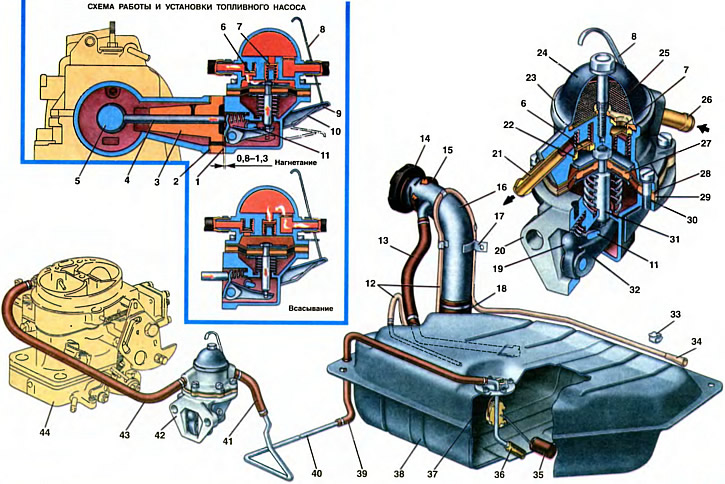
1. Adjusting lining of the fuel pump. 2. Adjusting gasket of the heat-insulating spacer. 3. Heat-insulating spacer. 4. Pusher. 5. Camshaft eccentric. 6. Discharge valve. 7. Suction valve. 8. Extension lever for manual fuel pumping. 9. Lever for manual fuel pumping. 10. Spring of the manual paging lever. 11. Cam. 12. Ventilation hose. 13. Filler hose. 14. Fuel tank cap. 15. Filler seal. 16. Tank filler neck. 17. Bracket for fastening the filler neck. 18. Filler hose. 19. Lever for mechanical fuel supply. 20. Lower case. 21. Discharge pipe. 22. Discharge valve seat. 23. Upper case. 24. Lid. 25. Pump filter. 26. Suction pipe. 27. Internal spacer. 28. Upper diaphragms. 29. External spacer. 30. Lower diaphragm. 31. Stock. 32. Balancer. 33. Hook for attaching the hose. 34. Tip of the ventilation hose. 35. Float. 36. Fuel pickup tube filter. 37. Fuel level sensor in the tank. 38. Fuel tank. 39. Fuel tank hose. 40. Fuel line. 41. Fuel supply hose to the fuel pump. 42. Fuel pump. 43. Fuel supply hose to the carburetor. 44. Carburetor.
The power supply system includes devices for supplying fuel and air to the carburetor, preparing a combustible mixture and exhaust gases. The power system consists of a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel lines, air filter, carburetor, mufflers and pipelines.
The fuel for the engine is AI-93 high-octane gasoline with an octane rating of 93, determined by the research method.
Fuel tank
Fuel tank 38 - stamped, welded from two steel halves. To increase corrosion resistance, the tank is tinned POS 35 on both sides and painted with black enamel. Fuel tank capacity 30 l including fuel reserve.
The tank is installed under the floor of the body and fastened with four nuts to the welded bolts of the body. From the side of the main muffler and exhaust pipes, the tank is covered with a screen that protects the fuel in the tank from heating. The filler neck 16 of the tank is led into a niche in the rear of the right side of the body and is closed with a sealed plastic plug 14. The plug has a tightening torque limiter (on some cars, a lock can be installed in a traffic jam). The filler neck is connected to the fuel tank pipe with a hose 18 made of petrol-resistant rubber.
To prevent leakage of fuel during refueling, the upper part of the filling pipe is connected to the tank pipe with a rubber hose 13, through which air is forced out of the tank during refueling.
A fuel level sensor 37 with a fuel receiving tube is fastened with nuts to the fuel tank from above through a sealing gasket. The fuel receiving tube has a mesh filter 36. When the remaining fuel reserve in the tank, the float lever 35 closes the contacts of the fuel reserve control lamp. The fuel level indicator with a fuel reserve warning lamp is installed on the instrument cluster in the passenger compartment.
For ventilation and access to atmospheric air, the fuel tank has a ventilation hose 12 made of a PVC tube with a tip 34 at the end. The hose is connected to the tank pipe, has a loop along the filler neck and is then laid on hooks along the rear edge of the tank. The fuel that has entered the lower part of the hose loop 12 when the car is moving on a rough road forms a liquid seal that prevents the gasoline from evaporating from the tank.
