 - front axle; 4 - clutch; 5 - gearbox; 6 - front propeller shaft; 7 - intermediate shaft; 8 - transfer case; 9 – the lever of a gear change of a distributing box; 10 - differential lock lever; 11 - rear driveshaft; 12 - rear axle; I - differential unlocked; II - differential is blocked; III - low gear is engaged; IV - neutral position; V - top gear engaged
Automobile «Niva» - all-wheel drive, i.e. all wheels are driving. Four-wheel drive - permanent: torque from the engine is always transmitted immediately to both axles (bridges don't turn off). Such a scheme increases the vehicle's cross-country ability, while simultaneously reducing the load on the transmission units, but slightly increases fuel consumption.
The front and rear axles are connected through a center differential, which allows the front and rear wheels to rotate at different angular speeds depending on the trajectory and driving conditions. The center differential is located in the transfer case and is similar to the center differentials located in the front and rear axles. However, unlike them, the center differential can be forcibly blocked (the lock lever is on the floor tunnel). In this case, the front and rear propeller shafts become rigidly interconnected and rotate at the same frequency. This greatly improves the car's handling (on slippery slopes, in mud, snow, etc.), but worsens handling and increases wear on transmission parts and tires on surfaces with good grip. Therefore, the differential lock can only be used to overcome difficult sections and at low speeds. To warn the driver that the lock mode is on, a warning lamp on the instrument panel is used.
You can turn on the differential lock while the car is moving, if the wheels do not slip. Locking the center differential does not save the car from danger «diagonal hanging», when one of the wheels on each axle loses traction with the ground - in this case, pour soil under the suspended wheels or dig it under the rest.
To increase the torque supplied to the wheels, the lowest gear in the transfer case is used, its gear ratio is 2.135. The top gear, designed for normal driving conditions, has a gear ratio of 1.20. Thus, the driver can use one of two rows of gear ratios - with a high or low gear in the transfer case. Total gear ratios «top» row (1st to 5th gear) – 4,40; 2,52; 1,63; 1,20; 0,98, «lower» - 7.82; 4.47; 2.90; 2.13; 1.75. The low gear in the transfer case is switched on before overcoming snowy, sandy areas, steep slopes, when towing loads, etc., when there is a lack of engine traction or for driving at very low speed. It is necessary to turn on the lower gear in the transfer case in advance, on a stationary car, since the gear shift clutch does not have synchronizers. With some skill, it is possible to turn on the highest gear even when driving at a speed of no higher than 30–35 km / h, however, if possible, it is better to slow down or stop.
A car with permanent all-wheel drive places special demands on tires. They should be the same not only in size, but also in the degree of wear. Different tire rolling radii will cause increased wear on the differentials under normal driving conditions, and when the lock is on, increased wear on other transmission parts and wheel spin.
