Input shaft 1 (pic. 77) made in the form of a block of gears rotating in two bearings. The drive gears of the input shaft are in constant engagement with the driven forward gears located on the secondary shaft 20 on needle bearings 19. In addition to them, two synchronizers 16 and 18 are installed on the secondary shaft. Together with the secondary shaft, the drive gear of the main gear is made. The differential is two-satellite. The preload in the differential bearings is adjusted by selecting the thickness of the ring 14. The driven gear 13 of the final drive is bolted to the flange of the differential box.
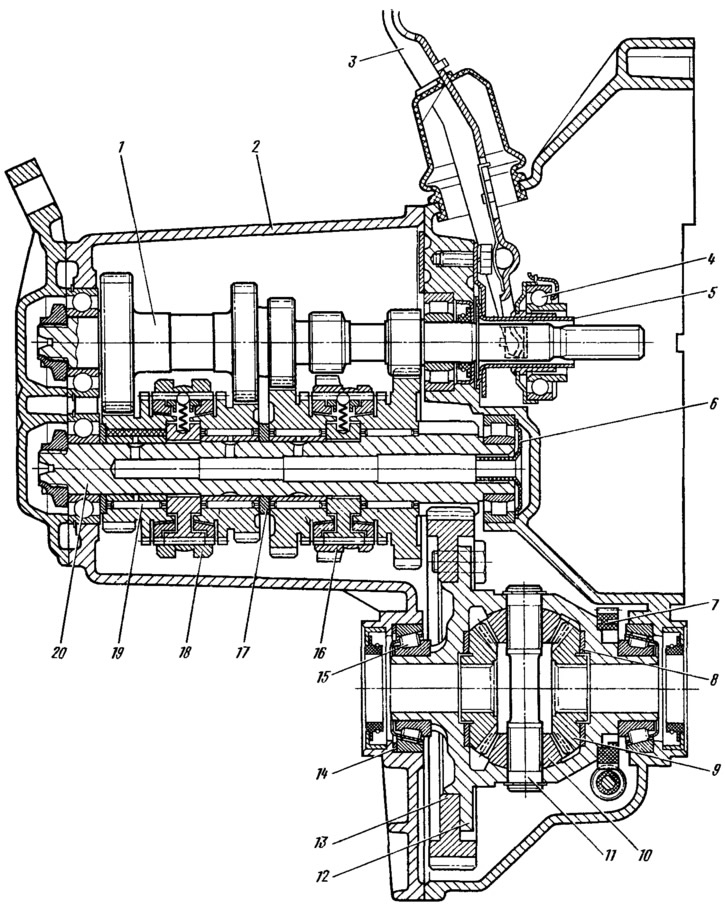
Pic. 77. Gearbox: 1 - input shaft; 2 - gearbox housing; 3 - clutch release fork; 4 - clutch release bearing; 5 - guide sleeve of the release bearing clutch; 6 - oil collector; 7 — a driving gear wheel of a drive of a speedometer; 8 - support washer of the axle gear; 9 - axle gear; 10 - satellite; 11 - the axis of the satellites; 12 - differential box, 13 - main gear driven gear; 14 adjusting ring; 15 - differential bearing; 16 - synchronizer of I and II gears; 17 - thrust ring; 18 - synchronizer III and IV gears; 19 - needle bearing of the gear of the secondary shaft; 20 - output shaft
The gearbox control drive consists of a lever 16 (pic. 78) gear shift, ball joint 19, thrust 15, hinge 10, 11, 12, gear selection rod 6 and mechanisms for selecting and shifting gears. To prevent spontaneous disengagement of gears due to axial movement of the power unit on its supports when the vehicle is moving, a reactive thrust 18 is introduced into the gearbox control drive, one end of which is rigidly connected to the power unit, and the other rests on the sleeve 17 of the lever support, the clip of which is attached to the floor body. In this sleeve, the jet thrust moves freely. The ball joint of the gear lever is not attached to the floor of the body, but to the jet thrust, so the axial movement of the power unit is not transmitted to the lever and the gear selection mechanism.
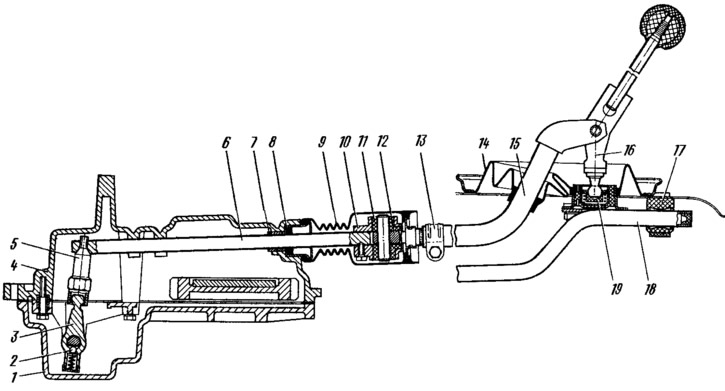
Pic. 78. Gearshift drive: 1 - gearbox housing; 2 - retainer; 3— gear selector lever; 4 - clutch housing; 5 — the lever of a stock of a choice of transfers; 6 - gear selection rod; 7 - stem bushing; 8 - stem gland; 9— protective cover; 10 - hinge body; 11 - hinge bushing; 12 - tip of the hinge; 13 - collar; 14 — a protective cover of draft; 15 — draft of a drive of a gear change; 16 - gear lever; 17 - jet thrust bushing; 18 - jet thrust; 19 - ball joint of the gear lever.
At the inner end of the gear selection rod 6, a lever 5 is fixed, into the socket of which the head of the two-arm lever 3 of the gear selection mechanism enters. This mechanism is made as a separate unit and is attached to the plane of the clutch housing 4.
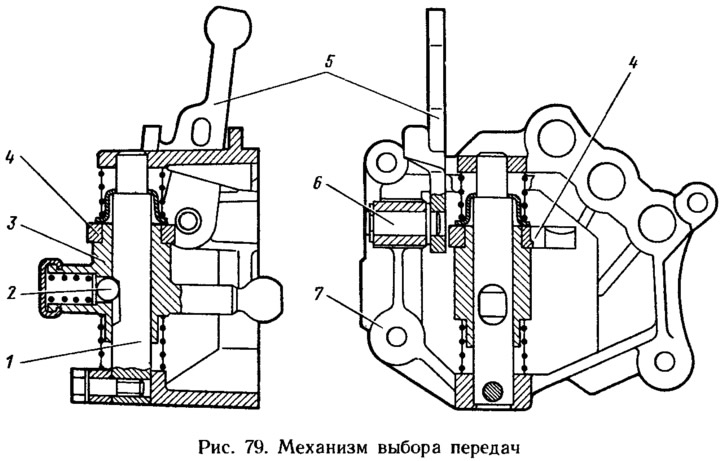
In building 7 (pic. 79) the gear selection mechanism is fixed with a locking bolt to axle 1, on which a two-arm gear selection lever 4 is installed. A ball lock 2 is located in its hub, and on the axle there is a recess for the lock ball. Lever 3 of the gear selection on both sides is bursting with springs, under the action of which it is set to the position of switching on the III and IV gears. In the case of the gear selection mechanism, an axle 6 is installed together with a reverse fork 5. The fork axle is fixed with a retaining ring, and the leash of the reverse rod head enters the fork socket.