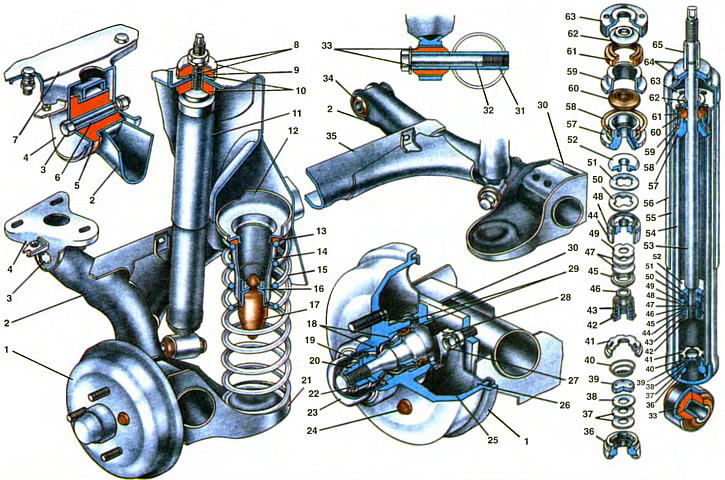
1. Brake drum with rear wheel hub. 2. Rear suspension arm. 3. A bolt of fastening of the suspension arm. 4. Arm of fastening of the suspension arm. 5. Rubber bushing of the lever joint. 6. Spacer sleeve of the hinge of the lever. 7. Body spar. 8. Shock absorber mounting washer. 9. Spacer. 10. Shock absorber mounting pad. 11. Rear suspension shock absorber. 12. The upper support cup of the suspension spring. 13. Suspension spring seal. 14. Rack of a clip of the buffer of a course of compression. 15. Rear suspension spring. 16. Cupboard compression stroke. 17. Buffer compression stroke. 18. Rear wheel hub bearings. 19. Thrust washer. 20. Adjusting nut. 21. Suspension arm bracket. 22. Cotter pin. 23. Wheel hub cap. 24. Plug. 25. Wheel hub seal. 28. Support shield of the brake mechanism. 27. Bolt of fastening of an axis of a nave of a wheel. 28. Wheel axle. 29. Dirt rings. 30. Flange suspension arm. 31. Bushing suspension arm. 32. Shock absorber mounting bolt. 33. Rubber-metal joint of the shock absorber head. 34. Rubber-metal hinge suspension arm. 35. Lever connector. 36. Compression valve housing. 37. Compression valve disks. 38. Throttle disc compression valve. 39. Compression valve plate. 40. Compression valve spring. 41. Clip of the compression valve. 42. Recoil valve nut. 43. Recoil valve spring. 44. Shock absorber piston. 45. Recoil valve plate. 46. Washer nut recoil valve. 47. Recoil valve discs. 48. Piston ring. 49. Throttle disk of the recoil valve. 50. Bypass valve plate. 51. Bypass valve spring. 52. Restrictive plate of the bypass valve. 53. Shock absorber rod. 54. Cylinder. 55. Reservoir. 56. Protective cover. 57. Stem guide bushing. 58. Tank O-ring. 59. Rod gland holder. 60. Stem seal. 61. Gasket of a protective ring of a rod. 62. Rod protection ring. 63. Tank nut. 64. Housing cover. 65. Spacer sleeve.
Rear suspension torsion bar type, independent. It consists of a guiding device, elastic and damping elements. The guiding device is formed by two levers 2 connected to each other by an elastic connector 35 of a U-shaped section. A flexurally rigid and torsionally flexible linkage is located in front of the wheels, approximately 1/3 of the linkage length from their pivot points. With such an arrangement of the connector, each wheel has an independent movement of the wheels, accompanied by elastic twisting of the lever connector.
The levers 2 of the rear suspension are made of electric-welded pipes. They are welded to the connector through lever reinforcements and together with the connector form a single beam pivotally suspended on brackets 4 to the body. Each suspension arm has a bushing in front, into which a rubber-metal hinge 34 is pressed, consisting of rubber bushings 5 and metal bushings 6. Bolts 3 pass through the spacer bushings 6 of the hinges, connecting the suspension arms with stamped brackets 4, the left of which is bolted to the side member 7 of the body, and the right one is welded to the side member. Nuts with spring washers are screwed onto the bolts of the levers.
Brackets 21 are welded to the rear of the levers, on which the springs rest. Flanges 30 with threaded holes are welded to these brackets for bolting the axle 28 of the rear wheel hub with the suspension arm. In front of the brackets, spacers 31 with a thread for cantilever fastening of the lower ends of the shock absorbers are entrusted to the lever tube. In addition to the suspension arms, brackets are welded for fastening the tips of the brake hoses and the sheath of the rear parking brake cable.
The elastic elements of the suspension consist of a spring 15 and a buffer 17 of the compression stroke. The spring is twisted, cylindrical, made of spring steel of round section. It is installed under the floor of the body: the lower part rests on the bracket 21 of the suspension arm, and the upper part - through the rubber insulating gasket 13 into the upper support 12, welded to the wheel arch and to the floor of the body.
Springs along the length under the control load are divided into two classes A and B. Class A springs are marked with yellow paint on the outer side of the middle coils, class B - green.