Fuel lines and hoses
The fuel line 40, which communicates the fuel tank with the fuel pump 42, is made of galvanized or lead-coated steel tube with a diameter of 6 mm. The fuel line 40 is connected to the fuel tank and the fuel pump with a rubber hose 39 and 41. The fuel pump is connected to the carburetor 44 with a rubber hose 43. The rubber hoses 39, 41 and 43 are attached to the nozzles with screw clamps.
Fuel pump
The fuel pump is a diaphragm type, with a mechanical drive, equipped with a lever 9 for manual fuel pumping with an extension 8 of the lever. The fuel pump is mounted on two studs of the drive housing from the side of the bulkhead plate through a heat-insulating spacer 3 and shims 1 and 2.
The pump is driven by a pusher 4 from the eccentric of the camshaft 5. The fuel supply by the pump is at least 50 l / h at a swing frequency of 2000±40 rpm. The pressure developed by the pump is 21...30 kPa.
The fuel pump consists of a lower housing 20 with drive levers, an upper housing 23 with valves and pipes, a diaphragm assembly and a cover 24.
The diaphragm assembly has three diaphragms: two upper 28 - working for supplying fuel, one lower 30 - safety, working in contact with crankcase oil and preventing fuel from entering the engine crankcase if the working diaphragms are damaged. Between the working and safety diaphragms, remote outer 29 and inner 27 gaskets are installed. The outer gasket has a hole for fuel to escape to the outside in case of damage to the working diaphragms. Diaphragms with plates and with an internal spacer 27 are mounted on the stem 31 and fixed on top with a nut.
The diaphragm assembly is installed between the upper and lower pump casings. A spring is installed on the rod under the diaphragm assembly. The rod 31 is inserted into the slot of the balancer 32 with a T-shaped shank. This design allows, without disassembling the diaphragm assembly, to remove it from the fuel pump.
In the lower housing 20, levers 19 of mechanical fuel supply and a balancer 32 are installed on the axle. In the lower housing, also on the axle with a cam 11, a lever 9 of manual fuel pumping is installed, which returns to its original position under the action of a spring. Lever 9 has an extension 8 to facilitate pumping fuel.
In the upper casing 23 of the pump, textolite hexagonal suction 7 and discharge 8 valves are installed. Valves are pressed against brass seats by springs. From above, a cover 24 is attached to the body with a central bolt. A plastic mesh filter 25 of the pump is installed between the cover and the body. Suction 26 and discharge 21 branch pipes are pressed into the upper casing of the pump.
When the engine is running, the camshaft eccentric 5 through the pusher 4 acts on the lever 19 and turns the balancer 32, which, by the rod 31, pulls the pump diaphragms down. At the same time, the diaphragm spring decreases even more, a vacuum is created in the working cavity above the diaphragm assembly, as a result of which fuel fills the working cavity through the suction valve 7. When the eccentric runs off the pusher, the lever 19, the balancer 32 and the rod 31 with diaphragms are released. The diaphragms, under the action of a compressed spring, create fuel pressure in the working cavity, the suction valve 7 closes, and the fuel is supplied through the discharge valve 8 to the carburetor float chamber.
With a small fuel consumption, the stroke of the diaphragms will be incomplete; in this case, the stroke of the lever 19 will be partially idle.
When manually pumping fuel through the extension 8, the lever 9 is pressed, the cam 11 acts on the balancer 32 and pulls the rod 31 with diaphragms. Fuel is sucked into the working cavity. When released, the lever 9 with the extension and the cam under the action of the spring 10 return to their original position, and the diaphragms pump fuel into the carburetor.
When installing the fuel pump on the engine, shims 1 and 2 are selected so that the minimum protrusion of the pusher 4 above the mating plane of the heat-insulating spacer 3 (taking into account the gasket between the spacer and the fuel pump) was 0.8... 1.3 mm. The minimum protrusion of the pusher is set by slowly turning the crankshaft of the engine.
Gaskets 1 are made in three types and have a thickness of 0.30; 0.75 and 1.25 mm. A shim 2 0.30 mm thick must always be placed between the heat-insulating spacer and the fuel pump drive housing.
To determine the serviceability of the fuel pump, disconnect the hose 43 from the discharge pipe of the pump and use the lever 9 for manual fuel pumping to check whether fuel is supplied. In this case, the crankshaft must be in a position in which the stroke of the lever 9 will be full. If fuel is not supplied, then disconnect the hose 41 from the suction pipe of the pump and check whether a vacuum is created at the inlet of this pipe. If vacuum is present, the fuel line 40 or hoses 39 and 41 may be damaged or clogged. If there is no vacuum, then the fuel pump is faulty. Removal and disassembly of the pump will be required to correct the malfunction.