The rubber buffer of the compression stroke is installed inside the spring. It is fixed with its mushroom-shaped nipple in the hole of the clip 16. which is welded to the stand 14 of the buffer support, and the stand, in turn, to the upper support of the suspension spring. When activated, the compression stroke buffer rests on the platform of the lever bracket
The axle 28 of the rear wheel is attached to the flange 30 of the suspension arm with three bolts. The shield 26 of the brake mechanism is attached together with the axle with the same bolts. On the axis on two tapered roller bearings 18 rotates the brake drum 1, made integral with the rear wheel hub. The brake drum is mounted on the axle with a castellated nut 20 with a thrust washer 19. The nut is fixed on the axle with a cotter pin 22. The wheel hub bearings on the inside of the drum are sealed with an oil seal 25 and two dirt-reflecting rings 29. one of which is welded to the flange of the wheel axle, and the other to the brake drum. The outer mudguard ring enters the annular groove of the axle flange. This creates a labyrinth seal to protect the stuffing box. From the outer end of the drum, the bearing cavity is sealed with a cap 23 pressed into the wheel hub seat.
The backlash in the rear wheel hub bearings is adjusted with a castellated nut. It should be within 0.02... 0.13 mm and should not exceed 0.20 mm. The wheel disc is attached to the brake drum with three nuts.
Shock absorber 11 of the rear suspension is hydraulic, telescopic, double-acting. It is unified with the car shock absorber VAZ-2101, except for the length dimensions, calibration parameters of the valve and the protective cover. The lower head of the shock absorber is mounted cantilever on the bushing 31 of the suspension arm with a bolt.
The upper part of the shock absorber is attached by a rod through rubber cushions 10 to a bracket welded to the rear wheel arch. A thrust washer 8 is installed between the self-locking nut and the upper rubber cushion, and a spacer sleeve 9 is installed between the casing cover 64 and the washer. To keep the stem from turning when tightening the nut, turnkey flats are made on the stem.
The shock absorber consists of reservoir 55, cylinder 54, compression valve, rod 53 complete with piston 44 and valves, guide bush 57 and sealing and mounting parts.
Tank 55 is made of a pipe, to the bottom of which a bottom with a lower lug is welded, and an internal thread for a nut 63 is cut in the upper part.
The compression valve is pressed into the lower part of the cylinder and pressed against the bottom of the tank when the nut 63 is tightened. It consists of a body 36, a clip 41, a plate 39, a package of disks 37 and 38 and a spring 40. The body has a central seat, against the chamfer of which the compression valve disks. In the upper and lower parts of the housing, cross-shaped cutouts are made for the passage of liquid. The disc pack consists of three flat discs, one of which (pos 38) has a cutout for fluid throttling. It is located at the top of the package. The discs are pressed against the chamfer of the socket by the spring 40 through the plate 39, which has four through holes for the passage of liquid and a cylindrical protrusion. With this protrusion, the plate is pressed against the edge of the inner hole of the throttle disc. Due to the cylindrical belt between the outer edges of the throttle disc and the plate, a gap is formed along the entire perimeter for the passage of fluid to the throttle cutout of the disc. A clip 41 is pressed onto the valve body from above. It has a seating belt with a flare for fitting into the cylinder bore 54. One central and six radial holes for the passage of fluid.
In the cylinder 54 moves the rod 53 assembled with the piston 44 and two bypass and return valves. The movement of the rod in the cylinder is guided by a ceramic-metal bushing 57. It is pressed into the upper part of the cylinder. The bushing has a channel for draining fluid from the annular cavity of the bushing into the reservoir cavity so that fluid pressure is not created on the stuffing box 60. Liquid enters the annular cavity of the bushing through the gap between the guide bushing and the stem. The bushing is sealed in the tank by a rubber ring 58, which is pressed against the collar of the bushing and to the surface of the tank by the clip 59 of the stuffing box. The same clip presses the gland 60 to the guide sleeve, the working edges of which cover the chrome-plated surface of the rod. So that during suspension moves the oil seal is not damaged from various deposits on the rod (frost, dirt, etc.), a mud deflector ring 62 is installed, which removes these deposits from the rod. A rubber gasket 61 insulating them is clamped between the ring and the stuffing box cage.
A cover 64 of a protective casing made of plastic rests on top of the nut. It protects the stem from contamination and mechanical damage. At the upper end of the rod, a turnkey flat is made to keep the rod from turning when it is removed or installed.
The following are installed in the lower part of the stem: restrictive plate 52 of the bypass valve, flat spring 51 and plate 50 of the bypass valve, piston 44 with a sealing ring 48, recoil valve disks, thrust plate 45, recoil valve spring 43 and a nut 42 is screwed on. It is fixed by punching the end of the rod.
The piston is ceramic-metal, has vertical channels located along two radii. Between themselves, the channels of each circle are connected by an annular groove. Channels located closer to the center of the piston are blocked from below by recoil valve discs (pos 47 and 49), and from above - further from the center - by the plate 50 of the bypass valve, pressed by the spring 51. The stroke of the plate is limited by the spring resting on the plate 52. The piston is sealed in the cylinder by ring 48.
The recoil valve disks are pressed against the lower end of the piston by a spring 43 through a plate 45. In this case, the spring presses the outer part of the disks, and the inner part of the disks 47 is tightly pressed against the piston by a nut 42 screwed onto the threaded end of the rod. To protect the recoil valve disks from damage and stabilize the valve operation, a washer 46 is installed between the disks and the nut.
The throttle disk 49 of the recoil valve has four cutouts on the outer diameter for the passage of fluid with a smooth recoil stroke.
The working process of the shock absorber is similar to that of the front suspension strut.
